
Anacondas or water boas are a group of large boas of the genus Eunectes. They are a semiaquatic group of snakes found in tropical South America. Three to five extant and one extinct species are currently recognized, including one of the largest snakes in the world, E. murinus, the green anaconda.

Armadillos are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. They form part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of different environments.

The jaguar is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus Panthera native to the Americas. With a body length of up to 1.85 m and a weight of up to 158 kg (348 lb), it is the biggest cat species in the Americas and the third largest in the world. Its distinctively marked coat features pale yellow to tan colored fur covered by spots that transition to rosettes on the sides, although a melanistic black coat appears in some individuals. The jaguar's powerful bite allows it to pierce the carapaces of turtles and tortoises, and to employ an unusual killing method: it bites directly through the skull of mammalian prey between the ears to deliver a fatal blow to the brain.

New Caledonia is a sui generis collectivity of overseas France in the southwest Pacific Ocean, south of Vanuatu, about 1,210 km (750 mi) east of Australia, and 17,000 km (11,000 mi) from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia subregion, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Chesterfield Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of Pines, and a few remote islets. The Chesterfield Islands are in the Coral Sea. French people, especially locals, call Grande Terre le Caillou, a nickname also used more generally for the entire New Caledonia. Pro-independence Kanak parties use the name (la) Kanaky to refer to New Caledonia, a term coined in the 1980s from the ethnic name of the indigenous Melanesian Kanak people who make up 41% of New Caledonia's population. New Caledonia is one of the European Union's Overseas Countries and Territories (OCTs), but it is not part of the European Union.
In biology, taxonomy is the scientific study of naming, defining (circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms.

Genus is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name, a binomen, binominal name, or a scientific name; more informally it is also historically called a Latin name. In the ICZN, the system is also called binominal nomenclature, "binomi'N'al" with an "N" before the "al", which is not a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system".
Panthera is a genus within the family Felidae, it is one of two extant genera in the subfamily Pantherinae, and contains the largest living members of the cat family. There are five living species: the jaguar, leopard, lion, snow leopard and tiger, as well as a number of extinct species.

Eucalyptus is a genus of more than 700 species of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae. Most species of Eucalyptus are trees, often mallees, and a few are shrubs. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including Corymbia and Angophora, they are commonly known as eucalypts or "gum trees". Plants in the genus Eucalyptus have bark that is either smooth, fibrous, hard, or stringy, the leaves have oil glands, and the sepals and petals are fused to form a "cap" or operculum over the stamens. The fruit is a woody capsule commonly referred to as a "gumnut".

Moths are a group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies. They were previously classified as suborder Heterocera, but the group is paraphyletic with respect to butterflies and neither subordinate taxon is used in modern classifications. Moths make up the vast majority of the order. There are approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, although there are also crepuscular and diurnal species.

Tilapia is the common name for nearly a hundred species of cichlid fish from the coelotilapine, coptodonine, heterotilapine, oreochromine, pelmatolapiine, and tilapiine tribes, with the economically most important species placed in the Coptodonini and Oreochromini. Tilapia are mainly freshwater fish inhabiting shallow streams, ponds, rivers, and lakes, and less commonly found living in brackish water. Historically, they have been of major importance in artisanal fishing in Africa, and they are of increasing importance in aquaculture and aquaponics. Tilapia can become a problematic invasive species in new warm-water habitats such as Australia, whether deliberately or accidentally introduced, but generally not in temperate climates due to their inability to survive in cold water.

A mongoose is a small terrestrial carnivorous mammal belonging to the family Herpestidae. This family is currently split into two subfamilies, the Herpestinae and the Mungotinae. The Herpestinae comprises 23 living species that are native to southern Europe, Africa and Asia, whereas the Mungotinae comprises 11 species native to Africa. The Herpestidae originated about 21.8 ± 3.6 million years ago in the Early Miocene and genetically diverged into two main genetic lineages between 19.1 and 18.5 ± 3.5 million years ago.
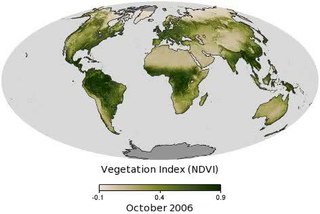
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader than the term flora which refers to species composition. Perhaps the closest synonym is plant community, but vegetation can, and often does, refer to a wider range of spatial scales than that term does, including scales as large as the global. Primeval redwood forests, coastal mangrove stands, sphagnum bogs, desert soil crusts, roadside weed patches, wheat fields, cultivated gardens and lawns; all are encompassed by the term vegetation.

Sardine and pilchard are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term 'sardine' was first used in English during the early 15th century; a somewhat dubious etymology says it comes from the Italian island of Sardinia, around which sardines were once supposedly abundant.

Colubridae is a family of snakes. With 249 genera, it is the largest snake family. The earliest fossil species of the family date back to the Late Eocene epoch, with earlier origins suspected. Colubrid snakes are found on every continent except Antarctica.

A piranha or piraña is any of a number of freshwater fish species in the family Serrasalmidae, or the subfamily Serrasalminae within the tetra family, Characidae in order Characiformes. These fish inhabit South American rivers, floodplains, lakes and reservoirs. Although often described as extremely predatory and mainly feeding on fish, their dietary habits vary extensively, and they will also take plant material, leading to their classification as omnivorous.

Endemism is the state of a species only being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be endemic to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an endemism or, in scientific literature, as an endemite.
Fauna Europaea is a database of the scientific names and distribution of all living multicellular European land and fresh-water animals. It serves as a standard taxonomic source for animal taxonomy within the Pan-European Species directories Infrastructure (PESI). As of June 2020, Fauna Europaea reported that their database contained 235,708 taxon names and 173,654 species names.

An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, invasive species, and climate change. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List lists the global conservation status of many species, and various other agencies assess the status of species within particular areas. Many nations have laws that protect conservation-reliant species which, for example, forbid hunting, restrict land development, or create protected areas. Some endangered species are the target of extensive conservation efforts such as captive breeding and habitat restoration.

A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet. For example, Boa constrictor is one of the species of the genus Boa, with constrictor being the species' epithet.















