
The Kingdom of the East Saxons, referred to as the Kingdom of Essex, was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex, Middlesex, much of Hertfordshire and west Kent. The last king of Essex was Sigered of Essex, who in 825 ceded the kingdom to Ecgberht, King of Wessex. From 825 Essex was ruled as part of a south-eastern kingdom of Essex, Kent, Sussex and Surrey. It was not until 860 that Essex was fully integrated into the crown of Wessex.

The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until England was unified in 927.

Mercia was one of the three main Anglic kingdoms founded after Sub-Roman Britain was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlands of England.

Offa was King of Mercia, a kingdom of Anglo-Saxon England, from 757 until his death. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æthelbald. Offa defeated the other claimant, Beornred. In the early years of Offa's reign, it is likely that he consolidated his control of Midland peoples such as the Hwicce and the Magonsæte. Taking advantage of instability in the kingdom of Kent to establish himself as overlord, Offa also controlled Sussex by 771, though his authority did not remain unchallenged in either territory. In the 780s he extended Mercian Supremacy over most of southern England, allying with Beorhtric of Wessex, who married Offa's daughter Eadburh, and regained complete control of the southeast. He also became the overlord of East Anglia and had King Æthelberht II of East Anglia beheaded in 794, perhaps for rebelling against him.

Æthelflæd, Lady of the Mercians ruled Mercia in the English Midlands from 911 until her death. She was the eldest daughter of Alfred the Great, king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex, and his wife Ealhswith.

Ecgberht, also spelled Egbert, Ecgbert, Ecgbriht, Ecgbeorht, and Ecbert, was King of Wessex from 802 until his death in 839. His father was King Ealhmund of Kent. In the 780s, Ecgberht was forced into exile to Charlemagne's court in the Frankish Empire by the kings Offa of Mercia and Beorhtric of Wessex, but on Beorhtric's death in 802, Ecgberht returned and took the throne.

Wulfhere or Wulfar was King of Mercia from 658 until 675 AD. He was the first Christian king of all of Mercia, though it is not known when or how he converted from Anglo-Saxon paganism. His accession marked the end of Oswiu of Northumbria's overlordship of southern England, and Wulfhere extended his influence over much of that region. His campaigns against the West Saxons led to Mercian control of much of the Thames valley. He conquered the Isle of Wight and the Meon valley and gave them to King Æthelwealh of the South Saxons. He also had influence in Surrey, Essex, and Kent. He married Eormenhild, the daughter of King Eorcenberht of Kent.
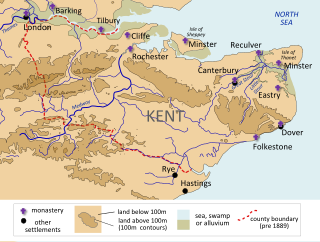
The Kingdom of the Kentish, today referred to as the Kingdom of Kent, was an early medieval kingdom in what is now South East England. It existed from either the fifth or the sixth century AD until it was fully absorbed into the Kingdom of Wessex in the late 9th century and later into the Kingdom of England in the early 10th century.

Æthelred, Lord of the Mercians became ruler of English Mercia shortly after the death or disappearance of its last king, Ceolwulf II in 879. Æthelred's rule was confined to the western half, as eastern Mercia was then part of the Viking-ruled Danelaw. His ancestry is unknown. He was probably the leader of an unsuccessful Mercian invasion of Wales in 881, and soon afterwards he acknowledged the lordship of King Alfred the Great of Wessex. This alliance was cemented by the marriage of Æthelred to Alfred's daughter Æthelflæd.

Wiglaf was King of Mercia from 827 to 829 and again from 830 until his death. His ancestry is uncertain: the 820s were a period of dynastic conflict within Mercia and the genealogy of several of the kings of this time is unknown. Wigstan, his grandson, was later recorded as a descendant of Penda of Mercia, so it is possible that Wiglaf was descended from Penda, one of the most powerful seventh-century kings of Mercia.

The Tribal Hidage is a list of thirty-five tribes that was compiled in Anglo-Saxon England some time between the 7th and 9th centuries. It includes a number of independent kingdoms and other smaller territories, and assigns a number of hides to each one. The list is headed by Mercia and consists almost exclusively of peoples who lived south of the Humber estuary and territories that surrounded the Mercian kingdom, some of which have never been satisfactorily identified by scholars. The value of 100,000 hides for Wessex is by far the largest: it has been suggested that this was a deliberate exaggeration.
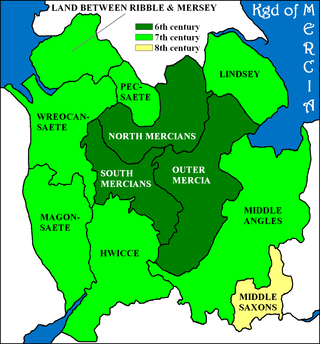
The Pecsætan, also called Peaklanders or Peakrills in modern English, were an Anglo-Saxon tribe who inhabited the central and northern parts of the Peak District area in England.

The Burghal Hidage is an Anglo-Saxon document providing a list of over thirty fortified places (burhs), the majority being in the ancient Kingdom of Wessex, and the taxes assigned for their maintenance. The document, so named by Frederic William Maitland in 1897, survives in two versions of medieval and early modern date. Version A, Cotton Otho B.xi was badly damaged in a fire at Ashburnham House in 1731 but the body of the text survives in a transcript made by the antiquary Laurence Nowell in 1562. Version B survives as a composite part of seven further manuscripts, usually given the title De numero hydarum Anglie in Britannia. There are several discrepancies in the lists recorded in the two versions of the document: Version A includes references to Burpham, Wareham and Bridport but omits Shaftesbury and Barnstaple which are listed in Version B. Version B also names Worcester and Warwick in an appended list.

The Middle Angles were an important ethnic or cultural group within the larger kingdom of Mercia in England in the Anglo-Saxon period.

The Wreocensæte, sometimes anglicized as the Wrekinsets, were one of the peoples of Anglo-Saxon Britain. Their name approximates to "Wrekin-dwellers". It is also suggested that Wrexham also derived from Wreocensæte.

The Gaini were an Anglo-Saxon tribe which occupied part of the kingdom of Mercia.

The Kingdom of the East Angles, informally known as the Kingdom of East Anglia, was a small independent kingdom of the Angles during the Anglo-Saxon period comprising what are now the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk and perhaps the eastern part of the Fens, the area still known as East Anglia.
Æthelred Mucel was an Anglo-Saxon noble from Mercia who was the father of Ealhswith, the wife of Alfred the Great.















