Belgium comprises 581 municipalities, 300 of them grouped into five provinces in Flanders and 262 others in five provinces in Wallonia, while the remaining 19 are in the Brussels Capital Region, which is not divided in provinces. In most cases, the municipalities are the smallest administrative subdivisions of Belgium, but in municipalities with more than 100,000 inhabitants, on the initiative of the local council, sub-municipal administrative entities with elected councils may be created. As such, only Antwerp, having over 500,000 inhabitants, became subdivided into nine districts. The Belgian arrondissements, an administrative level between province and municipality, or the lowest judicial level, are in English sometimes called districts as well.

The Federal Council is the federal cabinet of the Swiss Confederation. Its seven members also serve as the collective head of state and government of Switzerland. Since after World War II, the Federal Council is by convention a permanent grand coalition government composed of representatives of the country's major parties and language regions.

The Workers' Party of Belgium is a Marxist and socialist political party in Belgium. It is the only Belgian party represented in parliament that is a fully national party, representing both Flanders and Wallonia. Having historically been a small party, the PTB-PVDA has gained momentum since the 2010s, continuously scoring better at the elections, particularly in Wallonia and working-class communities in Brussels.

Elections in Spain encompass four different types: general elections, regional elections, local elections, and elections to the European Parliament. General elections and regional elections are typically conducted at the conclusion of the national or regional legislative mandate, which usually spans four years since the previous election. However, early elections can be called in certain circumstances. On the other hand, local council elections and elections to the European Parliament follow fixed dates, although some local government bodies, such as provincial councils, are not directly elected. In most elections, a party-list proportional representation (PR) system is employed, while the Senate utilizes the plurality system.

The Senate is one of the two chambers of the bicameral Federal Parliament of Belgium, the other being the Chamber of Representatives. It is considered to be the "upper house" of the Federal Parliament. Created in 1831 as a chamber fully equal to the Chamber of Representatives, it has undergone several reforms in the past, most notably in 1993 and 2014. The 2014 elections were the first without a direct election of senators. Instead, the new Senate is composed of members of community and regional parliaments and co-opted members. It is a chamber of the communities and regions and serves as a platform for discussion and reflection about matters between these federated entities. The Senate today plays a minor role in the federal legislative process. However, the Senate, together with the Chamber, has full competence for the Constitution and legislation on the organization and functioning of the Federal State and the federated entities. Since the reform of 2014, it holds about ten plenary sessions a year.

Elections in Belgium are organised for legislative bodies only, and not for executive functions. Direct elections take place for the European Parliament, the Chamber of Representatives, the Parliaments of the Regions, the Parliaments of the Communities, the provincial councils, the municipal councils and the councils of Districts of Antwerp. Voting is mandatory in federal elections, and all elections use proportional representation which in general requires coalition governments.
Switzerland elects on national level a collective head of state, the Federal Council, and a legislature, the Federal Assembly.

The Chamber of Deputies, abbreviated to the Chamber, is the unicameral national legislature of Luxembourg. The metonym Krautmaart is sometimes used for the Chamber, after the square on which the Hôtel de la Chambre is located.

Elections to the Swiss Federal Assembly, the federal parliament of Switzerland, were held on Sunday, 21 October 2007. In a few cantons, a second round of the elections to the Council of States was held on 11 November, 18 November, and 25 November 2007. For the 48th legislative term of the federal parliament (2007–2011), voters in 26 cantons elected all 200 members of the National Council as well as 43 out of 46 members of the Council of States. The other three members of the Council of States for that term of service were elected at an earlier date.

General elections were held in the Belgian Congo on 22 May 1960, in order to create a government to rule the country following independence as the Republic of the Congo (Congo-Léopoldville), scheduled for 30 June. The 137-seat Chamber of Deputies was elected by men over the age of 21. The seats were filled by district-based lists, although only two parties, the Mouvement National Congolais-Lumumba (MNC-L) and the Parti National du Progrès, submitted lists in more than one district.
The Politics of Saskatchewan relate to the Canadian federal political system, along with the other Canadian provinces. Saskatchewan has a lieutenant-governor, who is the representative of the Crown in right of Saskatchewan; a premier—currently Scott Moe—leading the cabinet; and a legislative assembly. As of the most recent provincial election in 2024, the province is divided into 61 electoral districts, each of which elects a representative to the legislature, who becomes their member, or MLA. In 2024, Moe's Saskatchewan Party was elected to a majority government. Regina is the provincial capital.

The Belgian provincial, municipal and district elections of 2012 took place on 14 October. As with the previous 2006 elections, these are no longer organised by the Belgian federal state but instead by the respective regions:
Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 29 October 1939. The Free Democratic Party emerged as the largest party in the National Council, winning 49 of the 187 seats. Due to the outbreak of World War II, there were no elections in nine of the 25 cantons; Appenzell Ausserrhoden, Lucerne, Neuchâtel, Schwyz, Solothurn, Ticino, Valais, Vaud and Zug. In what became known as "silent elections", a total of 55 candidates were elected unopposed.
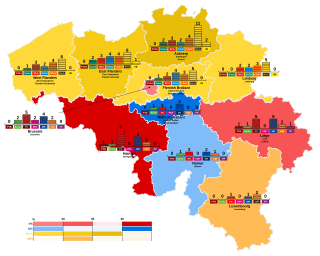
Federal elections were held in Belgium on 25 May 2014. All 150 members of the Chamber of Representatives were elected, whereas the Senate was no longer directly elected following the 2011–2012 state reform. These were the first elections held under King Philippe's reign.

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 18 October 2015 for the National Council and the first round of elections to the Council of States, with runoff elections to the Council of States being held in various cantons until 22 November.

Departmental elections to elect the membership of the departmental councils of France's 100 departments were held on 22 and 29 March 2015. In 2015 for the first time, the term "departmental elections" replaced "cantonal elections" ; as did the term "Departmental Council", replacing "General Council".
Canton is the name of an electoral ward in the west of the city of Cardiff, Wales, which covers its namesake community, Canton. The ward elects three county councillors to the County Council of the City and County of Cardiff.
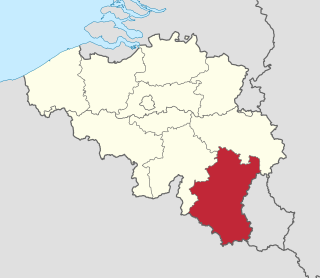
Luxembourg is one of the 11 multi-member constituencies of the Chamber of Representatives, the lower house of the Belgian Federal Parliament, the national legislature of Belgium. The constituency was established as Arlon-Marche-Bastogne-Neufchâteau-Virton in 1995 following the fourth Belgian state reform. It was renamed Luxembourg in 2003 following the re-organisation of constituencies across Belgium along provincial lines. It is conterminous with the province of Luxembourg. The constituency currently elects four of the 150 members of the Chamber of Representatives using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2019 federal election the constituency had 212,441 registered electors.
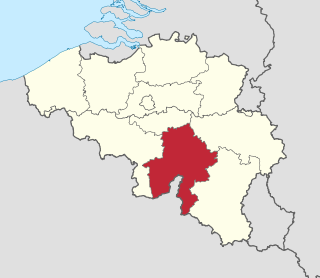
Namur is one of the 11 multi-member constituencies of the Chamber of Representatives, the lower house of the Belgian Federal Parliament, the national legislature of Belgium. The constituency was established as Namur-Dinant-Philippeville in 1995 following the fourth Belgian state reform. It was renamed Namur in 2003 following the re-organisation of constituencies across Belgium along provincial lines. It is conterminous with the province of Namur. The constituency currently elects six of the 150 members of the Chamber of Representatives using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2019 federal election the constituency had 379,299 registered electors.

Liège is one of the 11 multi-member constituencies of the Chamber of Representatives, the lower house of the Belgian Federal Parliament, the national legislature of Belgium. The constituency was established in 2003 following the re-organisation of constituencies across Belgium along provincial lines. It is conterminous with the province of Liège. The constituency currently elects 15 of the 150 members of the Chamber of Representatives using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2019 federal election the constituency had 794,378 registered electors.




















