
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek galaxias (γαλαξίας), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a thousand stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies.

A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars that is bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards its center. It can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars, all orbiting in a stable, compact formation. Globular clusters are similar in form to dwarf spheroidal galaxies, and though globular clusters were long held to be the more luminous of the two, discoveries of outliers had made the distinction between the two less clear by the early 21st century. Their name is derived from Latin globulus. Globular clusters are occasionally known simply as "globulars".

The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way, where Earth is located. It has a total diameter of roughly 3 megaparsecs (10 million light-years; 9×1019 kilometres), and a total mass of the order of 2×1012 solar masses (4×1042 kg). It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape; the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about 800 kiloparsecs (3×10^6 ly; 2×1019 km) and are moving toward one another with a velocity of 123 km/s. The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies.

Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, form part of the Hubble sequence. Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the bulge. These are often surrounded by a much fainter halo of stars, many of which reside in globular clusters.

The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately 8 kiloparsecs (26,000 ly) away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula.

A starburst galaxy is one undergoing an exceptionally high rate of star formation, as compared to the long-term average rate of star formation in the galaxy, or the star formation rate observed in most other galaxies.

The Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF) is a deep-field image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, containing an estimated 10,000 galaxies. The original data for the image was collected by the Hubble Space Telescope from September 2003 to January 2004 and the first version of the image was released on March 9, 2004. It includes light from galaxies that existed about 13 billion years ago, some 400 to 800 million years after the Big Bang.
A galactic halo is an extended, roughly spherical component of a galaxy which extends beyond the main, visible component. Several distinct components of a galaxy comprise its halo:

Omega Centauri is a globular cluster in the constellation of Centaurus that was first identified as a non-stellar object by Edmond Halley in 1677. Located at a distance of 17,090 light-years, it is the largest known globular cluster in the Milky Way at a diameter of roughly 150 light-years. It is estimated to contain approximately 10 million stars, with a total mass of 4 million solar masses, making it the most massive known globular cluster in the Milky Way.

A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is sometimes classified as a dwarf galaxy; others consider it a full-fledged galaxy. Dwarf galaxies' formation and activity are thought to be heavily influenced by interactions with larger galaxies. Astronomers identify numerous types of dwarf galaxies, based on their shape and composition.

NGC 6822 is a barred irregular galaxy approximately 1.6 million light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius. Part of the Local Group of galaxies, it was discovered by E. E. Barnard in 1884, with a six-inch refractor telescope. It is the closest non-satellite galaxy to the Milky Way, but lies just outside its virial radius. It is similar in structure and composition to the Small Magellanic Cloud. It is about 7,000 light-years in diameter.

The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye.

HE 0437-5439 is a massive, unbound hypervelocity star (HVS), also called HVS3. It is a main sequence B-type star located in the Dorado constellation. It was discovered in 2005 with the Kueyen 8.2-metre (320 in) telescope, which is part of the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope array. HE 0437-5439 is a young star, with an age of around 30 million years. The mass of the star is almost nine times greater than the mass of the Sun and the star is located 200,000 light years away in the direction of the Dorado constellation, 16 degrees northwest of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) and farther away than the LMC. The star appears to be receding at an extremely high velocity of 723 kilometres per second (449 mi/s), or 2,600,000 kilometres per hour (1,600,000 mph). At this speed, the star is no longer gravitationally bound and will leave the Milky Way galaxy system and escape into intergalactic space. It was thought to have originated in the LMC and been ejected from it soon after birth. This could happen if it originally was one of a pair of stars and if there is a supermassive black hole in the LMC.

NGC 7006 is a globular cluster in the constellation Delphinus. NGC 7006 resides in the outskirts of the Milky Way. It is about 135,000 light-years away, five times the distance between the Sun and the centre of the galaxy, and it is part of the galactic halo. This roughly spherical region of the Milky Way is made up of dark matter, gas and sparsely distributed stellar clusters.
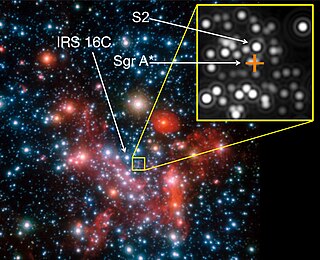
S2, also known as S0–2, is a star in the star cluster close to the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), orbiting it with a period of 16.0518 years, a semi-major axis of about 970 au, and a pericenter distance of 17 light hours – an orbit with a period only about 30% longer than that of Jupiter around the Sun, but coming no closer than about four times the distance of Neptune from the Sun. The mass when the star first formed is estimated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO) to have been approximately 14 M☉. Based on its spectral type, it probably has a mass of 10 to 15 solar masses.

Leo IV is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy situated in the Leo constellation, discovered in 2006 in the data obtained by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The galaxy is located at the distance of about 160 kpc from the Sun and moves away from the Sun with the velocity of about 130 km/s. It is classified as a dwarf spheroidal galaxy (dSph) meaning that it has an approximately round shape with the half-light radius of about 130 pc.

An intergalactic star, also known as an intracluster star or a rogue star, is a star not gravitationally bound to any galaxy. Although a source of much discussion in the scientific community during the late 1990s, intergalactic stars are now generally thought to have originated in galaxies, like other stars, before being expelled as the result of either galaxies colliding or of a multiple-star system traveling too close to a supermassive black hole, which are found at the center of many galaxies.

UDFy-38135539 is the Hubble Ultra Deep Field (UDF) identifier for a galaxy which was calculated as of October 2010 to have a light travel time of 13.1 billion years with a present proper distance of around 30 billion light-years.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to galaxies:
The Eridanus II Dwarf is a low-surface brightness dwarf galaxy in the constellation Eridanus. Eridanus II was independently discovered by two groups in 2015, using data from the Dark Energy Survey. This galaxy is probably a distant satellite of the Milky Way. Eridanus II contains a centrally located globular cluster; and is the smallest, least luminous galaxy known to contain a globular cluster. Crnojević et al., 2016. Eridanus II is significant, in a general sense, because the widely accepted Lambda CDM cosmology predicts the existence of many more dwarf galaxies than have yet been observed. The search for just such bodies was one of the motivations for the ongoing Dark Energy Survey observations. Eridanus II has special significance because of its apparently stable globular cluster. The stability of this cluster, near the center of such a small, diffuse, galaxy places constraints on the nature of dark matter.


















