
Kootenai County is located in the U.S. state of Idaho. As of the 2020 census, its population was 171,362, making it the third-most populous county in Idaho and the largest in North Idaho, the county accounting for 45.4% of the region's total population. The county seat and largest city is Coeur d'Alene. The county was established in 1864 and named after the Kootenai tribe. Kootenai County is coterminous with the Coeur d'Alene metropolitan area, which along with the Spokane metropolitan area comprises the Spokane–Coeur d'Alene combined statistical area.

Coeur d'Alene is a city and the county seat of Kootenai County, Idaho, United States. It is the most populous city in North Idaho and the principal city of the Coeur d'Alene Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 54,628 at the 2020 census. Coeur d'Alene is a satellite city of Spokane, which is located about thirty miles (50 km) to the west in the state of Washington. The two cities are the key components of the Spokane–Coeur d'Alene Combined Statistical Area, of which Coeur d'Alene is the third-largest city. The city is situated on the north shore of the 25-mile (40 km) long Lake Coeur d'Alene and to the west of the Coeur d'Alene Mountains. Locally, Coeur d'Alene is known as the "Lake City", or simply called by its initials, "CDA".

Spokane Valley is a city in Spokane County, Washington, United States, and the largest suburb of Spokane. It is located east of Spokane, west of Coeur d'Alene, Idaho, and surrounds the city of Millwood on three sides. The city incorporated as the City of Spokane Valley on March 31, 2003. The population was 102,976 at the 2020 census, making it the ninth-most populous city in Washington state. Spokane Valley is named after the valley of the Spokane River, in which it is located. The city and the general area is colloquially referred to as "The Valley" by residents of the Spokane–Coeur d'Alene area.

The Inland Northwest, historically and alternatively known as the Inland Empire, is a region of the American Northwest centered on the Greater Spokane, Washington Area, encompassing all of Eastern Washington and North Idaho. Under broader definitions, Northeastern Oregon and Western Montana may be included in the Inland Northwest. Alternatively, stricter definitions may exclude Central Washington and Idaho County, Idaho.

The Palouse is a distinct geographic region of the northwestern United States, encompassing parts of north central Idaho, southeastern Washington, and, by some definitions, parts of northeast Oregon. It is a major agricultural area, primarily producing wheat and legumes. Situated about 160 miles (260 km) north of the Oregon Trail, the region experienced rapid growth in the late 19th century.

The Spokane Valley is a valley of the Spokane River through the southern Selkirk Mountains in the U.S. state of Washington. The valley is home to the cities of Spokane and its suburbs Spokane Valley, Liberty Lake, and Millwood. The valley is bounded on the north and south by the Selkirk Mountains, on the west by the Columbia River Basalt Group, and on the east by the Rathdrum Prairie at the Idaho state border. Mica Peak, located south of the valley, is the southernmost peak in the Selkirk Range. The mountain, along with surrounding peaks, separates the Spokane Valley from the Palouse. The Valley contains part of the Spokane Valley–Rathdrum Prairie Aquifer.

Mullan Road was the first wagon road to cross the Rocky Mountains to the Inland of the Pacific Northwest. It was built by U.S. Army troops under the command of Lt. John Mullan, between the spring of 1859 and summer 1860. It led from Fort Benton, which at the time was in the Dakota Territory, then Idaho Territory from July 1863, and into Montana Territory beginning in May 1864. The road eventually stretched all the way from Fort Walla Walla, Washington Territory, near the Columbia River to the navigational head of the Missouri River, which at the time was the farthest inland port in the world). The road previewed the route approximately followed by modern-day Interstate 15 and Interstate 90 through present-day Montana, Idaho, and Washington.

The Silver Valley is a region in the northwest United States, in the Coeur d'Alene Mountains in northern Idaho. It is noted for its mining heritage, dating back to the 1880s.

The Trail of the Coeur d'Alenes is a rail trail in the Idaho Panhandle of the United States. It follows the right-of-way of the former Union Pacific Railroad from Mullan, a mountain mining town near the Montana border, westward to Plummer, a town on the prairie near the Washington border. Generally following the Coeur d'Alene River, the rail line was abandoned in 1991, and the trail officially opened in March 2004.

Interstate 90 (I-90) is a transcontinental Interstate Highway that runs east–west across the northern United States. Within the state of Idaho, the freeway travels for 74 miles (119 km) from the Washington border near Spokane to Coeur d'Alene and the panhandle region at the north end of the state. After traveling through the Silver Valley along the Coeur d'Alene River in the Bitterroot Range, I-90 crosses into Montana at Lookout Pass.

The Columbia Plateau ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) encompassing approximately 32,100 square miles (83,139 km2) of land within the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. The ecoregion extends across a wide swath of the Columbia River Basin from The Dalles, Oregon to Lewiston, Idaho to Okanogan, Washington near the Canada–U.S. border. It includes nearly 500 miles (800 km) of the Columbia River, as well as the lower reaches of major tributaries such as the Snake and Yakima rivers and the associated drainage basins. It is named for the Columbia Plateau, a flood basalt plateau formed by the Columbia River Basalt Group during the late Miocene and early Pliocene. The arid sagebrush steppe and grasslands of the region are flanked by moister, predominantly forested, mountainous ecoregions on all sides. The underlying basalt is up to 2 miles (3 km) thick and partially covered by thick loess deposits. Where precipitation amounts are sufficient, the deep loess soils have been extensively cultivated for wheat. Water from the Columbia River is subject to resource allocation debates involving fisheries, navigation, hydropower, recreation, and irrigation, and the Columbia Basin Project has dramatically converted much of the region to agricultural use.

Spokane, Washington has a rich sporting culture and the area residents are active in many spectator and participant sports. Although Spokane lacks any major, nationally recognized professional sports team, Spokane has a sports friendly atmosphere, and was recognized and rated #99 in the Sporting News 2006 "99 Best Sporting Cities" list. In 2009, Sports Business Journal rated Spokane as the fifth best minor league sports market in America out of 239 markets.

The economy of the Spokane metropolitan area plays a vital role as the hub for the commercial, manufacturing, and transportation center as well as the medical, shopping, and entertainment hub of the 80,000 square miles (210,000 km2) Inland Northwest region. Although the two have opted not to merge into a single Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) yet, the Coeur d'Alene MSA has been combined by the Census Bureau into the Spokane–Coeur d'Alene combined statistical area (CSA). The CSA comprises the Spokane metropolitan area and the Coeur d'Alene metropolitan area anchored by Coeur d'Alene, Idaho. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the Spokane metropolitan area has a workforce of about 287,000 people and an unemployment rate of 5.3 percent as of February 2020; the largest sectors for non–farm employment are education and health services, trade, transportation, and utilities, and government. The Coeur d'Alene metropolitan area has a workforce of 80,000 people and an unemployment rate of 6.8% as of June 2020; the largest sectors for non-farm employment are trade, transportation, and utilities, government, and education and health services as well as leisure and hospitality. In 2017, the Spokane–Spokane Valley metropolitan area had a gross metropolitan product of $25.5 billion while the Coeur d'Alene metropolitan area was $5.93 billion.

Latah Creek, also known as Hangman Creek, is a large stream in eastern Washington and north central Idaho in the United States. The creek flows northwest from the Rocky Mountains to Spokane, where it empties into the Spokane River. It drains 673 square miles (1,740 km2) in parts of Benewah and Kootenai counties in Idaho, Spokane County and a small portion of Whitman County in Washington, where over 64 percent of its watershed resides. Some major tributaries of the approximately 60-mile (97 km) creek include Little Latah Creek and Rock Creek. The average flow of the creek can range from 20 cubic feet per second (0.57 m3/s) to 20,000 cubic feet per second (570 m3/s). Latah Creek receives its name from a Nez Perce word likely meaning "fish". In 1854, the creek received another name, Hangman Creek, from a war between the Palouse Indians and white soldiers, which resulted in several Palouse being hanged alongside the creek.

The Battle of Spokane Plains was a battle during the Coeur d'Alene War of 1858 in the Washington Territory in the United States. The Coeur d'Alene War was part of the Yakima War, which began in 1855. The battle was fought west of Fort George Wright near Spokane, Washington, between elements of the United States Army and a coalition of Native American tribes consisting of Kalispel, Palus, Schitsu'umsh, Spokan, and Yakama warriors.

Mica is an unincorporated community in Spokane County, Washington, United States. Mica is located along State Route 27 12 miles (19 km) southeast of downtown Spokane. Mica had a post office with ZIP code 99023.
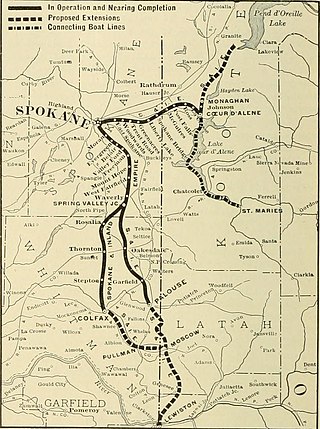
The Spokane and Inland Empire Railroad Company (S.&I.E.R.R.Co.) was an electrified interurban railway operating in Spokane, Washington and vicinity, extending into northern and central Idaho. The system originated in several predecessor roads beginning c. 1890, incorporated in 1904, and ran under its own name to 1929. It merged into the Great Northern Railway and later, the Burlington Northern Railroad, which operated some roads into the 1980s.

Freeman is an unincorporated community in Spokane County, Washington, United States. It is notable as being the location of the public elementary, middle and high schools serving a large area of rural southeast Spokane County.

The Ohio Match Company Railway was a logging railroad in northern Idaho that operated from Garwood, Idaho, around Hayden Lake and followed the Burnt Cabin Creek to the Little North Fork of the Coeur d'Alene River. The right of way roughly follows Ohio Match Road from Garwood, Idaho Burnt Cabin Road and then over the entirety of Burnt Cabin Road today. The Ohio Match railroad aided in harvesting white pine timber reserves that remained after the fire of 1910 for the production of matchsticks.

Latah/Hangman is a neighborhood in Spokane, Washington.

























