
Shearwaters are medium-sized long-winged seabirds in the petrel family Procellariidae. They have a global marine distribution, but are most common in temperate and cold waters, and are pelagic outside the breeding season.

The Manx shearwater is a medium-sized shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. The scientific name of this species records a name shift: Manx shearwaters were called Manks puffins in the 17th century. Puffin is an Anglo-Norman word for the cured carcasses of nestling shearwaters. The Atlantic puffin acquired the name much later, possibly because of its similar nesting habits.

The Balearic shearwater is a medium-sized shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. Puffinus is a Neo-Latin loanword based on the English "puffin" and its variants, that referred to the cured carcass of the fat nestling of the Manx shearwater, a former delicacy. The specific mauretanicus refers to Mauretania, an old name for an area of North Africa roughly corresponding to Morocco and Algeria. The Balearic Shearwater is listed critically endangered by the IUCN and is one of Europe's most endangered seabirds.

The little shearwater is a small shearwater in the petrel family Procellariidae. Despite the generic name, it is unrelated to the puffins, which are auks, the only similarity being that they are both burrow-nesting seabirds.

The Revillagigedo Islands or Revillagigedo Archipelago are a group of four volcanic islands in the Pacific Ocean, known for their unique ecosystem. They lie approximately 458 kilometres (285 mi) from Socorro Island south and southwest of Cabo San Lucas, the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula, and 698 to 1,092 kilometres west of Manzanillo. Historically linked to the Mexican state of Colima, to which they were granted in 1861 to establish a penal colony, the islands are under Mexican federal property and jurisdiction.

Socorro Island is a volcanic island in the Revillagigedo Islands, a Mexican possession lying 600 kilometres (370 mi) off the country's western coast. The size is 16.5 by 11.5 km, with an area of 132 km2 (51 sq mi). It is the largest of the four islands of the Revillagigedo Archipelago. The last eruption was in 1993.

The yelkouan shearwater, Levantine shearwater or Mediterranean shearwater is a medium-sized shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. It was formerly treated as a subspecies of the Manx shearwater.

The Christmas shearwater or ʻaoʻū is a medium-sized shearwater of the tropical Central Pacific. It is a poorly known species due to its remote nesting habits, and it has not been extensively studied at sea either.

The wedge-tailed shearwater is a medium-large shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. It is one of the shearwater species that is sometimes referred to as a muttonbird, like the sooty shearwater of New Zealand and the short-tailed shearwater of Australia. It is found throughout the tropical Pacific and Indian Oceans, roughly between latitudes 35°N and 35°S. It breeds on the islands off Japan, on the Islas Revillagigedo, the Hawaiian Islands, the Seychelles, the Northern Mariana Islands, and off Eastern and Western Australia.

The Sargasso shearwater, formerly known as Audubon's shearwater, is a common tropical seabird in the petrel family. Sometimes known as the dusky-backed shearwater, the specific epithet honours the French naturalist Félix Louis L'Herminier.

The short-tailed shearwater or slender-billed shearwater, also called yolla or moonbird, and commonly known as the muttonbird in Australia, is the most abundant seabird species in Australian waters, and is one of the few Australian native birds in which the chicks are commercially harvested. It is a migratory species that breeds mainly on small islands in Bass Strait and Tasmania and migrates to the Northern Hemisphere for the boreal summer.
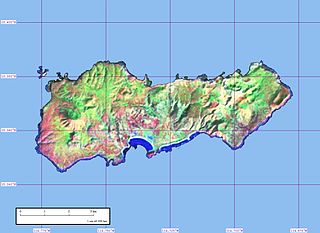
Clarion Island, formerly Santa Rosa, is the second largest, westernmost and most remote of Mexico's Revillagigedo Islands. The island is located 385 kilometres (239 mi) west of Socorro Island and just under 700 kilometres (430 mi) from the Mexican mainland.

San Benedicto, formerly Isla de los Inocentes, is an uninhabited island, and third largest island of the Revillagigedo Islands, located in the Pacific Ocean.

The flesh-footed shearwater is a medium-sized shearwater. Its plumage is black. It has pale pinkish feet, and a pale bill with a distinct black tip. Together with the equally light-billed pink-footed shearwater, it forms the Hemipuffinus group, a superspecies which may or may not have an Atlantic relative in the great shearwater. These large shearwaters are among those that have been separated into the genus Ardenna. Recent genetic analysis indicates evidence of strong divergence between Pacific colonies relative to those in South and Western Australia, thought to be explained by philopatry and differences in foraging strategies during the breeding season.

Newell's shearwater or Hawaiian shearwater (ʻaʻo), is a seabird in the family Procellariidae. It belongs to a confusing group of shearwaters which are difficult to identify and whose classification is controversial. It was formerly treated as a subspecies of the Manx shearwater and is now often placed in Townsend's shearwater. It is endemic to the Hawaiian Islands.

Buller's shearwater is a Pacific species of seabird in the family Procellariidae; it is also known as the grey-backed shearwater or New Zealand shearwater. A member of the black-billed wedge-tailed Thyellodroma group, among the larger shearwaters of the genus Ardenna, it forms a superspecies with the wedge-tailed shearwater.

The pink-footed shearwater is a species of seabird. The bird is 48 cm (19 in) in length, with a 109 cm (43 in) wingspan. It is polymorphic, having both darker- and lighter-phase populations. Together with the equally light-billed flesh-footed shearwater, it forms the Hemipuffinus group, a superspecies that may or may not have an Atlantic relative in the great shearwater. These are large shearwaters which are among those that could be separated in the genus Ardenna.

The black-vented shearwater is a species of seabird endemic to islands off of the Pacific coast of Mexico and the Gulf of California. It is a smaller shearwater, with a length of 30–38 cm, 76–89 cm wingspan and a mass of around 400 g. This species is pelagic and feeds mainly on small fish. It is nocturnal, and is most active in low light settings.

Seabirds include some of the most threatened taxa anywhere in the world. For example, of extant albatross species, 82% are listed as threatened, endangered, or critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. The two leading threats to seabirds are accidental bycatch by commercial fishing operations and introduced mammals on their breeding islands. Mammals are typically brought to remote islands by humans either accidentally as stowaways on ships, or deliberately for hunting, ranching, or biological control of previously introduced species. Introduced mammals have a multitude of negative effects on seabirds including direct and indirect effects. Direct effects include predation and disruption of breeding activities, and indirect effects include habitat transformation due to overgrazing and major shifts in nutrient cycling due to a halting of nutrient subsidies from seabird excrement. There are other invasive species on islands that wreak havoc on native bird populations, but mammals are by far the most commonly introduced species to islands and the most detrimental to breeding seabirds. Despite efforts to remove introduced mammals from these remote islands, invasive mammals are still present on roughly 80% of islands worldwide.




















