
100 Hekate is a large main-belt asteroid.

103 Hera is a moderately large main-belt asteroid with an orbital period of 4.44 years. It was discovered by Canadian-American astronomer James Craig Watson on September 7, 1868, and named after Hera, queen and fifth in power of the Olympian gods in Greek mythology. This is a stony S-type asteroid with a silicate surface composition.

109 Felicitas is a dark and fairly large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on October 9, 1869, and named after Felicitas, the Roman goddess of success. The only observed stellar occultation by Felicitas is one from Japan.

118 Peitho is a main-belt asteroid. It is probably an S-type asteroid, suggesting a siliceous mineralogy. It was discovered by R. Luther on March 15, 1872, and named after one of the two Peithos in Greek mythology. There have been two observed Peithoan occultations of a dim star: one was in 2000 and the other in 2003.

128 Nemesis is a large 180 km main-belt asteroid, of carbonaceous composition. It rotates rather slowly, taking about 78 hours to complete one rotation. Nemesis is the largest member of the Nemesian asteroid family bearing its name. It was discovered by J. C. Watson on 25 November 1872, and named after Nemesis, the goddess of retribution in Greek mythology.

201 Penelope is a large main belt asteroid that was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on August 7, 1879, in Pola. The asteroid is named after Penelope, the wife of Odysseus in Homer's The Odyssey. It is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.68 AU with an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.18 and a period of 4.381 years. The orbital plane is tilted at an angle of 5.8° to the plane of the ecliptic.

209 Dido is a main-belt asteroid with a diameter of 179±1 km. It was discovered by C. H. F. Peters on October 22, 1879, in Clinton, New York and was named after the mythical Carthaginian queen Dido. This asteroid is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 3.15 AU with an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.058 and a period of 5.59 yr. The orbital plane is tilted at an angle of 7.2° to the plane of the ecliptic.
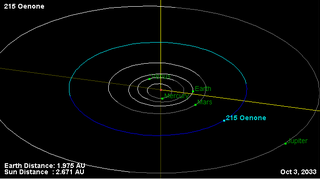
215 Oenone is a typical main belt asteroid. It was discovered by the Russian astronomer Viktor Knorre on April 7, 1880, in Germany, and was the second of his four asteroid discoveries. The asteroid is named after Oenone, a nymph in Greek mythology.

248 Lameia is a typical main belt asteroid. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on 5 June 1885 in Vienna and was named after the Lamia, a lover of Zeus in Ancient Greek mythology. 248 Lameia is orbiting the Sun with a period of 3.88 years and a low eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.067. The semimajor axis of 2.47 AU is slightly inward from the 3:1 Kirkwood Gap. Its orbital plane is inclined by 4° to the plane of the ecliptic.

321 Florentina is an S-type (stony) main belt asteroid with a diameter of 28 km. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 15 October 1891 in Vienna. He named the asteroid for his daughter, Florentine. Between 1874 and 1923, Palisa discovered a total of 122 asteroids.
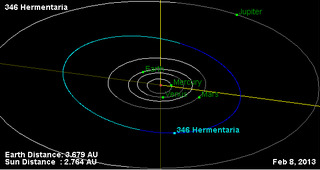
346 Hermentaria is a very large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 25 November 1892, in Nice. It is probably named for the town of Herment in the region of Auvergne, France. The asteroid is orbiting the Sun with a period of 4.68 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.10. The orbital plane is inclined by 8.7° to the plane of the ecliptic.
412 Elisabetha is a large main belt asteroid that was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf on 7 January 1896 in Heidelberg. It may have been named after his mother, Elise Wolf. This minor planet is orbiting at a distance of 2.76 AU from the Sun with a period of 4.59 years and an orbital eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.044. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 13.8° to the plane of the ecliptic.

699 Hela is a Mars crossing asteroid. It was discovered on 5 June 1910 at Heidelberg by German astronomer Joseph Helffrich, and may have been named after Hel, the Norse ruler of the underworld. This asteroid is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.61 AU with a period of 4.22 years and an eccentricity of 0.41. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 15.3° to the plane of the ecliptic.
718 Erida is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered at Vienna on September 29, 1911, by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa, and was named for Erida Leuschner, daughter of astronomer Armin Otto Leuschner. It is orbiting at a distance of 3.06 AU with a period of 5.34 yr and an eccentricity of 0.20. The orbital plane of this asteroid is inclined by an angle of 6.9° to the plane of the ecliptic.
738 Alagasta is a main belt asteroid. It was discovered from Heidelberg on 7 January 1913 by German astronomer Franz Kaiser. The asteroid was named in honor of Gau-Algesheim, previously Alaghastesheim, which is the home city of the discoverer's family. This body is orbiting at a distance of 3.04 AU with a period of 5.29 years and an eccentricity of 0.055. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 3.53° to the plane of the ecliptic.
741 Botolphia is a 29.6-km diameter minor planet orbiting in the asteroid belt, discovered by American astronomer Joel Hastings Metcalf on 10 February 1913 from Winchester. It is named after Saint Botolph, the semi-legendary founder of a 7th-century monastery that would become the town of Boston, Lincolnshire, England. This asteroid is orbiting at a distance of 2.72 AU from the Sun, with an orbital period of 4.49 yr and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.07. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 8.41° to the ecliptic.
754 Malabar is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered in 1906 by German astronomer August Kopff from Heidelberg, and was named in honor of a Dutch-German solar eclipse expedition to Christmas Island in 1922. Malabar is the name of a city and mountain in Indonesia. This object is orbiting at a distance of 2.99 AU from the Sun with a period of 5.16 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.048. Its orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 24.6° to the plane of the ecliptic.
757 Portlandia is a main-belt asteroid 32 km in diameter. It was discovered on 30 September 1908 from Taunton, Massachusetts by the amateur American astronomer Joel E. Metcalf. The asteroid was named for the city of Portland, Maine, where Hastings was a church minister at the time. In November 2015, amateur astronomers captured it with images of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Portlandia came to opposition in March 2016 at apparent magnitude 13.2.
782 Montefiore is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt that was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa on 18 March 1914 and named for Clarice Sebag-Montefiore, wife of Alfons von Rothschild of Vienna. It is orbiting 2.18 AU from the Sun with an eccentricity of 0.04 and a period of 3.22 yr. The orbital plane of this asteroid is inclined by an angle of 5.26° to the plane of the ecliptic.
1143 Odysseus, provisional designation 1930 BH, is a large Jupiter trojan located in the Greek camp of Jupiter's orbit. It was discovered on 28 January 1930, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany, and later named after Odysseus, the legendary hero from Greek mythology. The dark D-type asteroid has a rotation period of 10.1 hours. With a diameter of approximately 125 kilometers, it is among the 10 largest Jovian trojans.












