
The Carnian is the lowermost stage of the Upper Triassic Series. It lasted from 237 to 227 million years ago (Ma). The Carnian is preceded by the Ladinian and is followed by the Norian. Its boundaries are not characterized by major extinctions or biotic turnovers, but a climatic event occurred during the Carnian and seems to be associated with important extinctions or biotic radiations. Another extinction occurred at the Carnian-Norian boundary, ending the Carnian age.

In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between 247.2 Ma and 237 Ma. It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages.

The Ladinian is a stage and age in the Middle Triassic series or epoch. It spans the time between 242 Ma and ~237 Ma. The Ladinian was preceded by the Anisian and succeeded by the Carnian.

Asklepioceras is a genus in the Ceratitid family Arpaditidae from the Middle and Upper Triassic of Italy, Romania, Turkey, and British Columbia (Canada).

Arpadites is a genus of ceratitids in the family Trachyceratidae from the Middle and Upper Triassic of Nevada, Alps, Italy, Balkans, Himalayas, and Japan.

Megalancosaurus is a genus of extinct reptile from the Late Triassic Dolomia di Forni Formation and Zorzino Limestone of northern Italy, and one of the best known drepanosaurids. The type species is M. preonensis; a translation of the animal's scientific name would be "long armed reptile from the Preone Valley."

Bobosaurus is an extinct genus of sauropterygian reptile related to plesiosaurs. It is based on the holotype MFSN 27285, a partial skeleton found in Early Carnian-age rocks of the Rio del Lago Formation, northeastern Italy. Bobosaurus was named in 2006 by Fabio M. Dalla Vecchia and the type species is B. forojuliensis. It may be a pistosaurid, or closer to Plesiosauria. A recent cladistic analysis found it to be a pistosaur. It was relatively large animal, with more than 3 m (9.8 ft) in length.
Eosaurichthys is an extinct genus of saurichthyid ray-finned fish that lived during the late Permian epoch in what is now China.

Heptanema is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) of northern Italy and southern Switzerland.

Colobodus is an extinct genus of marine Triassic ray-finned fish of the family Colobodontidae and order Perleidiformes. Fossils have been found in Europe and China, encompassing the former Tethys Ocean. It could reach body lengths of about 70 cm.

Dipteronotus is an extinct genus of marine stem-neopterygian ray-finned fish that existed during the Middle and Late Triassic epochs in what is now Europe and Morocco. As a typical feature, it had several ridge scales in front of its dorsal fin that created a spine-like structure.

Sinosaurichthys is an extinct genus of saurichthyid ray-finned fish, which existed in south-western China during the Middle Triassic. Fossils have been found in the Upper Member of the Guanling Formation of two localities: Yangjuan of Panxian County, Guizhou Province, and Dawazi of Luoping, Yunnan Province, China.

Saurichthyiformes is an extinct order of ray-finned fish which existed in Asia, Africa, Australia, Europe and North America, during the late Permian to early Middle Jurassic. Saurichthyiiformes comprise two families, Saurichthyidae and Yelangichthyidae. Yelangichthyidae is monotypic, containing only the genus Yelangichthys. The gar or needlefish-like Saurichthyidae is primarily known from the genus Saurichthys. Additionally, the subgenera SaurorhynchusCostasaurichthys, Eosaurichthys, Lepidosaurichthys, and Sinosaurichthys are frequently used to group species, and are sometimes considered separate genera. Species are known from both marine end freshwater deposits. They had their highest diversity during the Early and Middle Triassic. Their phylogenetic position is uncertain, while they have often been considered members of Chondrostei, and thus related to living sturgeons and paddlefish, phylogenetic analysis of well-preserved remains has considered this relationship equivocal. They may actually belong to the stem-group of Actinopterygii, and thus not closely related to any living group of ray-finned fish.

Tholodus is an extinct genus of basal ichthyopterygian known from the Middle Triassic of Germany, northeastern Italy and possibly China. It was first named by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer in 1851 and the type species is Tholodus schmidi. It is known from many disarticulated and fragmentary remains, mainly teeth and jaw fragments. Most specimens were collected from various localities across the Ladinian-aged Muschelkalk, Germany, mainly from the Jena Formation of the upper Lower Muschelkalk, where the holotype was found. Dalla Vecchia (2004) recently described two additional specimens, a mandibular ramus and a maxilla, both bearing teeth and nearly uncrushed, and some postcranial remains, from a single late Anisian outcrop, from the southern Alps of Italy. The humerus resembled that of immature individuals of the Asian genus Chaohusaurus, suggesting possible affinities to Grippidia.

Ceratitidae is an extinct family of ammonite cephalopods.
The Schlern Formation, also known as Schlern Dolomite, and Sciliar Formation or Sciliar Dolomite in Italy, is a limestone, marl and dolomite formation in the Southern Limestone Alps in Kärnten, Austria and South Tyrol, Italy.
Carnepigondolella is an extinct genus of conodonts of the Late Triassic of Italy or Canada.
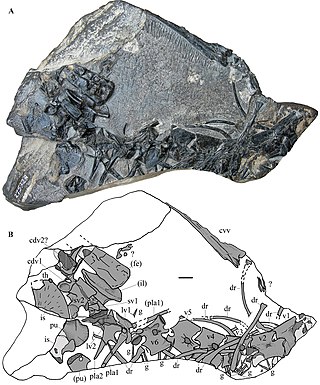
Raibliania is an extinct genus of tanystropheid archosauromorph discovered in the Calcare del Predil Formation in Italy. It lived during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic and it was related to Tanystropheus. Raibliania is distinct from Tanystropheus due to some distinct features of the cervical vertebrae and teeth. The type species is Raibliania calligarisi, named in 2020. The holotype consists of a partial post-cranial skeleton, with the known elements including vertebrae, a single tooth, several ribs, gastralia and parts of the pelvis.
The Zhuganpo Formation is a Triassic geologic unit found in southern China. It has historically been known as the Zhuganpo Member of the Falang Formation. A diverse fossil assemblage known as the Xingyi biota or Xingyi Fauna can be found in the upper part of the Zhuganpo Formation. Fossils of the Xingyi biota include articulated skeletons of marine reptiles, abundant fish, and a plentiful assortment of invertebrates indicating a Ladinian to Carnian age for the sediments of the formation.

Brotheotrachyceras is a genus of ammonite cephalopod belonging to the order Ceratitida. It was living during the Carnian age of the Late Triassic Epoch.

























