
Fornax is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere, partly ringed by the celestial river Eridanus. Its name is Latin for furnace. It was named by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1756. Fornax is one of the 88 modern constellations.

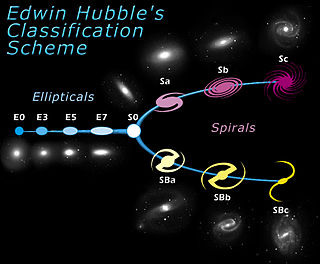
The Hubble sequence is a morphological classification scheme for galaxies published by Edwin Hubble in 1926. It is often colloquially known as the Hubble tuning-fork diagram because the shape in which it is traditionally represented resembles a tuning fork. It was invented by John Henry Reynolds and Sir James Jeans.

An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the four main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae, along with spiral and lenticular galaxies. Elliptical (E) galaxies are, together with lenticular galaxies (S0) with their large-scale disks, and ES galaxies with their intermediate scale disks, a subset of the "early-type" galaxy population.

Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, form part of the Hubble sequence. Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the bulge. These are often surrounded by a much fainter halo of stars, many of which reside in globular clusters.

An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure.

A lenticular galaxy is a type of galaxy intermediate between an elliptical and a spiral galaxy in galaxy morphological classification schemes. It contains a large-scale disc but does not have large-scale spiral arms. Lenticular galaxies are disc galaxies that have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing star formation. They may, however, retain significant dust in their disks. As a result, they consist mainly of aging stars. Despite the morphological differences, lenticular and elliptical galaxies share common properties like spectral features and scaling relations. Both can be considered early-type galaxies that are passively evolving, at least in the local part of the Universe. Connecting the E galaxies with the S0 galaxies are the ES galaxies with intermediate-scale discs.
Galaxy morphological classification is a system used by astronomers to divide galaxies into groups based on their visual appearance. There are several schemes in use by which galaxies can be classified according to their morphologies, the most famous being the Hubble sequence, devised by Edwin Hubble and later expanded by Gérard de Vaucouleurs and Allan Sandage. However, galaxy classification and morphology are now largely done using computational methods and physical morphology.

A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is sometimes classified as a dwarf galaxy; others consider it a full-fledged galaxy. Dwarf galaxies' formation and activity are thought to be heavily influenced by interactions with larger galaxies. Astronomers identify numerous types of dwarf galaxies, based on their shape and composition.

NGC 1097 is a barred spiral galaxy about 45 million light years away in the constellation Fornax. It was discovered by William Herschel on 9 October 1790. It is a severely interacting galaxy with obvious tidal debris and distortions caused by interaction with the companion galaxy NGC 1097A.

NGC 1316 is a lenticular galaxy about 60 million light-years away in the constellation Fornax. It is a radio galaxy and at 1400 MHz is the fourth-brightest radio source in the sky.

NGC 5010 is a lenticular galaxy located about 140 million light years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by John Herschel on May 9, 1831. It is considered a Luminous Infrared Galaxy (LIRG). As the galaxy has few young blue stars and mostly red old stars and dust, it is transitioning from being a spiral galaxy to being an elliptical galaxy, with its spiral arms having burned out and become dusty arms. From the perspective of Earth, the galaxy is facing nearly edge-on.

NGC 4452 is an edge-on lenticular galaxy that is part of the Virgo Cluster. NGC 4452 is about 60 million light-years (18 Mpc) away from Earth and 35 kly (11 kpc) in diameter. This galaxy was first seen by William Herschel in 1784 with his 47 cm (19 in) telescope.

NGC 4762 is an edge-on lenticular galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It is at a distance of 60 million light years and is a member of the Virgo Cluster. The edge-on view of this particular galaxy, originally considered to be a barred spiral galaxy, makes it difficult to determine its true shape, but it is considered that the galaxy consists of four main components — a central bulge, a bar, a thick disc and an outer ring. The galaxy's disc is asymmetric and warped, which could be explained by NGC 4762 mergering with a smaller galaxy in the past. The remains of this former companion may then have settled within NGC 4762's disc, redistributing the gas and stars and so changing the disc's morphology.

IC 2006 is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Eridanus. The galaxy was discovered on 3 October 1897 by the American astronomer Lewis A. Swift. It is estimated to be around 60 to 70 million light years away, in the Fornax Cluster. The galaxy is one of the smaller in the Fornax cluster, with a diameter of only 35 000 light-years.

NGC 1387 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Fornax, in the Fornax Cluster. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 25, 1835.

NGC 1375 is a barred lenticular galaxy in the constellation Fornax discovered by John Herschel on November 29, 1837. It is believed to be a member of the Fornax Cluster.

IC 4710 is a galaxy in southern constellation of Pavo, roughly 34 million light-years away.

NGC 1460 is a barred lenticular galaxy in the constellation Eridanus. It was discovered by John Herschel on November 28, 1837. It is moving away from the Milky Way at 1341 km/s.

IC 1993 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Fornax. It was discovered by Lewis Swift on November 19, 1897. At a distance of about 50 million light-years, and redshift of 1057 km/s, it is one of the closest to us of the 200 galaxies in the Fornax Cluster.

NGC 1379 is a low-luminosity elliptical galaxy in the southern constellation Fornax. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 25, 1835.




















