
The Florissant Formation is a sedimentary geologic formation outcropping around Florissant, Teller County, Colorado. The formation is noted for the abundant and exceptionally preserved insect and plant fossils that are found in the mudstones and shales. Based on argon radiometric dating, the formation is Eocene in age and has been interpreted as a lake environment. The fossils have been preserved because of the interaction of the volcanic ash from the nearby Thirtynine Mile volcanic field with diatoms in the lake, causing a diatom bloom. As the diatoms fell to the bottom of the lake, any plants or animals that had recently died were preserved by the diatom falls. Fine layers of clays and muds interspersed with layers of ash form "paper shales" holding beautifully-preserved fossils. The Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument is a national monument established to preserve and study the geology and history of the area.
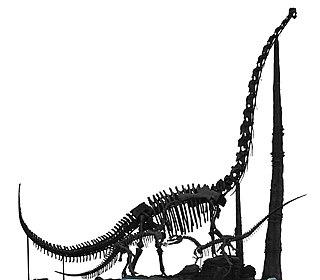
Chuanjiesaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaurs from the middle Jurassic Period. They lived in what is now China. The type species, Chuanjiesaurus anaensis, was first described by Fang, Pang, Lü, Zhang, Pan, Wang, Li and Cheng in 2000. Fossils of the species were found in the village of Chuanjie, Lufeng County, Yunnan Province, and are named after the location where the fossils were discovered. Holtz gave a length of 25 meters.

Anosteira is an extinct genus of carettochelyid turtle from the Eocene to the Oligocene of Asia and North America.

Stylemys is the first fossil genus of dry land tortoise belonging to the order Testudines discovered in the United States. The genus lived in temperate to subtropical areas of North America, Europe, and Asia, based on fossil distribution. The genus was first described in 1851 by Joseph Leidy. The tortoise was common in the prehistoric Badlands, especially Nebraska and South Dakota. The species has also been found in the formations in and around Badlands National Park. Fossil fragments have also been found in the Palm Park Formation of New Mexico.
Emarginachelys cretacea is a turtle belonging to the group Cryptodira, known from well preserved fossils from the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous of Montana. Its exact phylogenetic position within Cryptodira is uncertain; different authors considered it to be either the earliest described chelydrid or a fossil relative of kinosternoids.

Procolpochelys is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the Miocene of what is now Maryland, Virginia, and New Jersey. Its fossils have been found in the Calvert Formation. It was first named by Hay in 1908.

Manchurochelys is an extinct genus of turtle. It existed during the early Cretaceous of what is now northeast China. It has been found in the Jianshangou Bed of West Liaoning's Yixian Formation. However, it is a rarely found fossil.

Parapontoporia is an extinct genus of dolphin that lived off the Pacific coast of North America from the Late Miocene until the genus' extinction during the Pliocene. It is related to the baiji. Fossils have been found in California and Mexico. The Tulare Formation is predominately freshwater, which suggests Parapontoporia may have been tolerant of both salt and fresh water.
Promastodonsaurus is an extinct genus of capitosauroid temnospondyls within the family Mastodonsauridae. Fossils of the genus were found in the Ischigualasto Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina.

Vinctifer is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish erected by David Starr Jordan in 1919.

Baotianmansaurus is a genus of titanosaur sauropod dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in Upper Cretaceous rocks in Henan, China, within the Gaogou Formation. The type species is B. henanensis, described in 2009. The holotype is 41H III-0200. Remains of the fossils were vertebrae, ribs and scapula fragments. It was probably a close relative of Opisthocoelicaudia and Dongyangosaurus in Saltasauridae.

Barrosasaurus is a genus of titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur, first described by paleontologists Leonardo Salgado and Rodolfo Coria in 2009. The fossils, consisting of three fossil dorsal (back) vertebrae, are well-preserved but incomplete. They were discovered in the Anacleto Formation of the Neuquén province of western Argentina. The type species is Barrosasaurus casamiquelai. The genus name is named after the Sierra Barrosa in Neuquén. The specific epithet honours the Argentinian paleontologist Rodolfo Magín Casamiquela. It's been estimated to be 18 meters in length and 13.5 tonnes in weight.

The Fox Hills Formation is a Cretaceous geologic formation in the northwestern Great Plains of North America. It is present from Alberta on the north to Colorado in the south.
Flexomornis is a genus of enantiornithean birds known from fossils found in Texas rocks belonging to the Woodbine Formation dating to the middle Cenomanian age of the late Cretaceous period. It contains a single species, Flexomornis howei, named for the amateur fossil hunter Kris Howe, who discovered the site where the fossils were found.
Teyumbaita is an extinct genus of hyperodapedontine rhynchosaur from the Upper Triassic of southern Brazil. Its fossils were recovered from the early Norian-age Caturrita Formation, one of several fossiliferous formations exposed at Paleorrota Geopark in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. Teyumbaita is likely the youngest valid genus of rhynchosaur, as other members of the group likely died out before the start of the Norian.

Sphenopteris is a genus of seed ferns containing the foliage of various extinct plants, ranging from the Devonian to Late Cretaceous. One species, S. höninghausi, was transferred to the genus Crossotheca in 1911.

Carbonemys cofrinii is an extinct giant podocnemidid turtle known from the Middle Paleocene Cerrejón Formation of the Cesar-Ranchería Basin in northeastern Colombia. The formation is dated at around 60 to 57 million years ago, starting at about five million years after the KT extinction event.

The Brule Formation was deposited between 33 and 30 million years ago, roughly the Rupelian age (Oligocene). It occurs as a subunit of the White River Formation in Nebraska, Colorado, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Wyoming.

The Coihaique Group is a group of geological formations in northwestern Patagonia. From top to bottom the formations that make the group are Apeleg, Katterfeld and Toqui. The contact between the formations of the group are diachronous with Katterfeld Formation interfingering with the formations on top and below it. The lower and upper boundaries of the group are unconformities formed by erosion. The older parts of Coihaique Group represent a marine transgression while the younger parts evidences a return to non-marine conditions.
Tacuarembemys is an extinct genus of continental turtle from South America. It contains a single species, T. kusterae. The genus was described based on the external mold of a carapace and associated shell bone fragments found near the city of Tacuarembó, Uruguay. This fossil was found on the Tacuarembó Formation, whose estimated age ranges from late Jurassic to earliest Cretaceous.














