
The Minnesota House of Representatives is the lower house of the U.S. state of Minnesota's legislature. It operates in conjunction with the Minnesota Senate, the state's upper house, to craft and pass legislation, which is then subject to approval by the governor of Minnesota.

The Maine State Legislature is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Maine. It is a bicameral body composed of the lower house Maine House of Representatives and the upper house Maine Senate. The legislature convenes at the State House in Augusta, where it has met since 1832.

The 1936 United States Senate elections coincided with the reelection of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Great Depression continued and voters backed progressive candidates favoring Roosevelt's New Deal in races across the country. The Democrats gained 5 net seats during the election, and in combination with Democratic and Farmer–Labor interim appointments and the defection of George W. Norris from the Republican Party to become independent, the Republicans were reduced to 16 seats. Democrats gained a further two seats due to mid-term vacancies. The Democrats' 77 seats and their 62-seat majority remain their largest in history.

The 1890 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 4, 1890, with five states holding theirs early in between June and October. They occurred in the middle of President Benjamin Harrison's term. Elections were held for 332 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 44 states, to serve in the 52nd United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
The 1820–21 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 3, 1820, and August 10, 1821. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 17th United States Congress convened on December 3, 1821. They coincided with President James Monroe winning reelection unopposed.

Elections for the Massachusetts House of Representatives were held on November 7, 2006, with all of the 160 seats in the House up for election. The term of Representatives elected is two years, January 2007 until January 2009. The 2006 Massachusetts Senate election occurred on the same day as the House election, along with Federal and Gubernatorial elections.

The 2007 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 6. During this off-year election, the only seats up for election in the United States Congress were special elections held throughout the year. None of these congressional seats changed party hands. There were also several gubernatorial races and state legislative elections, and numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races in several major cities, and several types of local offices on the ballot.

The 1880 United States House of Representatives elections in South Carolina were held on November 2, 1880, to elect five representatives Representatives for two-year terms from the state of South Carolina. All five incumbents were re-elected and the composition of the state delegation remained solely Democratic.

2009 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 3. During this off-year election, the only seats up for election in the United States Congress were special elections held throughout the year. In total, only the seat representing New York's 23rd congressional district changed party hands, increasing the Democratic Party's majority over the Republicans in the United States House of Representatives, 258–177.

The 1881 United States Senate election in New York was held on January 18, 1881, by the New York State Legislature to elect a U.S. Senator to represent the State of New York in the United States Senate.

The 1878–79 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1878 and 1879, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.
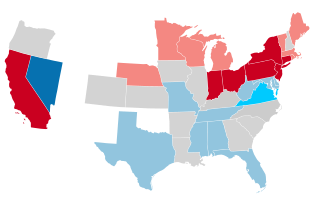
The 1880–81 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with the presidential election of 1880. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1880 and 1881, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1886–87 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1886 and 1887, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1810 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 24 to 26, 1810, to elect 17 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 12th United States Congress. At the same time, a vacancy was filled in the 11th United States Congress.

The 1812 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from December 15 to 17, 1812, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 13th United States Congress. At the same time, a vacancy was filled in the 12th United States Congress.

The 1816 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 23 to 25, 1816, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 15th United States Congress. At the same time, a vacancy was filled in the 14th United States Congress.

The 1818 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 28 to 30, 1818, to elect 27 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 16th United States Congress.

Partial general elections were held in Belgium on 9 June 1874. The result was a victory for the Catholic Party, which won 68 of the 124 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 34 of the 62 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 64.1%, although only 52,074 people were eligible to vote.
















