
Conscription, also known as the draft in American English, is the practice in which the compulsory enlistment in a national service, mainly a military service, is enforced by law. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day under various names. The modern system of near-universal national conscription for young men dates to the French Revolution in the 1790s, where it became the basis of a very large and powerful military. Most European nations later copied the system in peacetime, so that men at a certain age would serve 1 to 8 years on active duty and then transfer to the reserve force.
Military science is the study of military processes, institutions, and behavior, along with the study of warfare, and the theory and application of organized coercive force. It is mainly focused on theory, method, and practice of producing military capability in a manner consistent with national defense policy. Military science serves to identify the strategic, political, economic, psychological, social, operational, technological, and tactical elements necessary to sustain relative advantage of military force; and to increase the likelihood and favorable outcomes of victory in peace or during a war. Military scientists include theorists, researchers, experimental scientists, applied scientists, designers, engineers, test technicians, and other military personnel.

A veteran is a person who has significant experience and expertise in an occupation or field.

Military service is service by an individual or group in an army or other militia, air forces, and naval forces, whether as a chosen job (volunteer) or as a result of an involuntary draft (conscription).

The People's Progressive Party is a political party in the Gambia. It was the dominant ruling party of the House of Representatives and the presidency from 1962 to 1994. The president throughout this time period was Dawda Jawara. The People's Progressive Party lost power after the 1994 Gambian coup d'état, a military coup led by young, junior military officers. The Alliance for Patriotic Reorientation and Construction (APRC) then became the dominant party of the Gambia. The People's Progressive Party remains active, but lacking the same level of support it garnered in the 20th century.

Women have been serving in the military since the inception of organized warfare, in both combat and non-combat roles. Their inclusion in combat missions has increased in recent decades, often serving as pilots, mechanics, and infantry officers.
Counter-recruitment refers to activity opposing military recruitment, in some or all of its forms. Among the methods used are research, consciousness-raising, political advocacy and direct action. Most such activity is a response to recruitment by state armed forces, but may also target intelligence agencies, private military companies, and non-state armed groups.

Military recruitment refers to the activity of attracting people to, and selecting them for, military training and employment.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), maintains an active conscription system in accordance with the regulations set by the government of the Republic of China. All qualified male citizens of military age in the country are obligated to perform 1 year on active duty military service or receive 4 months of military training.
Charles Constantine Moskos, Jr. was a sociologist of the United States military and a professor at Northwestern University. Described as the nation's "most influential military sociologist" by The Wall Street Journal, Moskos was often a source for reporters from The New York Times, The Washington Post, Los Angeles Times, Chicago Tribune, USA Today, and other periodicals. He was the author of the "don't ask, don't tell" (DADT) policy, the compromise which allowed homosexual service members to serve, but prohibited them from acknowledging their sexual orientation from 1994 to 2011.

A military reserve force is a military organization whose members (reservists) have military and civilian occupations. They are not normally kept under arms, and their main role is to be available when their military requires additional manpower. Reserve forces are generally considered part of a permanent standing body of armed forces, and allow a nation to reduce its peacetime military expenditures and maintain a force prepared for war. During peacetime, reservists typically serve part-time alongside a civilian job, although most reserve forces have a significant permanent full-time component as well. Reservists may be deployed for weeks or months-long missions during peacetime to support specific operations. During wartime, reservists may be kept in service for months or years at a time, although typically not for as long as active duty soldiers.

Military personnel or military service members are members of the state's armed forces. Their roles, pay, and obligations differ according to their military branch, rank, and their military task when deployed on operations and on exercise.

Military sociology is a subfield within sociology. It corresponds closely to C. Wright Mills's summons to connect the individual world to broader social structures. Military sociology aims toward the systematic study of the military as a social group rather than as a military organization. This highly specialized sub-discipline examines issues related to service personnel as a distinct group with coerced collective action based on shared interests linked to survival in vocation and combat, with purposes and values that are more defined and narrow than within civil society. Military sociology also concerns civil-military relations and interactions between other groups or governmental agencies.

Civil–military relations describes the relationship between military organizations and civil society, military organizations and other government bureaucracies, and leaders and the military. CMR incorporates a diverse, often normative field, which moves within and across management, social science and policy scales. More narrowly, it describes the relationship between the civil authority of a given society and its military authority. "The goal of any state is to harness military professional power to serve vital national security interests, while guarding against the misuse of power that can threaten the well-being of its people." Studies of civil-military relations often rest on a normative assumption that it is preferable to have the ultimate responsibility for a country's strategic decision-making to lie in the hands of the civilian political leadership rather than a military.
Wendy Orent is an American anthropologist and science writer with a focus on pandemics, biological weapons, and the evolution of infectious diseases.

Children under the age of 18 have been used by national armed forces and other armed groups in Africa. Typically, this classification includes children serving in non-combatant roles, as well as those serving in combatant roles. In 2008, it was estimated that 40 percent of child soldiers worldwide were in Africa, and the use of child soldiers in armed conflict was increasing faster than any other continent. Additionally, average age of children recruited as soldiers appears to be decreasing. As of 2017, the UN listed that seven out of fourteen countries recruiting and using child soldiers in state forces or armed groups were in Africa: Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mali, Nigeria, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan.

Suicide in the military is the act of ending one's life during or after a career in the armed forces.

China's People's Liberation Army (PLA) began as an all-volunteer force. In 1955, as part of an effort to modernize the PLA, the first Military Service Law created a system of compulsory military service. Since the late 1970s, the Chinese conscription laws mandate a hybrid system that combines conscripts and volunteers. Due to sufficient volunteer recruitment, mandatory military service has not been enacted in China since 1949.

The Kyrgyz Ground Forces, or simply the Kyrgyz Army, is the land force branch of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Kyrgyzstan.
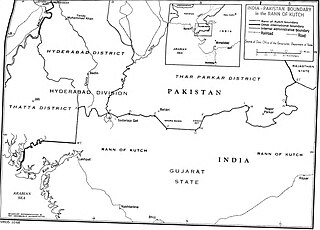
Operation Desert Hawk was the codename of a military operation planned and executed by the Pakistan Army in the Rann of Kutch area, the disputed area which was under Indian control from the long-standing status quo. The boundary of Rann of Kutch was one of the few un-demarcated boundaries pending since the 1947 partition of India.












