
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the first and oldest specialised agencies of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.
The Lisbon Recognition Convention, officially the Convention on the Recognition of Qualifications concerning Higher Education in the European Region, is an international convention of the Council of Europe elaborated together with the UNESCO. This is the main legal agreement on credential evaluation in Europe.
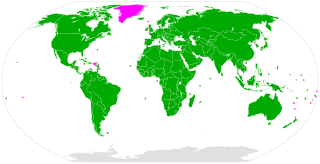
The Convention Concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour, known in short as the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, was adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in 1999 as ILO Convention No 182. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.
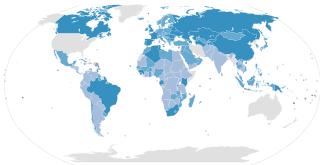
The ILO Convention Concerning Minimum Age for Admission to Employment C138, is a convention adopted in 1973 by the International Labour Organization. It requires ratifying states to pursue a national policy designed to ensure the effective abolition of child labour and to raise progressively the minimum age for admission to employment or work. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions. Convention C138 replaces several similar ILO conventions in specific fields of labour.
Social dialogue is the process whereby social partners negotiate, often in collaboration with the government, to influence the arrangement and development of work-related issues, labour market policies, social protection, taxation or other economic policies. It is a widespread procedure to develop public policies in Western Europe in particular.

The International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families is a United Nations multilateral treaty governing the protection of migrant workers and families. Signed on 18 December 1990, it entered into force on 1 July 2003 after the threshold of 20 ratifying States was reached in March 2003. The Committee on Migrant Workers (CMW) monitors implementation of the convention, and is one of the seven UN-linked human rights treaty bodies. The convention applies as of October 2022 in 58 countries.
The Valletta Treaty (formally the European Convention on the Protection of the Archaeological Heritage (Revised), also known as the Malta Convention) is a multilateral treaty of the Council of Europe. The 1992 treaty aims to protect the European archaeological heritage "as a source of European collective memory and as an instrument for historical and scientific study". All remains and objects and any other traces of humankind from past times are considered to be elements of the archaeological heritage. The archaeological heritage shall include structures, constructions, groups of buildings, developed sites, moveable objects, monuments of other kinds as well as their context, whether situated on land or under water." (Art. 1)
Labour Standards Convention, 1947 is an International Labour Organization Convention.

Abolition of Forced Labour Convention, 1957, the full title of which is Convention concerning the Abolition of Forced Labour, 1957, is one of the eight ILO fundamental conventions of the International Labour Organization, which cancels certain forms of forced labour still allowed under the Forced Labour Convention of 1930, such as punishment for strikes and as a punishment for holding certain political views.
The Indigenous and Tribal Peoples Convention, 1989 is an International Labour Organization Convention, also known as ILO Convention 169, or C169. It is the major binding international convention concerning indigenous peoples and tribal peoples, and a forerunner of the Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples.
Social Policy Convention, 1962 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Safety and Health in Mines Convention, 1995 is an International Labour Organization Convention. It was adopted at the 82nd International Labour Conference (ILC) of the International Labour Organization (ILO). The ILO is an agency under the United Nations that deals with international labor issues while promoting workers rights and opportunities. One of ILO's goals is to hold annual labor conventions to create legally binding contracts for participating nations to ratify. During the Safety and Health in Mines Convention (C176), it was recognized that there are inherent hazards in the mining workplace, and a need for a convention was mandatory.

The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international human rights treaty of the United Nations intended to protect the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities. Parties to the convention are required to promote, protect, and ensure the full enjoyment of human rights by persons with disabilities and ensure that persons with disabilities enjoy full equality under the law. The Convention serves as a major catalyst in the global disability rights movement enabling a shift from viewing persons with disabilities as objects of charity, medical treatment and social protection towards viewing them as full and equal members of society, with human rights. The convention was the first U.N. human rights treaty of the twenty-first century.
Tripartism is an economic system of neo-corporatism based on a mixed economy and tripartite contracts between employers' organizations, trade unions, and the government of a country. Each is to act as a social partner to create economic policy through cooperation, consultation, negotiation, and compromise. In Tripartism, the government has a large role in the economy and engages in negotiations between labor unions and business interest groups to establish economic policy.

The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) is an International Labour Organization (ILO) convention, number 186, established in 2006 as the fourth pillar of international maritime law and embodies "all up-to-date standards of existing international maritime labour Conventions and Recommendations, as well as the fundamental principles to be found in other international labour Conventions". The other pillars are the SOLAS, STCW and MARPOL. The treaties applies to all ships entering the harbours of parties to the treaty (port states), as well as to all ships flying the flag of state party (flag states, as of 2021: over 91 per cent).

The Convention on Domestic Workers, formally the Convention concerning Decent Work for Domestic Workers is a convention setting labour standards for domestic workers. It is the 189th ILO convention and was adopted during the 100th session of the International Labour Organization, in 16 June 2011. It entered into force on 5 September 2013.
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating Work and the workplace. The International Labour Organization and the World Trade Organization have been the main international bodies involved in reforming labour markets. The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank have indirectly driven changes in labour policy by demanding structural adjustment conditions for receiving loans or grants. Issues regarding Conflict of laws arise, determined by national courts, when people work in more than one country, and supra-national bodies, particularly in the law of the European Union, has a growing body of rules regarding labour rights.

Armenia was admitted into the United Nations on 2 March 1992, following its independence from the Soviet Union. In December 1992, the UN opened its first office in Yerevan. Since then, Armenia has signed and ratified several international treaties. There are 20 specialized agencies, programs, and funds operating in the country under the supervision of the UN Resident Coordinator. Armenia strengthened its relations with the UN by cooperating with various UN agencies and bodies such as the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, the World Food Programme, and with the financial institutions of the UN. Armenia is a candidate to preside as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council in 2031.










