
Alberta's rivers flow towards three different bodies of water, the Arctic Ocean, the Hudson Bay and the Gulf of Mexico. Alberta is located immediately east of the continental divide, so no rivers from Alberta reach the Pacific Ocean.

Alberta's rivers flow towards three different bodies of water, the Arctic Ocean, the Hudson Bay and the Gulf of Mexico. Alberta is located immediately east of the continental divide, so no rivers from Alberta reach the Pacific Ocean.
The north of the province is drained towards the Arctic Ocean, and the northern rivers have comparatively higher discharge rates than the southern ones, that flow through a drier area. Most of Alberta's southern half has waters flowing toward the Hudson Bay, the only exception being the Milk River and its tributaries, that flow south through the Missouri and Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico.
Albertan rivers in the Arctic Ocean watershed are drained through Great Slave Lake and Mackenzie River, except for Petitot River which is drained through Liard River directly into the Mackenzie River, thus bypassing the Great Slave Lake.
|
|
|
Albertan Rivers in the Hudson Bay watershed are drained through Saskatchewan River, Lake Winnipeg and Nelson River, except for Beaver River, which is drained through Churchill River.
The small areas drained by the Milk River in southern Alberta and southwestern Saskatchewan as well as the Poplar River in southern Saskatchewan are the only areas in Canada that drain into the Gulf of Mexico.
|

Canada has a vast geography that occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing a land border with the contiguous United States to the south and the U.S. state of Alaska to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast with a shared border on Hans Island. To the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area, Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world's largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.

The Continental Divide of the Americas is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic and Arctic Ocean, including those that drain into the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and Hudson Bay.

A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern.

The Mackenzie River is a river in the Canadian boreal forest. It forms, along with the Slave, Peace, and Finlay, the longest river system in Canada, and includes the second largest drainage basin of any North American river after the Mississippi.
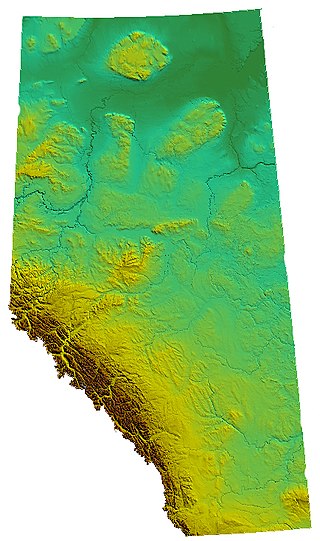
Alberta is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. Located in Western Canada, the province has an area of 661,190 km2 (255,290 sq mi) and is bounded to the south by the United States state of Montana along 49° north for 298 km (185 mi); to the east at 110° west by the province of Saskatchewan for 1,223 km (760 mi); and at 60° north the Northwest Territories for 644 km (400 mi). The southern half of the province borders British Columbia along the Continental Divide of the Americas on the peaks of the Rocky Mountains, while the northern half borders British Columbia along the 120th meridian west. Along with Saskatchewan it is one of only two landlocked provinces or territories.

Lake Athabasca is in the north-west corner of Saskatchewan and the north-east corner of Alberta between 58° and 60° N in Canada. The lake is 26% in Alberta and 74% in Saskatchewan.

The Churchill River is a major river in Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba, Canada. From the head of the Churchill Lake it is 1,609 kilometres (1,000 mi) long. It was named after John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough and governor of the Hudson's Bay Company from 1685 to 1691.

Triple Divide Peak is located in the Lewis Range, part of the Rocky Mountains in North America. The peak is a feature of Glacier National Park in the state of Montana in the United States. The summit of the peak, the hydrological apex of the North American continent, is the point where two of the principal continental divides in North America converge, the Continental Divide of the Americas and the Northern or Laurentian Divide.
North America is the third largest continent, and is also a portion of the third largest supercontinent if North and South America are combined into the Americas and Africa, Europe, and Asia are considered to be part of one supercontinent called Afro-Eurasia. With an estimated population of 580 million and an area of 24,709,000 km2 (9,540,000 mi2), the northernmost of the two continents of the Western Hemisphere is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west; the Atlantic Ocean on the east; the Caribbean Sea on the south; and the Arctic Ocean on the north.

Wollaston Lake is a lake in the north-eastern part of the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is about 550 kilometres (340 mi) north-east of Prince Albert. With a surface area of 2,286 square kilometres (883 sq mi), it is the largest bifurcation lake in the world — that is, a lake that drains naturally in two directions.

The Northwest Territories is a territory in Northern Canada, specifically in Northwestern Canada between Yukon Territory and Nunavut including part of Victoria Island, Melville Island, and other islands on the western Arctic Archipelago. Originally a much wider territory enclosing most of central and northern Canada, the Northwest Territories was created in 1870 from the Hudson's Bay Company's holdings that were sold to Canada from 1869-1870. In addition, Alberta and Saskatchewan were formed from the territory in 1905. In 1999, it was divided again: the eastern portion became the new territory of Nunavut. Yellowknife stands as its largest city and capital. It has a population of 42,800 and has an area of 532,643 sq mi (1,379,540 km2). The current territory lies west of Nunavut, north of latitude 60° north, and east of Yukon.

The Laurentian Divide also called the Northern Divide and locally the height of land, is a continental divide in central North America that separates the Hudson Bay watershed to the north from the Gulf of Mexico watershed to the south and the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence watershed to the southeast.

The McLeod River is a river in west-central Alberta, Canada. It forms in the foothills of the Canadian Rockies, and is a major tributary of the Athabasca River.

A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not connected to the open sea. Every continent on earth except Antarctica has at least one continental drainage divide; islands, even small ones like Killiniq Island on the Labrador Sea in Canada, may also host part of a continental divide or have their own island-spanning divide. The endpoints of a continental divide may be coastlines of gulfs, seas or oceans, the boundary of an endorheic basin, or another continental divide. One case, the Great Basin Divide, is a closed loop around an endorheic basin. The endpoints where a continental divide meets the coast are not always definite since the exact border between adjacent bodies of water is usually not clearly defined. The International Hydrographic Organization's publication Limits of Oceans and Seas defines exact boundaries of oceans, but it is not universally recognized. Where a continental divide meets an endorheic basin, such as the Great Divide Basin of Wyoming, the continental divide splits and encircles the basin. Where two divides intersect, they form a triple divide, or a tripoint, a junction where three watersheds meet.

A lake bifurcation occurs when a lake has outflows into two different drainage basins. In this case, the drainage divide cannot be defined exactly, as it is situated in the middle of the lake.

Watersheds of North America are large drainage basins which drain to separate oceans, seas, gulfs, or endorheic basins. There are six generally recognized hydrological continental divides which divide the continent into seven principal drainage basins spanning three oceans and one endorheic basin. The basins are the Atlantic Seaboard basin, the Gulf of Mexico basin, the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence basin, the Pacific basin, the Arctic basin, the Hudson Bay basin, and the Great Basin. Together, the principal basins span the continent with the exception of numerous smaller endorheic basins.

A triple divide or triple watershed is a point on Earth's surface where three drainage basins meet. A triple divide results from the intersection of two drainage divides. Triple divides range from prominent mountain peaks to minor side peaks, down to simple slope changes on a ridge which are otherwise unremarkable. The elevation of a triple divide can be thousands of meters to barely above sea level. Triple divides are a common hydrographic feature of any terrain that has rivers, streams and/or lakes.
The Committee's Punch Bowl is a small tarn on the continental divide straddling the border between the Canadian provinces of Alberta and British Columbia. George Simpson, governor of the Hudson's Bay Company, named the lake for the London-based managing committee of that company in 1824. While journeying on an important trade route in the company's trade area in what is now western Canada and parts of Alaska and the northwestern United States, he saw the lake at the summit of Athabasca Pass.