
The Ediacaran is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last period of the Proterozoic Eon as well as the last of the so-called "Precambrian supereon", before the beginning of the subsequent Cambrian Period marks the start of the Phanerozoic Eon, where recognizable fossil evidence of life becomes common.

The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era and succeeded by the Paleozoic era of the Phanerozoic eon, and is further subdivided into three periods, the Tonian, Cryogenian and Ediacaran.
The cloudinids, an early metazoan family containing the genera Acuticocloudina, Cloudina and Conotubus, lived in the late Ediacaran period about 550 million years ago. and became extinct at the base of the Cambrian. They formed millimetre-scale conical fossils consisting of calcareous cones nested within one another; the appearance of the organism itself remains unknown. The name Cloudina honors the 20th-century geologist and paleontologist Preston Cloud.

Dickinsonia is a genus of extinct organism, most likely an animal, that lived during the late Ediacaran period in what is now Australia, China, Russia, and Ukraine. It is one of the best known members of the Ediacaran biota. The individual Dickinsonia typically resembles a bilaterally symmetrical ribbed oval. Its affinities are presently unknown; its mode of growth has been considered consistent with a stem-group bilaterian affinity, though various other affinities have been proposed. It lived during the late Ediacaran. The discovery of cholesterol molecules in fossils of Dickinsonia lends support to the idea that Dickinsonia was an animal, though these results have been questioned.

Ausia fenestrata is a curious Ediacaran period fossil represented by only one specimen 5 cm long from the Nama Group, a Vendian to Cambrian group of stratigraphic sequences deposited in the Nama foreland basin in central and southern Namibia. It has similarity to Burykhia from Ediacaran (Vendian) siliciclastic sediments exposed on the Syuzma River of Arkhangelsk Oblast, northwest Russia. This fossil is of the form of an elongate bag-like sandstone cast tapering to a cone on one end. The surface of the fossil is covered with oval depressions ("windows") regularly spaced over the surface in the manner of concentric/parallel rows. The taxonomic identity of Ausia is unresolved.

Kimberella is an extinct genus of bilaterian known only from rocks of the Ediacaran period. The slug-like organism fed by scratching the microbial surface on which it dwelt in a manner similar to the gastropods, although its affinity with this group is contentious.

The rangeomorphs are a form taxon of frondose Ediacaran fossils that are united by a similarity to Rangea. Some researchers, such as Pflug and Narbonne, suggest that a natural taxon Rangeomorpha may include all similar-looking fossils. Rangeomorphs appear to have had an effective reproductive strategy, based on analysis of the distribution pattern of Fractofusus, which consisted of sending out a waterborne asexual propagule to a distant area, and then spreading rapidly from there, just as plants today spread by stolons or runners.

Yorgia waggoneri is a discoid Ediacaran organism. It has a low, segmented body consisting of a short wide "head", no appendages, and a long body region, reaching a maximum length of 25 cm (9.8 in). It is classified within the extinct animal phylum Proarticulata.
Chondroplon bilobatum is a medusoid Ediacaran fossil. It has sand-filled tubes, although these may not have been sand-filled in life. It has a shield-like shape, with one end different from the other, and bilateral symmetry, and although it has been suggested that it possesses glide reflection symmetry, such suggestions are based upon a taphonomic effect deforming some specimens. Chondroplon was originally described by Mary Wade in 1971 from fossils found in South Australia. It was named after chondrophores — chitinous floats found on some kinds of colonial floating hydroids.

The Ediacaranbiota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period. These were enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sessile, organisms. Trace fossils of these organisms have been found worldwide, and represent the earliest known complex multicellular organisms. The term "Ediacara biota" has received criticism from some scientists due to its alleged inconsistency, arbitrary exclusion of certain fossils, and inability to be precisely defined.

Marine invertebrates are the invertebrates that live in marine habitats. Invertebrate is a blanket term that includes all animals apart from the vertebrate members of the chordate phylum. Invertebrates lack a vertebral column, and some have evolved a shell or a hard exoskeleton. As on land and in the air, marine invertebrates have a large variety of body plans, and have been categorised into over 30 phyla. They make up most of the macroscopic life in the oceans.
The end-Ediacaran extinction is a mass extinction believed to have occurred near the end of the Ediacaran period, the final period of the Proterozoic eon. Evidence suggesting that such a mass extinction occurred includes a massive reduction in diversity of acritarchs, the sudden disappearance of the Ediacara biota and calcifying organisms, and the time gap before Cambrian organisms "replaced" them. Some lines of evidence suggests that there may have been two distinct pulses of the extinction event, one occurring 550 million years ago and the other 539 million years ago.
The Cambrian explosion is an interval of time approximately 538.8 million years ago in the Cambrian period of the early Paleozoic when a sudden radiation of complex life occurred, and practically all major animal phyla started appearing in the fossil record. It lasted for about 13 to 25 million years and resulted in the divergence of most modern metazoan phyla. The event was accompanied by major diversification in other groups of organisms as well.
Ediacaran type preservation relates to the dominant preservational mode in the Ediacaran period, where Ediacaran organisms were preserved as casts on the surface of microbial mats.

The Erniettomorphs are a form of Ediacaran fossil consisting of rows of airbed-like tubes arranged along a midline with a glide symmetry. Representative genera include Ernietta, Phyllozoon, Pteridinium, Swartpuntia. Undisputed Erniettomorphs were Ediacaran, but the species Erytholus, Rutgersella, and Protonympha, who have by some been included in this group but are by no means clear members, are found through to the Late Devonian. Their affinity is uncertain; they probably form a clade and are most likely a sister group to the rangeomorphs, which bear a similar construction. Placements within the metazoan crown-group have been rebutted, and it is most likely that these peculiar organisms lie in the stem group to the animals. There is no evidence that they possessed a mouth or gut. Because they may have been found in water which was too deep to permit photosynthesis – and in some cases, lived half-buried in sediment, it is speculated that they fed by osmosis from the sea water. Such a lifestyle requires a very high surface area to volume ratio – higher than is observed in fossils. However, this paradox can be resolved if much of the volume of the organisms was not metabolically active. Many Pteridinium fossils are found completely filled with sand; if this sand were present within the organism while it was alive, this would reduce its metabolically active volume enough to make osmotic feeding viable.

The Avalon explosion, named from the Precambrian faunal trace fossils discovered on the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland, eastern Canada, is a proposed evolutionary radiation of prehistoric animals about 575 million years ago in the Ediacaran period, with the Avalon explosion being one of three eras grouped in this time period. This evolutionary event is believed to have occurred some 33 million years earlier than the Cambrian explosion, which had been long thought to be when complex life started on Earth.

Until the late 1950s, the Precambrian was not believed to have hosted multicellular organisms. However, with radiometric dating techniques, it has been found that fossils initially found in the Ediacara Hills in Southern Australia date back to the late Precambrian. These fossils are body impressions of organisms shaped like disks, fronds and some with ribbon patterns that were most likely tentacles.

The petalonamids (Petalonamae) are an extinct group of archaic animals typical of the Ediacaran biota, also called frondomorphs, dating from approximately 635 million years ago to 516 million years ago. They are benthic and motionless animals, that have the shape of leaves, fronds (frondomorphic), feathers or spindles and were initially considered algae, octocorals or sea pens. It is now believed that there are no living descendants of the group, which shares a probable relation to the Ediacaran animals known as Vendozoans.
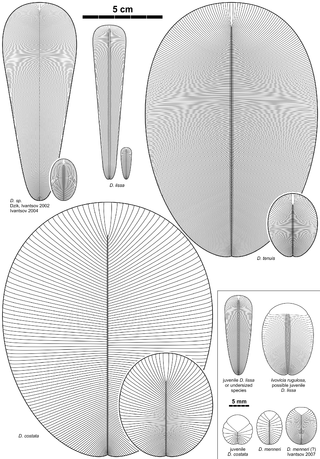
Dipleurozoa are extinct proarticulate organisms of the Ediacaran period, which had a flat and more or less ovoid shape. Polychaete worms were treated, however it seems more likely that they were vendobionts. The most representative genus is Dickinsonia, which gives the name to the class.




















