Related Research Articles

Keratin is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as scleroproteins. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only among sauropsids.

Keratin 1 is a Type II intermediate filament (IFs) of the intracytoplasmatic cytoskeleton. Is co-expressed with and binds to Keratin 10, a Type I keratin, to form a coiled coil heterotypic keratin chain. Keratin 1 and Keratin 10 are specifically expressed in the spinous and granular layers of the epidermis. In contrast, basal layer keratinocytes express little to no Keratin 1. Mutations in KRT1, the gene encoding Keratin 1, have been associated with variants of the disease bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma in which the palms and soles of the feet are affected. Mutations in KRT10 have also been associated with bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma; however, in patients with KRT10 mutations the palms and soles are spared. This difference is likely due to Keratin 9, rather than Keratin 10, being the major binding partner of Keratin 1 in acral keratinocytes.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 also known as cytokeratin-10 (CK-10) or keratin-10 (K10) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT10 gene. Keratin 10 is a type I keratin.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19 also known as cytokeratin-19 (CK-19) or keratin-19 (K19) is a 40 kDa protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT19 gene. Keratin 19 is a type I keratin.

Keratin 18 is a type I cytokeratin. It is, together with its filament partner keratin 8, perhaps the most commonly found products of the intermediate filament gene family. They are expressed in single layer epithelial tissues of the body. Mutations in this gene have been linked to cryptogenic cirrhosis. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.

Spermidine is a polyamine compound found in ribosomes and living tissues and having various metabolic functions within organisms. It was originally isolated from semen.
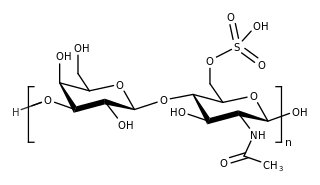
Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone. It is also synthesized in the central nervous system where it participates both in development and in the glial scar formation following an injury. Keratan sulfates are large, highly hydrated molecules which in joints can act as a cushion to absorb mechanical shock.

Desmoplakin is a protein in humans that is encoded by the DSP gene. Desmoplakin is a critical component of desmosome structures in cardiac muscle and epidermal cells, which function to maintain the structural integrity at adjacent cell contacts. In cardiac muscle, desmoplakin is localized to intercalated discs which mechanically couple cardiac cells to function in a coordinated syncytial structure. Mutations in desmoplakin have been shown to play a role in dilated cardiomyopathy and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, where it may present with acute myocardial injury; striate palmoplantar keratoderma, Carvajal syndrome and paraneoplastic pemphigus.

Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8 also known as cytokeratin-8 (CK-8) or keratin-8 (K8) is a keratin protein that is encoded in humans by the KRT8 gene. It is often paired with keratin 18.

Keratin 5, also known as KRT5, K5, or CK5, is a protein that is encoded in humans by the KRT5 gene. It dimerizes with keratin 14 and forms the intermediate filaments (IF) that make up the cytoskeleton of basal epithelial cells. This protein is involved in several diseases including epidermolysis bullosa simplex and breast and lung cancers.

Sucrase-isomaltase is a bifunctional glucosidase located on the brush border of the small intestine, encoded by the human gene SI. It is a dual-function enzyme with two GH31 domains, one serving as the isomaltase, the other as a sucrose alpha-glucosidase. It has preferential expression in the apical membranes of enterocytes. The enzyme’s purpose is to digest dietary carbohydrates such as starch, sucrose and isomaltose. By further processing the broken-down products, energy in the form of ATP can be generated.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit alpha (CAMKIIα), a.k.a.Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha, is one subunit of CamKII, a protein kinase (i.e., an enzyme which phosphorylates proteins) that in humans is encoded by the CAMK2A gene.

Dystonin(DST), also known as bullous pemphigoid antigen 1 (BPAG1), isoforms 1/2/3/4/5/8, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DST gene.

Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 78 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT78 gene.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT23 gene.
Maltase-glucoamylase, intestinal is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MGAM gene.

Keratin 79 also known as KRT79 is a protein which humans is encoded by the KRT79 gene.
Sucrose α-glucosidase is an enzyme with systematic name sucrose-α-D-glucohydrolase. It catalyses the hydrolysis of sucrose and maltose by an α-D-glucosidase-type action.
Giuseppe Veneziano is an Italian painter and one of the leading figures of Italian art groups "New Pop" and "Italian Newbrow".

Don W. Cleveland is an American cancer biologist and neurobiologist.
References
- ↑ Quaroni, A.; Calnek, D.; Quaroni, E.; Chandler, J. S. (25 June 1991). "Keratin expression in rat intestinal crypt and villus cells. Analysis with a panel of monoclonal antibodies". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 266 (18): 11923–11931. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)99046-0 . ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 1711043 . Retrieved 4 December 2022.