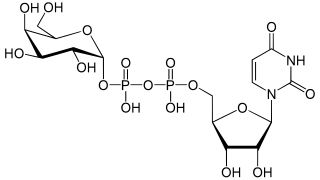
Uridine diphosphate galactose (UDP-galactose) is an intermediate in the production of polysaccharides. It is important in nucleotide sugars metabolism, and is the substrate for the transferase B4GALT5.
In enzymology, an UDP-glucosamine 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
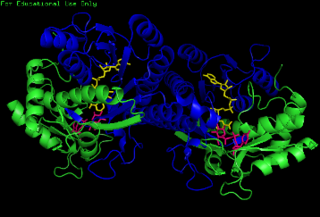
The enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, also known as UDP-galactose 4-epimerase or GALE, is a homodimeric epimerase found in bacterial, fungal, plant, and mammalian cells. This enzyme performs the final step in the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, catalyzing the reversible conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. GALE tightly binds nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a co-factor required for catalytic activity.
In enzymology, an UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-glucuronate 5'-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme UDP-glucuronate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.35) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a UDP-N-acetylmuramate—L-alanine ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1,4-beta-D-xylan synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a galactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a linamarin synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lipopolysaccharide 3-alpha-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lipopolysaccharide glucosyltransferase I is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a xylosylprotein 4-beta-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an UTP—xylose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a protein xylosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction in which a beta-D-xylosyl residue is transferred from UDP-D-xylose to the sidechain oxygen atom of a serine residue in a protein.
David Sidney Feingold was an American biochemist.
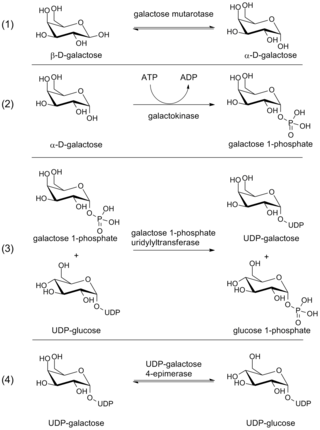
The Leloir pathway is a metabolic pathway for the catabolism of D-galactose. It is named after Luis Federico Leloir, who first described it.






