
Luxembourg, also known as Luxembourg City, is the capital city of Luxembourg and the country's most populous commune. Standing at the confluence of the Alzette and Pétrusse rivers in southern Luxembourg, the city lies at the heart of Western Europe, situated 213 km (132 mi) by road from Brussels and 209 km (130 mi) from Cologne. The city contains Luxembourg Castle, established by the Franks in the Early Middle Ages, around which a settlement developed.

A grand duchy is a country or territory whose official head of state or ruler is a monarch bearing the title of grand duke or grand duchess.
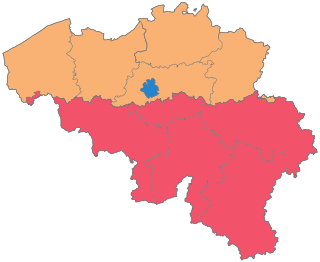
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province, nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration.

Forêts was a department of the French First Republic, and later the First French Empire, in present-day Belgium, Luxembourg, and Germany. Its name, meaning 'forests', comes from the Ardennes forests. It was formed on 24 October 1795, after the Austrian Netherlands had been annexed by France on 1 October. Before annexation, the territory was part of the Duchy of Luxembourg and small parts of the Duchy of Bouillon. Its capital was Luxembourg City.
Elections in Luxembourg are held to determine the political composition of the representative institutions of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. Luxembourg is a liberal representative democracy, with universal suffrage guaranteed under its constitution. Elections are held regularly, and are considered to be fair and free.

The Chamber of Deputies, abbreviated to the Chamber, is the unicameral national legislature of Luxembourg. The metonym Krautmaart is sometimes used for the Chamber, after the square on which the Hôtel de la Chambre is located.

The Duchy of Luxembourg was a state of the Holy Roman Empire, the ancestral homeland of the noble House of Luxembourg. The House of Luxembourg became one of the most important political forces in the 14th century, competing against the House of Habsburg for supremacy in Central Europe. They would be the heirs to the Přemyslid dynasty in the Kingdom of Bohemia, succeeding to the Kingdom of Hungary and contributing four Holy Roman Emperors until their own line of male heirs came to an end and the House of Habsburg received the territories that the two Houses had originally agreed upon in the Treaty of Brünn in 1364.

Pierre Prüm was a Luxembourgish politician and jurist. He was the 14th prime minister of Luxembourg, serving for a year, from 20 March 1925 until 16 July 1926.
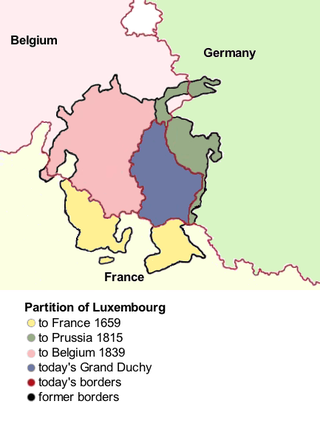
There were three Partitions of Luxembourg between 1659 and 1839. Together, the three partitions reduced the territory of the Duchy of Luxembourg from 10,700 km2 (4,100 sq mi) to the present-day area of 2,586 km2 (998 sq mi) over a period of 240 years. The remainder forms parts of modern-day Belgium, France, and Germany.

The Constitution of Luxembourg is the supreme law of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The modern constitution was adopted on 17 October 1868.
The Constituent Assembly of Luxembourg was a constituent assembly called in 1848 in Luxembourg to write and pass a new national constitution.
General elections were held in Belgium on 29 August 1831. They were the first elections to the new bicameral parliament created by the constitution adopted in February 1831.
Partial legislative elections were held in Belgium on Tuesday 8 June 1841 in which 48 of the 95 seats in the Chamber of Representatives were elected. Voter turnout was 77.0%, although only 24,887 people were eligible to vote. Under the alternating system, elections were only held in five out of the nine provinces: Antwerp, Brabant, Luxembourg, Namur and West Flanders.

Early general elections were held in Luxembourg on 20 October 2013. The elections were called after Prime Minister Jean-Claude Juncker, at the time the longest-serving head of government in the European Union, announced his resignation over a spy scandal involving the Service de Renseignement de l'État (SREL). The review found Juncker deficient in his control over the service.

The Reuter Ministry was the government in office in Luxembourg from 28 September 1918 until 20 March 1925, headed by Émile Reuter. It resulted from the Chamber elections of 28 July and 4 August 1918 and was reshuffled on 5 January 1920 as a result of the elections of 26 October 1919. There was a further reshuffle on 15 April 1921, when the Liberals left the government.
The Assembly of Estates was the legislature of Luxembourg from 1841 to 1848, and again from 1856 to 1868.

General elections were held in Luxembourg on 14 October 2018. All 60 seats of the Chamber of Deputies were renewed.
Diekirch was a constituency used to elect a single member of the Belgian Chamber of Representatives between 1831 and 1841. In 1839, under the stipulations of the Treaty of London, a portion of Diekirch, along with the constituencies of Grevenmacher and Luxembourg, became parts of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
Grevenmacher was a constituency, centred on the town of Grevenmacher, used to elect a single member of the Belgian Chamber of Representatives between 1831 and 1839. It also sent two deputies to the National Congress of Belgium in 1830. It was initially one of eight constituencies in the Province of Luxembourg to take part in the 1831 Belgian general election, the others being Arlon, Bastogne, Diekirch, Luxembourg, Marche, Neufchâteau, and Virton – each electing one member. In 1839, however, under the stipulations of the Treaty of London, Grevenmacher, along with the constituencies of Diekirch and Luxembourg, became parts of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
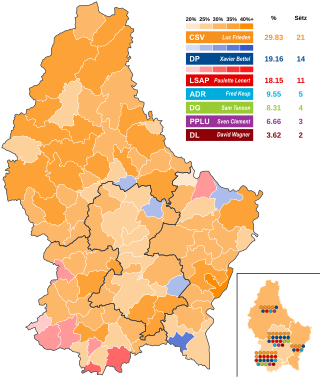
General elections were held in Luxembourg on 8 October 2023 to elect all 60 seats of the Chamber of Deputies.












