Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have many possible underlying causes. Paresthesias are usually painless and can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly occur in the arms and legs.

Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) defines septic shock as a subset of sepsis in which particularly profound circulatory, cellular, and metabolic abnormalities are associated with a greater risk of mortality than with sepsis alone. Patients with septic shock can be clinically identified by requiring a vasopressor to maintain a mean arterial pressure of 65 mm Hg or greater and having serum lactate level greater than 2 mmol/L (>18 mg/dL) in the absence of hypovolemia. This combination is associated with hospital mortality rates greater than 40%.
Alkalosis is the result of a process reducing hydrogen ion concentration of arterial blood plasma (alkalemia). In contrast to acidemia, alkalemia occurs when the serum pH is higher than normal. Alkalosis is usually divided into the categories of respiratory alkalosis and metabolic alkalosis or a combined respiratory/metabolic alkalosis.

Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L, while levels less than 2.1 mmol/L are defined as hypocalcemic. Mildly low levels that develop slowly often have no symptoms. Otherwise symptoms may include numbness, muscle spasms, seizures, confusion, or in extreme cases cardiac arrest.
Hyperventilation syndrome (HVS), also known as chronic hyperventilation syndrome (CHVS), dysfunctional breathing hyperventilation syndrome, cryptotetany, spasmophilia, latent tetany, and central neuronal hyper excitability syndrome (NHS), is a respiratory disorder, psychologically or physiologically based, involving breathing too deeply or too rapidly (hyperventilation). HVS may present with chest pain and a tingling sensation in the fingertips and around the mouth (paresthesia), in some cases resulting in the hands 'locking up' or cramping. HVS may accompany a panic attack.
Hypoparathyroidism is decreased function of the parathyroid glands with underproduction of parathyroid hormone (PTH). This can lead to low levels of calcium in the blood, often causing cramping and twitching of muscles or tetany, and several other symptoms. It is a very rare disease. The condition can be inherited, but it is also encountered after thyroid or parathyroid gland surgery, and it can be caused by immune system-related damage as well as a number of rarer causes. The diagnosis is made with blood tests, and other investigations such as genetic testing depending on the results. The primary treatment of hypoparathyroidism is calcium and vitamin D supplementation. Calcium replacement or vitamin D can ameliorate the symptoms but can increase the risk of kidney stones and chronic kidney disease. Additionally, medications such as recombinant human parathyroid hormone or teriparatide may be given by injection to replace the missing hormone.
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) is a group of metabolic abnormalities that can occur as a complication from the treatment of cancer, where large amounts of tumor cells are killed off (lysed) from the treatment, releasing their contents into the bloodstream. This occurs most commonly after the treatment of lymphomas and leukemias and in particular when treating non-Hodgkin lymphoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. This is a potentially fatal complication and patients at increased risk for TLS should be closely monitored while receiving chemotherapy and should receive preventive measures and treatments as necessary. TLS can also occur on its own although this is less common.

Hypereosinophilic syndrome is a disease characterized by a persistently elevated eosinophil count in the blood for at least six months without any recognizable cause, with involvement of either the heart, nervous system, or bone marrow.

Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, acid–base balance and much more. Electrolyte imbalances can develop by consuming too little or too much electrolyte as well as excreting too little or too much electrolyte. Examples of electrolytes include calcium, chloride, magnesium, phosphate, potassium, and sodium.
Hypermagnesemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a high level of magnesium in the blood. Symptoms include weakness, confusion, decreased breathing rate, and decreased reflexes. Complications may include low blood pressure and cardiac arrest.
Hypocapnia, also known as hypocarbia, sometimes incorrectly called acapnia, is a state of reduced carbon dioxide in the blood. Hypocapnia usually results from deep or rapid breathing, known as hyperventilation.
The Chvostek sign is a clinical sign that someone may have a low blood calcium level. The Chvostek sign is the abnormal twitching of muscles that are activated (innervated) by the facial nerve. When the facial nerve is tapped in front of the ear, the facial muscles on the same side of the face will contract sporadically. The muscles that control the nose, lips and eyebrows are often the ones that will spasm.
Trousseau sign is the name of two distinct phenomena observed in clinical medicine. Both are attributed to Armand Trousseau:
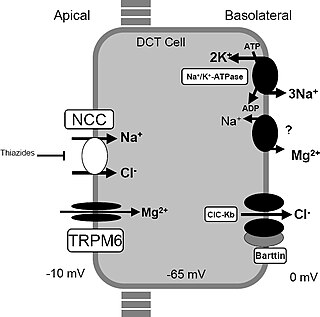
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. It is the most frequent hereditary salt-losing tubulopathy. Gitelman syndrome is caused by disease-causing variants on both alleles of the SLC12A3 gene. The SLC12A3 gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter, which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney.

Armand Trousseau was a French internist. His contributions to medicine include Trousseau sign of malignancy, Trousseau sign of latent tetany, Trousseau–Lallemand bodies. He is sometimes credited with the quip "use new drugs quickly, while they still work", though Michel-Philippe Bouvart had said the same over 40 years earlier.

Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare inherited disease characterised by a defect in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which results in low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increased blood pH (alkalosis), and normal to low blood pressure. There are two types of Bartter syndrome: neonatal and classic. A closely associated disorder, Gitelman syndrome, is milder than both subtypes of Bartter syndrome.
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS), also known as Asherson's syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disease in which widespread, intravascular clotting causes multi-organ failure. The syndrome is caused by antiphospholipid antibodies that target a group of proteins in the body that are associated with phospholipids. These antibodies activate endothelial cells, platelets, and immune cells, ultimately causing a large inflammatory immune response and widespread clotting. CAPS was first described by Ronald Asherson in 1992. The syndrome exhibits thrombotic microangiopathy, multiple organ thromboses, and in some cases tissue necrosis and is considered an extreme or catastrophic variant of the antiphospholipid syndrome.
The Trousseau sign of malignancy or Trousseau's syndrome is a medical sign involving episodes of vessel inflammation due to blood clot (thrombophlebitis) which are recurrent or appearing in different locations over time. The location of the clot is tender and the clot can be felt as a nodule under the skin. Trousseau's syndrome is a rare variant of venous thrombosis that is characterized by recurrent, migratory thrombosis in superficial veins and in uncommon sites, such as the chest wall and arms. This syndrome is particularly associated with pancreatic, gastric and lung cancer and Trousseau's syndrome can be an early sign of cancer sometimes appearing months to years before the tumor would be otherwise detected. Heparin therapy is recommended to prevent future clots. The Trousseau sign of malignancy should not be confused with the Trousseau sign of latent tetany caused by low levels of calcium in the blood.
Tetany or tetanic seizure is a medical sign consisting of the involuntary contraction of muscles, which may be caused by disorders that increase the action potential frequency of muscle cells or of the nerves that innervate them.
Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 2 (KCS2) is an extremely rare autosomal dominant genetic condition characterized by dwarfism, hypermetropia, microphthalmia, and skeletal abnormalities. This subtype of Kenny-Caffey syndrome is caused by a heterozygous mutation in the FAM111A gene (615292) on chromosome 11q12.









