
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.
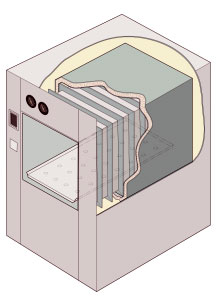
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites.

Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life and other biological agents present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic.

In biochemistry, cellulose acetate refers to any acetate ester of cellulose, usually cellulose diacetate. It was first prepared in 1865. A bioplastic, cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some coatings, and as a frame material for eyeglasses; it is also used as a synthetic fiber in the manufacture of cigarette filters and playing cards. In photographic film, cellulose acetate film replaced nitrate film in the 1950s, being far less flammable and cheaper to produce.

Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex cross-sections; and to work materials that are brittle, because the material encounters only compressive and shear stresses. It also creates excellent surface finish and gives considerable freedom of form in the design process.

The kraft process (also known as kraft pulping or sulfate process) is a process for conversion of wood into wood pulp, which consists of almost pure cellulose fibres, the main component of paper. The kraft process involves treatment of wood chips with a hot mixture of water, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and sodium sulfide (Na2S), known as white liquor, that breaks the bonds that link lignin, hemicellulose, and cellulose. The technology entails several steps, both mechanical and chemical. It is the dominant method for producing paper. In some situations, the process has been controversial because kraft plants can release odorous products and in some situations produce substantial liquid wastes.

A materials recovery facility, materials reclamation facility, materials recycling facility or multi re-use facility is a specialized plant that receives, separates and prepares recyclable materials for marketing to end-user manufacturers. Generally, there are two different types: clean and dirty materials recovery facilities.
Continuous production is a flow production method used to manufacture, produce, or process materials without interruption. Continuous production is called a continuous process or a continuous flow process because the materials, either dry bulk or fluids that are being processed are continuously in motion, undergoing chemical reactions or subject to mechanical or heat treatment. Continuous processing is contrasted with batch production.

A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use specialized equipment, units, and technology in the manufacturing process. Other kinds of plants, such as polymer, pharmaceutical, food, and some beverage production facilities, power plants, oil refineries or other refineries, natural gas processing and biochemical plants, water and wastewater treatment, and pollution control equipment use many technologies that have similarities to chemical plant technology such as fluid systems and chemical reactor systems. Some would consider an oil refinery or a pharmaceutical or polymer manufacturer to be effectively a chemical plant.

Continuous distillation, a form of distillation, is an ongoing separation in which a mixture is continuously fed into the process and separated fractions are removed continuously as output streams. Distillation is the separation or partial separation of a liquid feed mixture into components or fractions by selective boiling and condensation. The process produces at least two output fractions. These fractions include at least one volatile distillate fraction, which has boiled and been separately captured as a vapor condensed to a liquid, and practically always a bottoms fraction, which is the least volatile residue that has not been separately captured as a condensed vapor.
A mechanical biological treatment (MBT) system is a type of waste processing facility that combines a sorting facility with a form of biological treatment such as composting or anaerobic digestion. MBT plants are designed to process mixed household waste as well as commercial and industrial wastes.
Mechanical heat treatment (MHT) is an alternative waste treatment technology. This technology is also commonly termed autoclaving. MHT involves a mechanical sorting or pre-processing stage with technology often found in a material recovery facility. The mechanical sorting stage is followed by a form of thermal treatment. This might be in the form of a waste autoclave or processing stage to produce a refuse derived fuel pellet. MHT is sometimes grouped along with mechanical biological treatment. MHT does not however include a stage of biological degradation.
Heat setting is a term used in the textile industry to describe a thermal process usually taking place in either a steam atmosphere or a dry heat environment. The effect of the process gives fibers, yarns or fabric dimensional stability and, very often, other desirable attributes like higher volume, wrinkle resistance or temperature resistance. Very often, heat setting is also used to improve attributes for subsequent processes.

Single-stream recycling refers to a system in which all paper fibers, plastics, metals, and other containers are mixed in a collection truck, instead of being sorted by the depositor into separate commodities and handled separately throughout the collection process. In single-stream, both the collection and processing systems are designed to handle this fully commingled mixture of recyclables, with materials being separated for reuse at a materials recovery facility.

Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, often mixed with air and/or an aerosol of liquid water droplets. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Steam that is saturated or superheated is invisible; however, wet steam, a visible mist or aerosol of water droplets, is often referred to as "steam".

A waste converter is a machine used for the treatment and recycling of solid and liquid refuse material. A converter is a self-contained system capable of performing the following functions: pasteurization of organic waste; sterilization of pathogenic or biohazard waste; grinding and pulverization of refuse into unrecognizable output; trash compaction; dehydration. Because of the wide variety of functions available on converters, this technology has found application in diverse waste-producing industrial segments. Hospitals, clinics, municipal waste facilities, farms, slaughterhouses, supermarkets, ports, sea vessels, and airports are the primary beneficiaries of on-site waste conversion.

A dewatering screw press is a screw press that separates liquids from solids. A screw press can be used in place of a belt press, centrifuge, or filter paper. It is a simple, slow moving device that accomplishes dewatering by continuous gravitational drainage. Screw presses are often used for materials that are difficult to press, for example those that tend to pack together. The screw press squeezes the material against a screen or filter and the liquid is collected through the screen for collection and use.
As an extension of the fluidized bed family of separation processes, the flash reactor (FR) employs turbulent fluid introduced at high velocities to encourage chemical reactions with feeds and subsequently achieve separation through the chemical conversion of desired substances to different phases and streams. A flash reactor consists of a main reaction chamber and an outlet for separated products to enter downstream processes.
A void or a pore is three-dimensional region that remains unfilled with polymer and fibers in a composite material. Voids are typically the result of poor manufacturing of the material and are generally deemed undesirable. Voids can affect the mechanical properties and lifespan of the composite. They degrade mainly the matrix-dominated properties such as interlaminar shear strength, longitudinal compressive strength, and transverse tensile strength. Voids can act as crack initiation sites as well as allow moisture to penetrate the composite and contribute to the anisotropy of the composite. For aerospace applications, a void content of approximately 1% is still acceptable, while for less sensitive applications, the allowance limit is 3-5%. Although a small increase in void content may not seem to cause significant issues, a 1-3% increase in void content of carbon fiber reinforced composite can reduce the mechanical properties by up to 20%
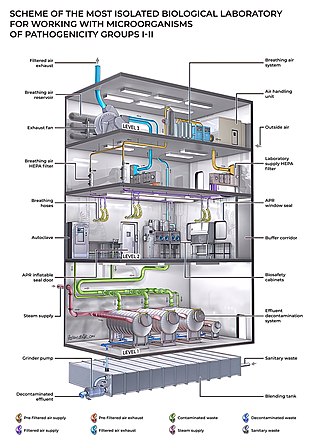
An effluent decontamination system (EDS) is a device, or suite of devices, designed to decontaminate or sterilise biologically active or biohazardous materials in fluid and liquid waste material. Facility types that may utilise an EDS include hospitals, food and beverage industry plants, research laboratories, agricultural and animal research facilities, pharmaceutical production facilities, and governmental or military facilities. In fact, all facilities in the United States of America that produce liquid waste of Biosafety Level 2 and above must decontaminate their waste before discharging it into a public sewer system. Examples of liquids sterilised in an EDS include the shower water from personnel decontamination rooms, and the waste water from washing down animal rooms in laboratory environments.














