
Chimaphila maculata is a small, perennial, evergreen herb native to eastern North America and Central America, from southern Quebec west to Illinois, and south to Florida and Panama.

Rudbeckia fulgida, the orange coneflower or perennial coneflower, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, native to eastern North America.

Rhododendron minus var. chapmanii, also known as Chapman's rhododendron, is an endangered variety, endemic to Florida, of the evergreen Piedmont rhododendron.

Stewartia malacodendron, the silky camellia, silky stewartia or Virginia stewartia, is a species of flowering plant in the family Theaceae. It grows slowly into a large deciduous shrub or small tree, typically 3–4.5 m (10–15 ft) tall, but sometimes as tall as 9 m (30 ft). It is native to the southeastern United States.

Eurybia is a genus of plants in the family Asteraceae that were previously included in the genus Aster. Most species are native to North America, although one is also present in northern Eurasia. There are 23 species in the genus, including 1 natural hybrid. The name was first applied by Alexandre de Cassini in 1820. The name is derived from Ancient Greek εὐρύς (eurús), meaning "wide", and βαιός (baiós), meaning "few", perhaps in reference to the small number of relatively wide ray florets.
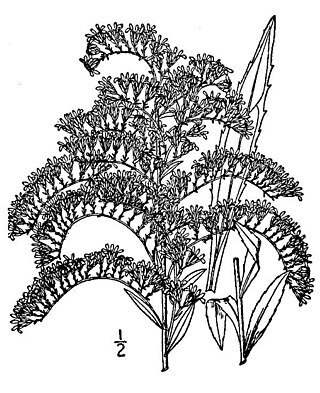
Solidago shortii, commonly known as Short's goldenrod, is a species of goldenrod in the family Asteraceae. The only known populations of Short's goldenrod occur around the Blue Licks Battlefield State Park area of Kentucky and Harrison-Crawford State Forest in Indiana. It was listed on the Federal Register of Endangered Species on September 5, 1985, and was given a global rank of G1 on February 29, 2000.
Senecio lamarckianus, the bois de chèvre, is a species of flowering plant in the aster family and a member of the genus Senecio. It is endemic to the island of Mauritius and is threatened by habitat loss.

Coreopsis auriculata, the lobed tickseed or mouse-ear tickseed, is a North American plant species of the family Asteraceae. It is native to the southeastern and east-central United States, from Louisiana east to the Florida Panhandle and as far north as Kentucky, Maryland, and West Virginia.

Coreopsis basalis, commonly known as the goldenmane tickseed, is a North American plant species in the sunflower family. It is native to the southeastern and south-central United States from Texas to the Carolinas. Isolated populations have been reported from Connecticut, Illinois, and California.

Coreopsis tripteris is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is widespread across much of eastern and central North America from the Florida Panhandle west as far as eastern Texas and north to Québec and Ontario. Its common names include tall tickseed, tall coreopsis, and Atlantic coreopsis.

Eupatorium altissimum, with the common names tall thoroughwort and tall boneset, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the Asteraceae family with a native range including much of the eastern and central United States and Canada. It is a tall plant found in open woods, prairies, fields, and waste areas, with white flowers that bloom in the late summer and fall.

Helianthus decapetalus, known by the common names thinleaf sunflower and thin-leaved sunflower, is a perennial forb in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the Eastern and Central United States and Canada, from New Brunswick west to Iowa, Wisconsin, and Ontario, south as far as Georgia and Louisiana. It produces yellow composite flowers in late summer or early fall.
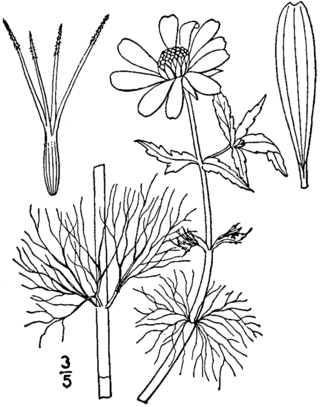
Bidens beckii, commonly called Beck's water-marigold or simply water marigold is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to Canada and the northern United States.

Cirsium altissimum is a North American species of plants in the tribe Cardueae within the family Asteraceae. Common names are tall thistle or roadside thistle. The species is native to the eastern and Central United States.

Erigeron tweedyi, or Tweedy's fleabane, is a perennial herb in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the Rocky Mountains in Montana, Idaho and Wyoming.

Festuca brachyphylla, commonly known as alpine fescue or short-leaved fescue, is a grass native to Eurasia, North America, and the Arctic. The grass is used for erosion control and revegetation. The specific epithet brachyphylla means "short-leaved". The grass has a diploid number of 28, 42, or 44. This species was first described in 1827.

Mairia petiolata is a tufted, variably hairy, perennial plant of up to 15 cm (6 in) assigned to the family Asteraceae. Its leaves are in a ground rosette, and have a stalk of mostly 2–5 cm long and an inverted egg-shaped to elliptic, 61⁄2–9 cm (2.6–4.6 in) long and 2–3 cm wide leaf blade, with a toothed margin. It mostly has two flower heads at the tip of the branches of each erect, dark reddish brown scape. The flower heads have a bell- to cup-shaped involucre that consists of 20–24, purplish, overlapping bracts in 3–4 whorls. These protect 12–16 pink, ray florets, surrounding many yellow disc florets. This species was only seen flowering once, in December. It is known from one location in the Langeberg, Western Cape province of South Africa.

Mairia hirsuta is a tufted perennial, herbaceous plant of up to 40 cm high, that is assigned to the family Asteraceae. Most of its narrow to broad elliptic or inverted egg-shaped leaves are part of the basal rosette, have margin that is rolled under, with rounded or pointy teeth or with some peg-like extensions, lightly woolly on the upper surface and densely woolly on the underside, but always the green remains visible. Flower heads have been found from July to November, mostly after a fire or when the soil has been disturbed. The species can be found in the southern mountains of the Western Cape province of South Africa.

Glyceria canadensis is a species of grass in the genus Glyceria which is known by the common name rattlesnake mannagrass. It is native to North America, from British Columbia to Newfoundland and south to North Carolina. It is commonly found in wet areas.

Symphyotrichum chapmanii is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae native to the Apalachicola River drainage basin of Alabama and Florida. Commonly known as savanna aster, it is a perennial, herbaceous plant that may reach 30 to 80 centimeters tall. Its flowers have purple to blue-lavender ray florets and pale yellow disk florets. It is a wetland species and is of conservation concern. It may be extirpated in Alabama.


















