
Vitex agnus-castus is a plant native of the Mediterranean region. It is one of the few temperate-zone species of Vitex, which is on the whole a genus of tropical and subtropical flowering plants. Vitex is a cross-pollinating plant, but its self-pollination has been recorded.

The Solomon Islands rain forests are a terrestrial ecoregion covering the Solomon Islands archipelago.

Canarium is a genus of about 120 species of tropical and subtropical trees, in the family Burseraceae. They grow naturally across tropical Africa, south and southeast Asia, Indochina, Malesia, Australia and western Pacific Islands; including from southern Nigeria east to Madagascar, Mauritius, Sri Lanka and India; from Burma, Malaysia and Thailand through the Malay Peninsula and Vietnam to south China, Taiwan and the Philippines; through Borneo, Indonesia, Timor and New Guinea, through to the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, New Caledonia, Fiji, Samoa, Tonga and Palau.

Cerbera is a genus of evergreen trees or shrubs, native to tropical Asia, Australia, Madagascar, and various islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Freycinetia is one of the five extant genera in the flowering plant family Pandanaceae. As of November 2024, the genus comprises approximately 300 species. The type species is Freycinetia arborea.

Intsia bijuga, commonly known as Borneo teak, ipil, Johnstone River teak, and kwila, amongst many other names, is a species of tree in the flowering plant family Fabaceae, native to coastal areas from east Africa, through India and Southeast Asia to Australia and the western Pacific. It has significant importance to indigenous cultures in many parts of its range, but is also threatened by illegal logging due to its high quality timber. It is most commonly found in tropical coastal forests.

Vitex is a genus of flowering plants in the sage family Lamiaceae. It has about 250 species. Common names include chaste tree or chastetree, traditionally referring to V. agnus-castus, but often applied to other species, as well.

Vitex parviflora is a species of plant in the family Lamiaceae, also known as smallflower chastetree or the molave tree. The name "molave" is from Spanish, derived from mulawin, the Tagalog word for the tree. It is also known as tugas in Visayan languages. It yields one of two woods from the same genus called molave wood, the other being Vitex cofassus.
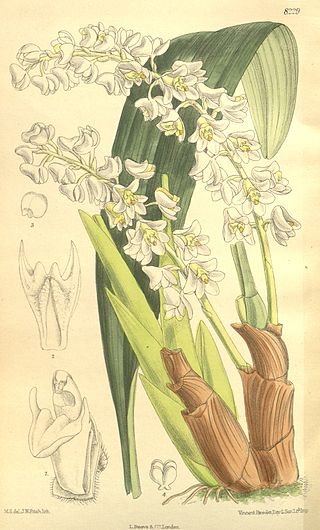
Bryobium, commonly known as urchin orchids or 藓兰属 , is a genus of flowering plants in the family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus are epiphytic or lithophytic plants with large, fleshy pseudobulbs, each with up to three leathery leaves and small, often hairy flowers. These orchids are found from tropical Asia to northern Australia.

Cerbera floribunda, commonly known as cassowary plum, grey milkwood, or rubber tree, is a plant in the family Apocynaceae which is native to the region from Sulawesi to the Solomon Islands, including north east Queensland.

Vitex rotundifolia, the roundleaf chastetree or beach vitex, is a species of flowering plant in the sage family Lamiaceae. It is native to seashores throughout the Pacific. Its range includes continents and islands stretching from India east to Hawaii and from Korea south to Australia. This shrub typically grows approximately 1 m in height. It has a sprawling growth habit and produces runners that root regularly at nodes. This rooting pattern allows the plant to spread rapidly. At maturity, V. rotundifolia produces blue-purple flowers that are borne in clusters and ultimately yield small brown-black fruits. Its leaves are rounded at the tips with green upper surfaces and silver lower surfaces. While the plant is a seashore obligate, it grows over a wide latitude range. It has been used for medicinal purposes throughout its native range. More recently, it was imported to the eastern United States where it has become a seashore invasive. Control efforts are presently underway to protect the fragile beach dune ecosystem.

Phaleria octandra is a flowering plant in the Thymelaeaceae family. It is a shrub found in tropical Australia. It is also naturally found in the New Guinea, Indonesia, Malaysia and the Solomon Islands.
Canarium vitiense is a rainforest tree species, of the plant family Burseraceae, growing naturally in Fiji, the Solomon Islands, Samoa, Tonga, New Guinea, Bismarck Archipelago, Admiralty Islands, Louisiade Archipelago, Torres Strait Islands and in lowland north-eastern Queensland, Australia.
The Lae Botanic Gardens are located in Bumneng, Eriku and Lae City in the Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. Within this location is the Papua New Guinea Forest Research Unit, the Papua New Guinea National Herbarium and the Lae War Cemetery.

Trachoma, commonly known as spectral orchids, is a genus of flowering plants in the family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus are epiphytic plants with leafy stems, crowded, leathery leaves arranged in two ranks and a large number of relatively small, short-lived flowers that often open in successive clusters. The sepals and petals are free from and more or less similar to each other, except that the petals are often smaller. The labellum is rigidly fixed to the column and is more or less sac-shaped. There are about 17 species distributed from Assam to the Western Pacific Ocean. Most species grow in rainforests, often on emergent trees such as hoop pine.
Vitex thyrsiflora is a species of woody vine in the family Lamiaceae. It is native to tropical West and Central Africa. Its hollow stem is used as a home by an aggressive species of ant.
Pimelodendron amboinicum is a tree species in the Euphorbiaceae family. It is found from the Solomon Islands in the southwest Pacific, west to Sulawesi in Indonesia. The timber is used locally, though larger-scale illegal logging is apparent.
Campnosperma brevipetiolatum is a species of tree in the Anacardiaceae family. It is native to an area in the west Pacific and Malesia from the Santa Cruz Islands to the Caroline Islands and Sulawesi. It is commonly used for its timber, including for canoe making, but also for oil-production and medicine. It has been used as an indicator species to identify 19th century sites of indigenous occupation in the Solomon Islands.

Pometia is a genus of 2 species of rainforest trees, constituting part of the plant family Sapindaceae.
Vitex glabrata, commonly known as smooth chastetree, bush currant, black plum, black fruit, and black grape, is a species medium-sized deciduous tree in the family Lamiaceae. It is native to Australia, Bangladesh, Brunei, Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Marianas, Myanmar, New Caledonia, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Solomon Islands, Thailand, and Vietnam.















