
Trachylepis is a skink genus in the subfamily Mabuyinae found mainly in Africa. Its members were formerly included in the "wastebin taxon" Mabuya, and for some time in Euprepis. As defined today, Trachylepis contains the clade of Afro-Malagasy mabuyas. The genus also contains a species from the Brazilian island of Fernando de Noronha, T. atlantica, and may occur in mainland South America with Trachylepis tschudii and Trachylepis maculata, both poorly known and enigmatic. The ancestors of T. atlantica are believed to have rafted across the Atlantic from Africa during the last 9 million years.
Lomi's blind legless skink is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Little Namaqualand in South Africa.

The wedge-snouted skink or sharp-lipped mabuya is a species of skink found in Namibia, Angola, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and South Africa.
Trachylepis ferrarai, also known commonly as Ferrara's mabuya, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Somalia.
Trachylepis brauni, also known commonly as Braun's mabuya and the Ukinga montane skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is found in Tanzania and Malawi.
Trachylepis rodenburgi, also known commonly as Rodenburg's mabuya, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to West Africa.

Trachylepis boettgeri, commonly known as Boettger's mabuya, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Madagascar.
Chondrodactylus fitzsimonsi, also known commonly as the button-scaled gecko, FitzSimons' thick-toed gecko, Fitzsimons's thick-toed gecko, and FitzSimons' tubercled gecko, is a species of gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is native to southwestern Africa.
Pedioplanis inornata, known commonly as the plain sand lizard or the western sand lizard, is a species of lizard in the family Lacertidae. The species is endemic to Southern Africa.

Benson's mabuya is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to Western Africa.

Trachylepis bocagii, also known commonly as Bocage's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to southern Africa.
Trachylepis boulengeri, also known commonly as Boulenger's mabuya, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is indigenous to southeastern Africa.
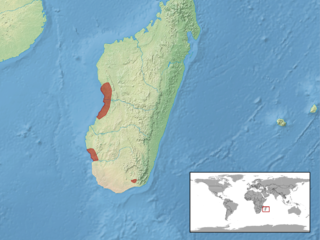
Trachylepis dumasi is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Madagascar.

Trachylepis gravenhorstii, also known commonly as Gravenhorst's mabuya, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Madagascar.
Trachylepis hemmingi, also known commonly as the Somali mabuya, is a species of skink, a lizard in the subfamily Mabuyinae of the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Somalia.

Trachylepis nancycoutuae, also known commonly as Nancy Coutu's mabuya and Nancy Coutu's skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Madagascar.
Trachylepis raymondlaurenti, also known commonly as Laurent's long-tailed skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Africa.

Sepsina alberti, also known commonly as Albert's skink and Albert's burrowing skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Namibia.
Sepsina copei, also known commonly as Cope's reduced-limb skink or the sepsina skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Angola.
Typhlacontias punctatissimus, also known commonly as the dotted blind dart skink, the speckled burrowing skink, and the speckled western burrowing skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is native to southern Africa. Three subspecies are recognized.









