The Via della Vittoria was a military road between Bardia in Italian Libya and Sidi Barrani in western Egypt.

The Via della Vittoria was a military road between Bardia in Italian Libya and Sidi Barrani in western Egypt.
The "Via della Vittoria" (Victory Road), was built by Italian engineers during World War II, between September and December 1940. The road went from Sidi Barrani, Egypt, to the border of Italian Libya and connected to the Via Balbia. It was 11 metres (12 yd) wide and asphalted.
It was officially called Via della Vittoria nell'Africa Settentrionale Italiana in order to distinguish it from another "Via della Vittoria" built in 1939 in Ethiopia/Africa Orientale Italiana. [1]
The Italian Army invaded Egypt in summer 1940 and penetrated until Sidi Barrani. The need of communication in order to supply the Army forced the construction of this new road. [2]
Proceeding in an orderly, colonial fashion, the Italian commander in Egypt, General Mario Berti, deployed the advanced units of his Army (1st and 2nd Libyan, 3 January Blackshirt, Cirene and Catanzaro Divisions, as well as Maletti’s motorised brigade group) in a ring of strong-points around Sidi Barrani, and began work on extending the Via Balbia into Egypt....
— Edmund Hall [2]
In fall 1940 Italian Marshal Rodolfo Graziani ordered his Army in western Egypt to complete this new coastal road extending the Via Balbia 100 kilometres (60 mi) inside Egypt, even in order to create an infrastructure for a planned Italian invasion of the Nile Delta in January/February 1941.
In December 1940 the new road was used by the British forces during Operation Compass. In the next two years the road was damaged by the continuous changes in the front between Axis forces under Erwin Rommel and the Allies.

Sidi Barrani is a town in Egypt, near the Mediterranean Sea, about 95 km (59 mi) east of the Egypt–Libya border, and around 240 km (150 mi) from Tobruk, Libya.

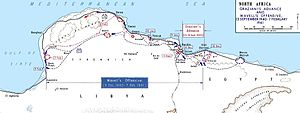
Operation Compass was the first large British military operation of the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) during the Second World War. British, Empire and Commonwealth forces attacked Italian forces of the 10th Army in western Egypt and Cyrenaica, the eastern province of Libya, from December 1940 to February 1941.

Operation Sonnenblume was the name given to the dispatch of German troops to North Africa in February 1941, during the Second World War. The Italian 10th Army had been destroyed by the British, Commonwealth, Empire and Allied Western Desert Force attacks during Operation Compass (9 December 1940 – 9 February 1941). The first units of the new Deutsches Afrikakorps departed Naples for Africa and arrived on 11 February 1941. On 14 February, advanced units of the 5th Light Afrika Division, Aufklärungsbataillon 3 and Panzerjägerabteilung 39 arrived in Tripoli, Libya and were sent immediately to the front line east of Sirte.

The Western Desert campaign took place in the deserts of Egypt and Libya and was the main theatre in the North African campaign of the Second World War. Military operations began in June 1940 with the Italian declaration of war and the Italian invasion of Egypt from Libya in September. Operation Compass, a five-day raid by the British in December 1940, was so successful that it led to the destruction of the Italian 10th Army over the following two months. Benito Mussolini sought help from Adolf Hitler, who sent a small German force to Tripoli under Directive 22. The Afrika Korps was formally under Italian command, as Italy was the main Axis power in the Mediterranean and North Africa.

The Italian colonizationof Libya began in 1911 and it lasted until 1943. The country, which was previously an Ottoman possession, was occupied by Italy in 1911 after the Italo-Turkish War, which resulted in the establishment of two colonies: Italian Tripolitania and Italian Cyrenaica. In 1934, the two colonies were merged into one colony which was named the colony of Italian Libya. In 1937, this colony was divided into four provinces, and in 1939, the coastal provinces became a part of metropolitan Italy. The colonization lasted until Libya's occupation by Allied forces in 1943, but it was not until the 1947 Paris Peace Treaty that Italy officially renounced all of its claims to Libya's territory.
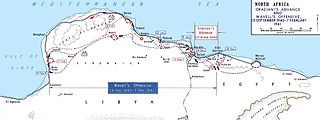
The rapid British advance during Operation Compass forced the Italian 10th Army to evacuate Cyrenaica, the eastern province of Libya. In late January, the British learned that the Italians were retreating along the Litoranea Balbo from Benghazi. The 7th Armoured Division was dispatched to intercept the remnants of the 10th Army by moving through the desert, south of the Jebel Akhdar via Msus and Antelat as the 6th Australian Division pursued the Italians along the coast road, north of the jebel. The terrain was hard going for the British tanks and Combeforce, a flying column of wheeled vehicles, was sent ahead across the chord of the jebel.
Major General Sir Michael O'Moore Creagh, was a British Army officer who served in both the world wars. He commanded the 7th Armoured Division, the Desert Rats, between 1939 and 1941.

The Frontier Wire was a 271 km (168 mi) obstacle in Italian Libya, along the length of the border of British-held Egypt, running from El Ramleh, in the Gulf of Sollum south to Jaghbub parallel to the 25th meridian east, the Libya–Egypt and Libya–Sudan borders. The frontier wire and its line of covering forts was built by the Italians during the Second Italo-Senussi War (1923–1931), as a defensive system to contain the Senussi population, who crossed from Egypt during their resistance against Italian colonisers.

The action at Mechili was an engagement between units of the British 7th Armoured Division of the Western Desert Force and Italian forces of the 10th Army during Operation Compass.

Mario Berti was an Italian officer during World War I and a general in the Spanish Civil War and World War II.

The Italian invasion of Egypt was an offensive in the Second World War, against British, Commonwealth and Free French forces in the Kingdom of Egypt. The invasion by the Italian 10th Army ended border skirmishing on the frontier and began the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) proper. The Italian strategy was to advance from Libya along the Egyptian coast to seize the Suez Canal. After numerous delays, the scope of the offensive was reduced to an advance as far as Sidi Barrani and the engagement of any British forces in the area.

Pietro Maletti was an Italian General and war criminal who participated in World War I, the Italian colonization of Libya, the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, and World War II. He was killed in action during the early stages of the North Africa Campaign.

The Libyan Coastal Highway, formerly the Litoranea Balbo, is a highway that is the only major road that runs along the entire east-west length of the Libyan Mediterranean coastline. It is a section in the Cairo–Dakar Highway #1 in the Trans-African Highway system of the African Union, Arab Maghreb Union and others.

The Maletti Group(Italian: Raggruppamento Maletti) was an ad hoc mechanised unit formed by the Italian Royal Army in Italian North Africa, during the initial stages of the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. The Italian army had three armoured divisions in Europe but all were needed for the occupation of Albania and the forthcoming invasion of Greece, which began on 28 October 1940. The Raggruppamento Maletti was formed in June 1940, as part of the 10th Army and contained all of the M11/39 medium tanks in Libya.

Combeforce or Combe Force was an ad hoc flying column of the British Army during the Second World War, commanded by Lieutenant-Colonel John Combe. It comprised parts of the 7th Armoured Division of the Western Desert Force. The rapid British advance during Operation Compass forced the Italian 10th Army to evacuate Cyrenaica, the eastern province of Libya. In late January, the British learned that the Italians were retreating from Benghazi, along the coast road. The 7th Armoured Division was dispatched to intercept the remnants of the 10th Army by moving through the desert, south of the Jebel Akhdar via Msus and Antelat, as the 6th Australian Division pursued the Italians along the coast road, north of the jebel.
The 2nd Libyan Division was an infantry division of the Royal Italian Army during World War II. In December 1940 the division formed, together with the 1st CC.NN. Division "23 Marzo" and 2nd CC.NN. Division "28 Ottobre", the XXIII Army Corps. The corps participated in the Italian invasion of Egypt and was destroyed during the Battle of Sidi Barrani.

Giuseppe Tellera was a general in the Italian Army during World War II.

The Battle of Sidi Barrani(10–11 December 1940) was the opening battle of Operation Compass, the first big British attack of the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. Sidi Barrani, on the Mediterranean coast in Egypt, had been occupied by the Italian 10th Army, during the Italian invasion of Egypt (9–16 September 1940) and was attacked by British, Commonwealth and imperial troops, who re-captured the port.

Italian Benghazi was the name used during the Italian colonization of Libya for the port-city of Benghazi in Italian Cyrenaica.

The Attack on Nibeiwa took place on 9 December 1940 near Nibeiwa, Egypt, when the Italian fortified camp held by the Maletti Group, the armoured force of the 10th Army, was overrun by British and Indian troops. The attack was the opening engagement of Operation Compass a British raid which, if successful, would be followed up to try to expel the Italians from Egypt. Italy had declared war on France and Britain on 10 June and in the Italian invasion of Egypt from 9 to 16 September 1940, the Italian 10th Army had reached Sidi Barrani and dug in to await the completion of the Via della Vittoria, an extension of the Via Balbia, being built from the frontier; the Maletti Group garrisoned a camp at Nibeiwa,12 mi (19 km) south of the port of Sidi Barrani.