
The Umchabezi River is a tributary of the Mzingwane River in Beitbridge District and Gwanda District, Zimbabwe. The main dam on the river is Makado Dam, which supplies water for commercial irrigation. [1]

The Umchabezi River is a tributary of the Mzingwane River in Beitbridge District and Gwanda District, Zimbabwe. The main dam on the river is Makado Dam, which supplies water for commercial irrigation. [1]

A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions.

The Akosombo Dam, also known as the Volta Dam, is a hydroelectric dam on the Volta River in southeastern Ghana in the Akosombo gorge and part of the Volta River Authority. The construction of the dam flooded part of the Volta River Basin and led to the subsequent creation of Lake Volta. Lake Volta is the largest man-made lake in the world by surface area. It covers 8,502 square kilometres (3,283 sq mi), which is 3.6% of Ghana's land area. With a volume of 148 cubic kilometers, Lake Volta is the world's third largest man-made lake by volume; the largest being Lake Kariba which contains 185 cubic kilometers of water.
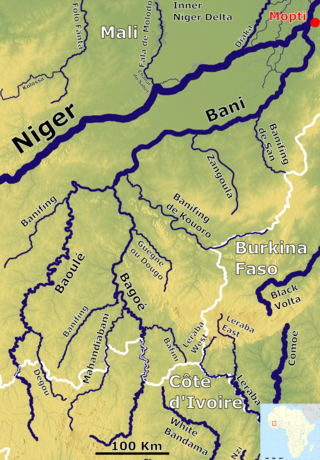
The Bani River is the principal tributary of the Niger River in Mali. The river is formed from the confluence of the Baoulé and Bagoé rivers some 160 km (99 mi) east of Bamako and it merges with the Niger near Mopti. Its length is about 1,100 km (680 mi).

Kallanai is an ancient dam built by Karikala of Chola dynasty in 150 CE. It is built across the Kaveri river flowing from Tiruchirapalli District to Thanjavur district, Tamil Nadu, India. The dam is located in Thanjavur district, 15 km from Tiruchirapalli and 45 km from Thanjavur. It is the fourth oldest water-diversion or water-regulator structure in the world and the oldest in India that is still in use. Because of its spectacular architecture, it is one of the prime tourist spots in Tamil Nadu.

Hartbeespoort Dam is an arch type dam situated in the North West Province of South Africa. It lies in a valley to the south of the Magaliesberg mountain range and north of the Witwatersberg mountain range, about 35 kilometres north west of Johannesburg and 20 kilometres west of Pretoria. The name of the dam means "dam at the gorge of the hartebeest" in Afrikaans. This "poort" in the Magaliesberg was a popular spot for hunters, where they cornered and shot the hartebeest. The dam was originally designed for irrigation, which is currently its primary use, as well as for domestic and industrial use. The dam has suffered from a hypertrophic state since the early 1970s. Mismanagement of waste water treatment from urban zones within the Hartbeespoort Dam catchment area is largely to blame, having distorted the food web with over 280 tons of phosphate and nitrate deposits.

White sturgeon is a species of sturgeon in the family Acipenseridae of the order Acipenseriformes. They are an anadromous (migratory) fish species ranging in the Eastern Pacific; from the Gulf of Alaska to Monterey, California. However, some are landlocked in the Columbia River Drainage, Montana, and Lake Shasta in California, with reported sightings in northern Baja California, Mexico.
Environmental flows describe the quantity, timing, and quality of water flows required to sustain freshwater and estuarine ecosystems and the human livelihoods and well being that depend on these ecosystems. In the Indian context river flows required for cultural and spiritual needs assumes significance. Through implementation of environmental flows, water managers strive to achieve a flow regime, or pattern, that provides for human uses and maintains the essential processes required to support healthy river ecosystems. Environmental flows do not necessarily require restoring the natural, pristine flow patterns that would occur absent human development, use, and diversion but, instead, are intended to produce a broader set of values and benefits from rivers than from management focused strictly on water supply, energy, recreation, or flood control.

The Sefid-Rud is a river approximately 670 kilometres (416 mi) long, rising in the Alborz mountain range of northwestern Iran and flowing generally northeast to enter the Caspian Sea at Rasht.

The Mwenezi River, originally known as the Nuanetsi River, is a major tributary of the Limpopo River. The Mwenezi River starts up in south central Zimbabwe and flows south-east along what is known as the Mwenezi River Valley that bisects the district into two sectors. The river is found in both Zimbabwe and Mozambique. In Zimbabwe it has been known as the Nuanetsi or Nuanetzi River in the past, a name it retains in Mozambique.
Water resources management is a key element of Brazil's strategy to promote sustainable growth and a more equitable and inclusive society. Brazil's achievements over the past 70 years have been closely linked to the development of hydraulic infrastructure for hydroelectric power generation and just recently to the development of irrigation infrastructure, especially in the Northeast region.
The Philippines' water supply system dates back to 1946, after the country declared independence. Government agencies, local institutions, non-government organizations, and other corporations are primarily in charge of the operation and administration of water supply and sanitation in the country.

WAFLEX is a spreadsheet-based model. It can be used to analyse upstream-downstream interactions, dam management options and water allocation and development options.
Zhovhe Dam is a reservoir on the Mzingwane River, Zimbabwe with a capacity of 133 million cubic metres. It supplies water for commercial irrigation and the town of Beitbridge.

Oakley Block Dam is a proposed reservoir on the Mzingwane River, south of West Nicholson, Zimbabwe with a capacity of 41 million cubic metres.
The Mtetengwe River is a tributary of the Mzingwane River in Beitbridge District, Zimbabwe. There are two dams on its tributaries: Tongwe Dam on the Tongwe River, which provides water for an irrigation scheme, and Giraffe Dam which supplies water for cattle.
Chulabhorn Dam (เขื่อนจุฬาภรณ์) is a dam in Tambon Thung Lui Lai, Khon San District, Chaiyaphum Province, Thailand. It impounds the Phrom River, a tributary of the Mekong. The dam has diverted the Nam Phrong River. As water leaves its turbines, it empties into the Choen River. The dam is named for Princess Chulabhorn of Thailand.

Sand dams are a simple, low-cost and low-maintenance, replicable rainwater harvesting technology. They provide a clean, local water supply for domestic and farming use and are suited to semi-arid areas of the world.

The Bakolori Dam is in Sokoto State in northwest Nigeria. It was completed in 1978 and its reservoir filled by 1981. It is a major reservoir on the Sokoto River, a tributary of the Rima River, which in turn feeds the Niger River. Water from the dam supplies the Bakolori Irrigation Project.
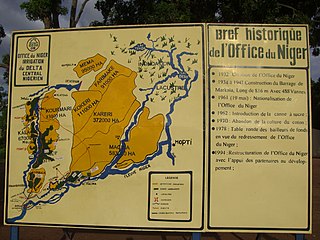
The Office du Niger is a semi-autonomous government agency in Mali that administers a large irrigation scheme in the Ségou Region of the country. Water from the Niger River is diverted into a system of canals at the Markala dam 35 kilometres (22 mi) downstream of Ségou. The water is used to irrigate nearly 100,000 hectares (390 sq mi) of the flat alluvial plains to the north and northeast of Markala that form part of the Delta mort. Although the French colonial administration constructed the system to produce cotton for the textile industry, the main agricultural product is now rice. Around 320,000 tons are grown each year representing 40 percent of the total Malian production. Large quantities of sugar cane are also grown in joint ventures between a Chinese company and the Malian state. The irrigation scheme uses 2.7 km3 (0.65 cu mi) of water each year corresponding to around 10 percent of the total flow of the Niger River.

Sedimentation enhancing strategies are environmental management projects aiming to restore and facilitate land-building processes in deltas. Sediment availability and deposition are important because deltas naturally subside and therefore need sediment accumulation to maintain their elevation, particularly considering increasing rates of sea-level rise. Sedimentation enhancing strategies aim to increase sedimentation on the delta plain primarily by restoring the exchange of water and sediments between rivers and low-lying delta plains. Sedimentation enhancing strategies can be applied to encourage land elevation gain to offset sea-level rise. Interest in sedimentation enhancing strategies has recently increased due to their ability to raise land elevation, which is important for the long-term sustainability of deltas.