
The diving petrels form a genus, Pelecanoides, of seabirds in the family Procellariidae. There are four very similar species of diving petrels, distinguished only by small differences in the coloration of their plumage, habitat, and bill construction. They are only found in the southern hemisphere. The diving petrels were formerly placed in their own family, the Pelecanoididae.

Deinotherium is an extinct genus of large, elephant-like proboscideans that lived from about the middle-Miocene until the early Pleistocene. Although its appearance is reminiscent of modern elephants, Deinotherium possessed a notably more flexible neck, with limbs adapted to a more cursorial lifestyle, as well as tusks which grew down and curved back from the mandible, as opposed to the forward-growing maxillary tusks of extant elephants. Deinotherium was a widespread genus, ranging from East Africa, north to southern Europe, and east to the Indian subcontinent. They were primarily browsing animals, with a diet largely consisting of leaves. The genus most likely went extinct due to environmental changes, such as forested areas gradually being replaced by open grasslands, during the latter half of the Neogene. Deinotherium thrived the longest in Africa, where they were found into the early Pleistocene.

The mousebirds are birds in the order Coliiformes. They are the sister group to the clade Cavitaves, which includes the Leptosomiformes, Trogoniformes (trogons), Bucerotiformes, Piciformes and Coraciformes. This group is now confined to sub-Saharan Africa, and it is the only bird order confined entirely to that continent, with the possible exception of turacos which are considered by some as the distinct order Musophagiformes, and the cuckoo roller, which is the only member of the order Leptosomiformes, and which is found in Madagascar but not mainland Africa. Mousebirds had a wider range in the Paleogene, with a widespread distribution in Europe and North America during the Paleocene.

The black geese of the genus Branta are waterfowl belonging to the true geese and swans subfamily Anserinae. They occur in the northern coastal regions of the Palearctic and all over North America, migrating to more southerly coasts in winter, and as resident birds in the Hawaiian Islands. Alone in the Southern Hemisphere, a self-sustaining feral population derived from introduced Canada geese is also found in New Zealand.

Dromornis is a genus of large to enormous prehistoric birds native to Australia during the Oligocene to Pliocene epochs. The species were flightless, possessing greatly reduced wing structures but with large legs, similar to the modern ostrich or emu. They were likely to have been predominantly, if not exclusively, herbivorous browsers. The male of the largest species, Dromornis stirtoni, is a contender for the tallest and heaviest bird, and possibly exhibited aggressive territorial behaviour. They belong to the family Dromornithidae, extinct flightless birds known as mihirungs.
Barawertornis tedfordi was a dromornithid (mihirung), a large flightless fowl hailing from Late Oligocene to Early Miocene. The only species in the genus Barawertornis, its fossil remains are found in strata of the Riversleigh deposits located at two sites in Northwestern Queensland, Australia.

Ciconia is a genus of birds in the stork family. Six of the seven living species occur in the Old World, but the maguari stork has a South American range. In addition, fossils suggest that Ciconia storks were somewhat more common in the tropical Americas in prehistoric times.

The blue-naped mousebird, also formerly called the blue-naped coly is a species of bird belonging to the family Coliidae within the order Coliiformes. They are the sister group to the clade Eucavitaves, which contains the families Leptosomiformes, Trogoniformes (trogons), Bucerotiformes, Piciformes and Coraciformes.

Osteodontornis is an extinct seabird genus. It contains a single named species, Osteodontornis orri, which was described quite exactly one century after the first species of the Pelagornithidae was. O. orri was named after Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History paleontologist Phil C. Orr, for his recognition of the importance of the specimen.

Amphicyon is an extinct genus of large carnivorans belonging to the family Amphicyonidae, subfamily Amphicyoninae, from the Miocene epoch. Members of this family received their vernacular name for possessing bear-like and dog-like features. They ranged over North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Megapaloelodus is an extinct genus of stem flamingo of the family Palaelodidae. Megapaloelodus is primarily known from Miocene America, from South Dakota and Oregon in the north to Argentina in the south, but the species Megapaloelodus goliath was found in Europe. Additionally, one unnamed species was discovered in Miocene sediments from Namibia. Due to a lack of skull material, little can be said about the ecology of Megapaloelodus. Species of this genus are typically larger than those of Palaelodus and appear to have inhabited similar brackish lake environments. Additionally, they may have been capable of "locking" their legs in a standing position.

Lybiidae is a family of birds also known as the African barbets. There are 42 species ranging from the type genus Lybius of forest interior to the tinkerbirds (Pogoniulus) of forest and scrubland. They are found throughout sub-Saharan Africa, with the exception of the far south-west of South Africa.

The red-faced mousebird is a species of mousebird or coly. It is a common in southern Africa from the Democratic Republic of Congo, Zambia and Tanzania south to the Cape. Its habitat is savanna with thickets, fynbos scrub, other open woodland, gardens and orchards.

Colius is a genus of mousebirds in the family Coliidae. The four species are widely distributed in Africa. Two other African mousebirds are placed in the genus Urocolius.

Euthecodon is an extinct genus of long-snouted crocodile. It was common throughout much of Africa during the Neogene, with fossils being especially common in Kenya, Ethiopia, and Libya. Although superficially resembling that of gharials, the long snout was a trait developed independently from that of other crocodilians and suggests a diet of primarily fish. Euthecodon coexisted with a wide range of other crocodiles in the areas it inhabited before eventually going extinct during the Pleistocene.

Palaelodidae is a family of extinct birds in the group Phoenicopteriformes, which today is represented only by the flamingos. They were widespread during the Neogene, with fossil remains found on all continents other than Antarctica. The oldest remains referred to this group appeared in the fossil record during the Oligocene in Egypt and Belgium, before palaelodids reached their peak diversity during the Miocene. Following this the group declined in the early Pliocene before going extinct on most continents. However, remains found near Cooper Creek in the Lake Eyre Basin indicate that palaelodids managed to survive in Australia until the Pleistocene. Currently three genera are recognized by scientists: Adelalopus, Palaelodus and Megapaloelodus. Most fossil remains stem from Europe and have been assigned to the type species, Palaelodus ambiguus. Due to the fragmentary nature of most of these species, little is known about their ecology. They appear to have preferred brackish lakes and lagoons. Palaelodus has previously been thought to be a wader or diver, but recent research indicates that they were better suited for swimming and possibly fed on insect larvae and other aquatic invertebrates. At least Megapaloelodus appears to have adaptations for "locking" their legs in a standing position.
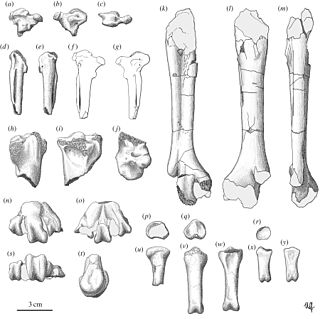
Garganornis is an extinct genus of enormous flightless anatid waterfowl from the Late Miocene of Gargano, Italy. The genus contains one species, G. ballmanni, named by Meijer in 2014. Its enormous size is thought to have been an adaptation to living in exposed, open areas with no terrestrial predators, and as a deterrent to the indigenous aerial predators like the eagle Garganoaetus and the giant barn owl Tyto gigantea.
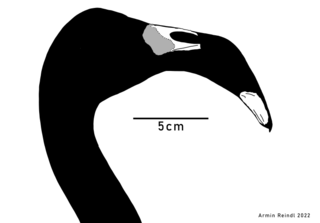
Leakeyornis is an extinct genus of flamingo from the early to middle Miocene of Kenya, primarily in the area of modern day Lake Victoria. Initially described as a species of Phoenicopterus based on an incomplete skull and various limb bones, it was later found to show a mixture of traits found across modern flamingo genera and subsequently placed in its own genus. It contains a single species, Leakeyornis aethiopicus.
Diamantofelis is an extinct genus of felids that lived in what is now Namibia during the Early Miocene. It contains a single species, Diamantofelis ferox.
Caerulonettion is an extinct genus of anatid birds from the Miocene Epoch of Europe. The genus contains a single species, C. natator, known from various limb and girdle bones. The Caerulonettion fossil material was originally assigned to various other anatid genera before being recognized as a distinct genus.


















