
Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).
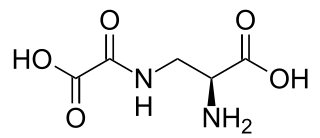
Oxalyldiaminopropionic acid (ODAP) is a structural analogue of the neurotransmitter glutamate found in the grass pea Lathyrus sativus. It is the neurotoxin responsible for the motor neuron degeneration syndrome lathyrism.
In enzymology, a leucine 2,3-aminomutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 10-hydroxytaxane O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,3-diaminopropionate N-oxalyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.58) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acridone synthase (EC 2.3.1.159) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-pyrazolylalanine synthase (EC 2.5.1.51) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cysteine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dimethylallylcistransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a homospermidine synthase (spermidine-specific) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-mimosine synthase (EC 2.5.1.52) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a zeatin 9-aminocarboxyethyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an indole-3-acetate beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sterol 3beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Pterocarpans are derivatives of isoflavonoids found in the family Fabaceae. It is a group of compounds which can be described as benzo-pyrano-furano-benzenes which can be formed by coupling of the B ring to the 4-one position.
Pseudotropine acyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name acyl-CoA:pseudotropine O-acyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Omega-hydroxypalmitate O-feruloyl transferase is an enzyme with systematic name feruloyl-CoA:16-hydroxypalmitate feruloyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4-aminobutyrate---pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme with systematic name 4-aminobutanoate:pyruvate aminotransferase. This enzyme is a type of GABA transaminase, which degrades the neurotransmitter GABA. The enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Pisatin (3-hydroxy-7-methoxy-4′,5′-methylenedioxy-chromanocoumarane) is the major phytoalexin made by the pea plant Pisum sativum. It was the first phytoalexin to be purified and chemically identified. The molecular formula is C17H14O6.




