
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 3 July 1918. They were the first elections held after a series of reforms that introduced universal male suffrage and pure proportional representation, replacing the previous two-round system in single member constituencies. This change was known as the Pacification of 1917, which also included the introduction of state financing of religious schools, and led to the start of consociational democracy.

Parliamentary elections were held in Norway on 11 September 1961. The result was a victory for the Labour Party, which won 74 of the 150 seats in the Storting. Although it lost the absolute majority it had held since 1945, the Labour Party was able to continue in government.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 12 January 1912. Although the Social Democratic Party (SPD) had received the most votes in every election since 1890, it had never won the most seats, and in the 1907 elections, it had won fewer than half the seats won by the Centre Party despite receiving over a million more votes. However, the 1912 elections saw the SPD retain its position as the most voted-for party and became the largest party in the Reichstag, winning 110 of the 397 seats.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 25 January 1907. Despite the Social Democratic Party (SPD) receiving a clear plurality of votes, they were hampered by the unequal constituency sizes that favoured rural seats. As a result, the Centre Party remained the largest party in the Reichstag after winning 101 of the 397 seats, whilst the SPD won only 43. Voter turnout was 84.7%.
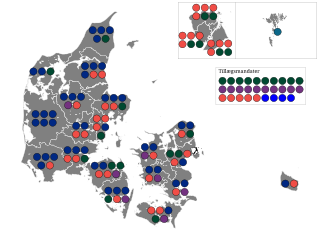
Folketing elections were held in Denmark on 26 April 1920, except in the Faroe Islands, where they were held on 20 May. The election campaign was the most aggressive and bitter in Denmark in the 20th century. Voter turnout was 80.6% in Denmark proper and 58.8% in the Faroe Islands.

General elections were held in Belgium on 17 February 1946. The result was a victory for the Christian Social Party, which won 92 of the 202 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 51 of the 101 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 90.3%.

General elections were held in Belgium on 4 June 1950. The result was a victory for the Christian Social Party, which won 108 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 54 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 92.6%. This election was the last one in Belgian history where a single party achieved an absolute majority. Elections for the nine provincial councils were also held.

General elections were held in Belgium on 11 April 1954. The dominant Christian Social Party won 95 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 49 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 93.2%. Elections for the nine provincial councils were also held.

General elections were held in Belgium on 1 June 1958. The result was a victory for the Christian Social Party, which won 104 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 53 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 93.6% in the Chamber election and 93.7% in the Senate election. Elections for the nine provincial councils were also held.

General elections were held in Belgium on 23 May 1965. The result was a victory for the Christian Social Party, which won 77 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 44 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 91.6%. Elections for the nine provincial councils were also held.

General elections were held in Belgium on 31 March 1968. The Christian Social Party remained the largest party. Voter turnout was 90.0%. Elections for the nine provincial councils were also held.

General elections were held in Belgium on 7 November 1971. The result was a victory for the Christian People's Party, which won 40 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 34 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 91.5%. Elections to the nine provincial councils were also held.

General elections were held in Belgium on 10 March 1974. The Belgian Socialist Party emerged as the largest faction in the Chamber of Representatives with 59 of the 212 seats. Voter turnout was 90.3%. Elections were also held for the nine provincial councils, as well as for the Council of the German Cultural Community for the first time.

General elections were held in Belgium on 17 April 1977. The result was a victory for the Christian People's Party, which won 56 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 28 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 95.1%. Elections were also held for the nine provincial councils and for the Council of the German Cultural Community.

General elections were held in Belgium on 17 December 1978. The Christian People's Party emerged as the largest party, with 57 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 29 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 94.8%. Elections were also held for the nine provincial councils and for the Council of the German Cultural Community.

General elections were held in Belgium on 27 November 1932. The Catholic Party won 79 of the 187 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 42 of the 93 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 94.3%.

Full general elections were held in Belgium on 14 October 1894, with run-off elections held on 21 October 1894.

Partial legislative elections were held in Belgium on 22 May 1898, with run-off elections held on 29 May. Under the alternating system, elections for the Chamber of Representatives were held in only four out of the nine provinces: Hainaut, Limburg, Liège and East Flanders. Thus, only 75 seats out of the 152 seats in the Chamber of Representatives were up for election. The Catholic Party retained their absolute majority.

Partial general elections were held in Belgium on 24 May 1914. The result was a victory for the Catholic Party, which won 41 of the 88 seats up for election in the Chamber of Representatives.

General elections were held in Belgium on 24 May 1936. The result was a victory for the Belgian Labour Party, which won 70 of the 202 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 39 of the 101 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 94.7%.

























