
The southern right whale is a baleen whale, one of three species classified as right whales belonging to the genus Eubalaena. Southern right whales inhabit oceans south of the Equator, between the latitudes of 20° and 60° south. In 2009 the global population was estimated to be approximately 13,600.

The South Island robin, also known in Māori as the Kakaruwai., is a sparrow-sized bird found only in New Zealand, where it has the status of a protected endemic species. The birds are sparsely distributed through the South Island and Stewart Island/Rakiura, although the distribution is not continuous. The nominate, and the Stewart Island robin are the two subspecies. The species is closely related to the North Island robin, and also to the extremely rare black robin of the Chatham Islands.

Cordyline is a genus of about 24 species of woody monocotyledonous flowering plants in family Asparagaceae, subfamily Lomandroideae. The subfamily has previously been treated as a separate family Laxmanniaceae, or Lomandraceae. Other authors have placed the genus in the Agavaceae. Cordyline is native to the western Pacific Ocean region, from New Zealand, eastern Australia, southeastern Asia and Polynesia, with one species found in southeastern South America.
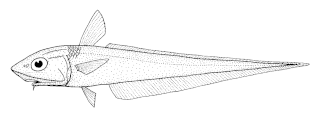
Coelorinchus australis, the javelin, javelinfish, or southern whiptail, is a species of fish found around Australia and New Zealand at depths of between 80 and 500 m. Its length is between 25 and 50 cm. It is a brownish color with 8 or 9 pale longitudinal stripes, and a small chin barbel. It feeds on octopus, fishes, and decapod crustaceans.

The New Zealand eagle ray or Australian eagle ray is an eagle ray of the family Myliobatidae, found in bays, estuaries, and near rocky reefs around New Zealand and southern Australia on the inner continental shelf. It is a common species and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".

Utricularia dichotoma, commonly known as fairy aprons, is a variable, perennial species of terrestrial bladderwort. It is a widespread species with mauve or purple fan-shaped flowers on a slender stalk and usually grows in wet locations.

Utricularia gibba, commonly known as the humped or floating bladderwort, is a small, mat-forming species of carnivorous aquatic bladderwort. It is found on all continents except Antarctica.

Cotula australis is a species of plant in the daisy family known by the common names bachelor's buttons, annual buttonweed, southern waterbuttons and Australian waterbuttons. This small plant is native to Australia and New Zealand, but it is known in other areas of the world as a common weed.
Utricularia sect. Meionula is a section in the genus Utricularia. The four species in this section are small terrestrial carnivorous plants native to Southeast Asia and Australia. Constantine Samuel Rafinesque originally published some of the species in this section under two genera, Meionula and Trixapias, in 1838. Peter Taylor published the section as it currently stands in 1986, including three additional Australian and New Zealand species which are now circumscribed in their own section, Australes.

Utricularia chrysantha, the sun bladderwort, is a medium-sized annual, terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. U. chrysantha is endemic to southern New Guinea and Australia. It grows as a terrestrial species in wet grasslands or Melaleuca-Acacia savannas at low altitudes near sea level. It was originally described and published by Robert Brown in 1810.

Utricularia sect. Australes is a section in the genus Utricularia. The three species in this section are small terrestrial carnivorous plants native to Australia and New Zealand. Peter Taylor originally described and published this section in his 1989 taxonomic treatment of the genus, splitting off species from section Meionula. Taylor originally placed this section within subgenus Utricularia. More recent phylogenetic data and revisions have reinstated subgenus Bivalvaria and have placed this section within it.

Acanthopagrus australis, the yellowfin bream, also known as sea bream, surf bream, silver bream or eastern black bream, is a species of marine and freshwater fish of the porgy family, Sparidae. It is a deep-bodied fish, occasionally confused with Acanthopagrus butcheri, but is generally distinguished by its yellowish ventral and anal fins. It is a popular target for recreational fishermen due to its capacity to fight well above its weight coupled with its table quality.

The southern Mandarin dogfish is a species of Mandarin dogfish shark in the genus Cirrhigaleus. It was distinguished from Cirrhigaleus barbifer, which lives in the North Pacific, on an expedition in the coral reefs near Australia in 2007. It is now known to live in the temperate waters in south-eastern Australia and from the Bay of Plenty region in New Zealand, at depths of 146–640 metres.
There are fourteen species of carnivorous plants occurring in New Zealand, and four species that have been known to occur in the past.
A. australis may refer to:

Amanita australis is a species of fungus in the family Amanitaceae. It is found only in New Zealand, where it occurs in Leptospermum and Nothofagus forest. The species was first described by New Zealand mycologist Greta Stevenson in 1962; in the same publication Stevenson also described what she thought was a unique species, Limacella macrospora, but over 30 years later this was reduced to synonymy with A. australis.
Phenacoleachiidae is a family of scale insects commonly known as the phenacoleachiids. They are found only in the South Island of New Zealand, and on certain offshore islands. There are two species in a single genus.

Australia has one of the world's richest carnivorous plant floras, with around 187 recognised species from 6 genera.
Aedes australis is a brackish water mosquito species from the subgenus Halaedes. It is native to Australia. It was first found in New Zealand in 1961 and is now present in the southern half of the South Island.














