A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic pain, painful urination (dysuria), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever or flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear bloody. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age.

Urolagnia is a paraphilia in which sexual excitement is associated with the sight or thought of urine or urination. The term has origins in the Greek language. Golden shower is slang for the practice of urinating on another person for sexual pleasure, while watersports is the more inclusive term. However, Urophilia is not exclusively associated with sexual excitement.

Urination is the release of urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Urine is released through the urethra and exits the penis or vulva through the urinary meatus in placental mammals, but is released through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, uresis, or, rarely, emiction, and known colloquially by various names including peeing, weeing, pissing, and euphemistically number one. The process of urination is under voluntary control in healthy humans and other animals, but may occur as a reflex in infants, some elderly individuals, and those with neurological injury. It is normal for adult humans to urinate up to seven times during the day.
Activities of daily living (ADLs) is a term used in healthcare to refer to an individual's daily self-care activities. Health professionals often use a person's ability or inability to perform ADLs as a measure of their functional status. The concept of ADLs was originally proposed in the 1950s by Sidney Katz and his team at the Benjamin Rose Hospital in Cleveland, Ohio. Since then, numerous researchers have expanded on the concept of ADLs. For instance, many indexes that assess ADLs now incorporate measures of mobility.

A urinal is a sanitary plumbing fixture similar to a toilet, but for urination only. Urinals are often provided in men's public restrooms in Western countries. They are usually used in a standing position. Urinals can be equipped with manual flushing, automatic flushing, or without flushing, as is the case for waterless urinals. They can be arranged as single sanitary fixtures, or in a trough design without privacy walls.

A public toilet, restroom, bathroom or washroom is a room or small building with toilets and sinks for use by the general public. The facilities are available to customers, travelers, employees of a business, school pupils or prisoners. Public toilets are typically found in many different places: inner-city locations, offices, factories, schools, universities and other places of work and study. Similarly, museums, cinemas, bars, restaurants, and entertainment venues usually provide public toilets. Railway stations, filling stations, and long distance public transport vehicles such as trains, ferries, and planes usually provide toilets for general use. Portable toilets are often available at large outdoor events.

Fountain is a readymade sculpture by Marcel Duchamp in 1917, consisting of a porcelain urinal signed "R. Mutt". In April 1917, an ordinary piece of plumbing chosen by Duchamp was submitted for the inaugural exhibition of the Society of Independent Artists, to be staged at the Grand Central Palace in New York. When explaining the purpose of his readymade sculpture, Duchamp stated they are "everyday objects raised to the dignity of a work of art by the artist's act of choice." In Duchamp's presentation, the urinal's orientation was altered from its usual positioning. Fountain was not rejected by the committee, since Society rules stated that all works would be accepted from artists who paid the fee, but the work was never placed in the show area. Following that removal, Fountain was photographed at Alfred Stieglitz's studio, and the photo published in the Dada journal The Blind Man. The original has been lost.
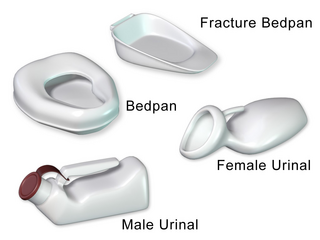
A bedpan or bed pan is a device used as a receptacle for the urine and/or feces of a person who is confined to a bed and therefore not able to use a toilet or chamber pot.

Potty parity is equal or equitable provision of public toilet facilities for females and males within a public space. Parity can be defined by equal floorspace or by number of fixtures within the washrooms, sometimes adjusted for the longer average time taken and more frequent visits to the washroom for females, among other factors.

Unisex public toilets are public toilets that are not separated by sex or gender.

Nursing in Australia is a healthcare profession. Nurses and midwives form the majority (54%) of Australian health care professionals. Nurses are either registered or enrolled. Registered nurses have broader and deeper education than enrolled nurses. Nurse practitioners complete a yet higher qualification. Nurses are not limited to working in hospitals, instead working in a variety of settings. Australian nurses are in demand as traveling nurses, particularly those with advanced qualifications.
Patient advocacy is a process in health care concerned with advocacy for patients, survivors, and caregivers. The patient advocate may be an individual or an organization, concerned with healthcare standards or with one specific group of disorders. The terms patient advocate and patient advocacy can refer both to individual advocates providing services that organizations also provide, and to organizations whose functions extend to individual patients. Some patient advocates are independent and some work for the organizations that are directly responsible for the patient's care.
A urine collection device or UCD is a device that allows the collection of urine for analysis or for purposes of simple elimination. UCDs of the latter type are sometimes called piddle packs.

A female urination device (FUD), personal urination device (PUD), female urination aid, or stand-to-pee device (STP) is a device that can be used to more precisely aim the stream of urine while urinating standing upright. Variations range from basic disposable funnels to more elaborate reusable designs. Personal urination devices have increased in popularity since the 1990s. They are used for outdoor occupations & recreation, gender affirmation/safety, and medical reasons.

A female urinal is a urinal designed for the female anatomy to allow for ease of use by women and girls. Different models enable urination in standing, semi-squatting, or squatting postures, but usually without direct bodily contact with the toilet. Sitting models also exist, and are designed for body contact with the urinal.
Urologic diseases or conditions include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder control problems, and prostate problems, among others. Some urologic conditions do not affect a person for that long and some are lifetime conditions. Kidney diseases are normally investigated and treated by nephrologists, while the specialty of urology deals with problems in the other organs. Gynecologists may deal with problems of incontinence in women.

Nursing is a health care profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alleviation of suffering through compassionate presence". Nurses practice in many specialties with varying levels of certification and responsibility. Nurses comprise the largest component of most healthcare environments. There are shortages of qualified nurses in many countries.
In health care, toileting is the act of assisting a dependent patient with their elimination needs.

A hospital bed or hospital cot is a bed specially designed for hospitalized patients or others in need of some form of health care. These beds have special features both for the comfort and well-being of the patient and for the convenience of health care workers. Common features include adjustable height for the entire bed, the head, and the feet, adjustable side rails, and electronic buttons to operate both the bed and other nearby electronic devices.
Healthcare standards in Qatar are generally high. Qatari citizens are covered by a national health insurance scheme, while expatriates must either receive health insurance from their employers, or in the case of the self-employed, purchase insurance. Qatar's healthcare spending is among the highest in the Middle East, with $4.7 billion being invested in healthcare in 2014. This was a $2.1 billion increase from 2010. The premier healthcare provider in the country is the Hamad Medical Corporation, established by the government as a non-profit healthcare provider, which runs a network of hospitals, an ambulance services, and a home healthcare service, all of which are accredited by the Joint Commission.

















