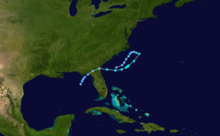
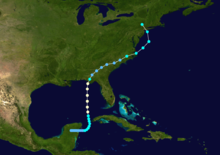
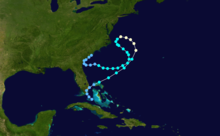
The 1986 Atlantic hurricane season was a very inactive season that produced 10 depressions, 6 named storms, 4 hurricanes, and no major hurricanes. The season officially began on June 1, 1986, and lasted until November 30, 1986. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. During the 1986 season, the first subtropical depression formed in the first week of June, while the last tropical cyclone dissipated at the end of the third week of November. The 1986 season had lower than average activity because of an ongoing El Niño event, and was the least active season in the North Atlantic since the 1983 Atlantic hurricane season. This was also the first season since 1972 to have no major hurricanes.

The 2004 Atlantic hurricane season was notable as one of the deadliest and most costly Atlantic hurricane seasons on record. It officially began on June 1, 2004, and ended on November 30, although storm activity continued into December. This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipations. The timeline includes information which was not operationally released, meaning that information from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as information on a storm that was not operationally warned upon, has been included.

The 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was the second most active Atlantic hurricane season in recorded history, and the most extreme in the satellite era. Officially, the season began on June 1, 2005 and ended on November 30, 2005. These dates, adopted by convention, historically delimit the period in each year when most tropical systems form. The season's first storm, Tropical Storm Arlene, developed on June 8. The final storm, Tropical Storm Zeta, formed in late December and persisted until January 6, 2006. Zeta is only the second December Atlantic storm in recorded history to survive into January, joining Hurricane Alice in 1955.

The 2007 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. A near average Atlantic hurricane season, September had a record-tying eight storms, although the strength and duration of most of the storms was low. Also, for only the second time in recorded history, an Atlantic hurricane, Felix, and an eastern Pacific hurricane, Henriette, made landfall on the same day.

The 2008 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. An above-average Atlantic hurricane season season, it was the first on record to have a major hurricane in every month from July to November.

The 1995 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. This Atlantic hurricane season saw a near-record number of named tropical storms. This extremely active season followed four consecutive years in which there was below normal activity. The season officially began on June 1, 1995 and ended on November 30, 1995. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical systems form. The season's first system, Hurricane Allison, developed on June 3; its last, Hurricane Tanya, became extratropical on November 2.

The 2001 Atlantic hurricane season was an above-average Atlantic hurricane season in which fifteen named storms formed. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates that conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The season's first tropical cyclone, Tropical Storm Allison, formed on June 5 while the season's final system, Hurricane Olga, dissipated on December 6.

The 1983 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was the least active Atlantic hurricane season in 53 years, during which four storms formed. The season officially began on June 1, 1983 and ended November 30, 1983. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most systems form. The first named storm, Hurricane Alicia, formed on August 15. The last storm of the season, Tropical Storm Dean, dissipated on September 30.

The 1982 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was an inactive Atlantic hurricane season, during which only five tropical cyclones formed. The season officially began on June 1, 1982 and ended November 30, 1982. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most systems form. this year, however, most tropical activity was constrained to the month of September.

The 1994 Atlantic hurricane season was a below-average Atlantic hurricane season that produced seven named tropical cyclones. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally limit the period of each year when tropical cyclones tend to form in the Atlantic. The first named storm, Tropical Storm Alberto, formed on June 30. The last storm of the season, Hurricane Gordon, dissipated on November 21. This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipation during the season. The timeline also includes information which was not operationally released, such as post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center.

The 1974 Atlantic hurricane season was a cycle of the annual tropical cyclone season in the Atlantic Ocean in the Northern Hemisphere. There was near-average activity during the season, which officially began on June 1, 1974 and ended on November 30, 1974. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical systems form. The first system of the season, Tropical Depression One, formed on June 22. The final system of the season, Tropical Depression Seventeen, dissipated on November 11.

The 2009 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the North Atlantic Ocean. It was a below-average Atlantic hurricane season with nine named storms, the fewest since the 1997 season. The season officially began on June 1, 2009, and ended on November 30, 2009, dates that conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic basin. The first storm to form was Tropical Depression One on May 28, 2009, while the last storm, Hurricane Ida, dissipated on November 10.
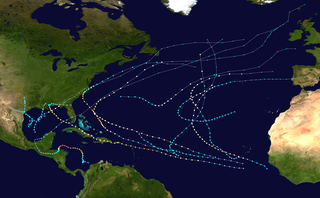
The 1998 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. This Atlantic hurricane season saw an above-average number of named tropical storms, and included a single-day record for number of hurricanes simultaneously in progress, with four active on September 25: Georges, Ivan, Jeanne and Karl. The season officially began on June 1, 1998 and ended on November 30, 1998. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical systems form. Even so, this season's first storm, Tropical Storm Alex, did not form until July 27, while its last, Hurricane Nicole, dissipated on December 1.

The 2002 Atlantic hurricane season was an average Atlantic hurricane season in which twelve named storms formed. Although Tropical Storm Arthur formed on July 14, the season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates that conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic basin. The season's final storm, Tropical Depression Fourteen, dissipated on October 16.

The 1990 Atlantic hurricane season featured the most named storms of any hurricane season at the time. During the season, 14 tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean became named storms. The season officially started on June 1, 1990, and ended on November 30. These dates, adopted by the convention, historically delimit the period each year when most Atlantic tropical systems form. However, storm formation is possible at any time of the year, as was the case this season, when Tropical Depression One formed on May 24; Hurricane Nana, the season's final storm, dissipated on October 21.

The 2010 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was one of the most active Atlantic hurricane seasons since record keeping began in 1851 as 19 named storms formed. The season officially began on June 1, 2010, and ended on November 30, 2010, dates that conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic basin. The first storm to form was Hurricane Alex, on June 25; and the last to dissipate was Hurricane Tomas, on November 7.

The 1985 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual Atlantic hurricane season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It featured average activity overall, with thirteen tropical cyclones, eleven tropical storms, seven hurricanes, and three major hurricanes. The season officially began on June 1, 1985 and ended November 30, 1985. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most systems form. The season's first storm, Tropical Storm Ana, developed on July 15; the season's final storm, Tropical Depression Thirteen, dissipated on December 9.

The 2012 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual hurricane season in the north Atlantic Ocean. For the third year in a row there were 19 named storms. The season officially began on June 1, 2012, and ended on November 30, 2012, dates that conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic basin. Surprisingly, two preseason storms formed: Alberto on May 19, and Beryl on May 26. This was the first such occurrence since the 1951 season. The final storm to dissipate was Sandy, on October 29. Altogether, ten storms became hurricanes, of which two intensified into major hurricanes.

The 2013 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual hurricane season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It featured below-average tropical cyclone activity, with the fewest hurricanes since the 1982 season. The season officially began on June 1, 2013 and ended on November 30, 2013. These dates, adopted by convention, historically delimit the period in each year when most tropical systems form. The season's first storm, Tropical Storm Andrea formed on June 5, and its final storm, an unnamed subtropical storm, dissipated on December 7. Altogether, there were 13 named tropical storms during the season. Two of which attained hurricane strength, but neither intensified into a major hurricane, the first such occurrence since the 1994 season.
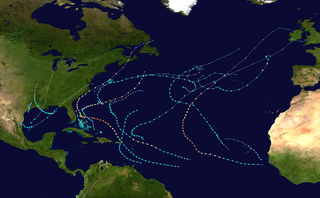
The 2019 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was the fourth consecutive above-normal Atlantic hurricane season. The season officially began on June 1, 2019, and ended on November 30, 2019. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical systems form. However, storm formation is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated in 2019 by the formation of the season's first named storm, Subtropical Storm Andrea, on May 20. The final storm of the season, Tropical Storm Sebastien, transitioned to an extratropical cyclone on November 25.