
The 40th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1867, to March 4, 1869, during the third and fourth years of Andrew Johnson's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1860 United States census. Both chambers had a Republican majority. In the Senate, the Republicans had the largest majority a party has ever held.

The 1912–13 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. They were the last U.S. Senate elections before the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, establishing direct elections for all Senate seats. Senators had been primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1912 and 1913, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. Some states elected their senators directly even before passage of Seventeenth Amendment. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.
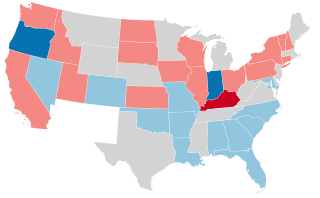
The 1908–09 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1906 and 1907, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. However, some states had already begun direct elections during this time. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.

The 1867 United States Senate election in New York was held on January 15, 1867, by the New York State Legislature to elect a U.S. Senator to represent the State of New York in the United States Senate. Incumbent Senator Ira Harris was not renominated for a second term in office. U.S. Representative Roscoe Conkling was elected to succeed him.

The 1869 United States Senate election in New York was held on January 19, 1869, by the New York State Legislature. Incumbent Senator Edwin D. Morgan stood for a second term in office, but lost the support of the Republican legislative caucus in favor of Reuben Fenton.

The 1875 United States Senate election in New York was held on January 19 and 20, 1875, by the New York State Legislature. The legislature, with a Republican Senate and Democratic Assembly, jointly elected Democrat Francis Kernan Senator. Kernan became the first Democrat to represent New York since 1851.

The 1868–69 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1868 and 1869, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1874–75 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1874 and 1875, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1904–05 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with President Theodore Roosevelt's landslide election to a full term and the 1904 House of Representatives elections. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1904 and 1905, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1890–91 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1890 and 1891, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.

The 1906–07 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1906 and 1907, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1892–93 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with former Democratic President Grover Cleveland's return to power. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1892 and 1893, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1866–67 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1866 and 1867, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.

The 1862–63 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, occurring during the American Civil War. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1862 and 1863, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.
The 1851 United States Senate election in Massachusetts was held during January 1851. Free Soil Party candidate Charles Sumner was elected by a coalition of Free-Soil and Democratic legislators over Whig incumbent Robert C. Winthrop, who had been appointed to finish the term of retiring Senator Daniel Webster.
The 1857 United States Senate election in Massachusetts was held in January 1857. Incumbent Charles Sumner was re-elected to a second term in office as a member of the Republican Party. Sumner was elected in 1851 by a single vote after twenty-five inconclusive ballots by a coalition of Free-Soil and Democratic legislators. He had since become a founding member of the Massachusetts Republican Party.
The 1863 United States Senate election in Massachusetts was held on January 9, 1863. Incumbent Charles Sumner was re-elected to a third term in office.
The 1883 United States Senate election in Massachusetts was held in January 1883. Incumbent Republican Senator George Frisbie Hoar was re-elected to a second term in office despite a serious challenge from Democrats and members of his own party.
The 1913 United States Senate election in Massachusetts was held during January 1913. Incumbent Republican Senator Winthrop Crane retired and was succeeded by Republican John Wingate Weeks.
The 1850–51 Massachusetts gubernatorial election consisted of an initial popular held on November 11, 1850 that was followed by a legislative vote that was conducted on January 11, 1851. It saw the election of Democratic Party nominee Emory Washburn. The ultimate task of electing the governor had been placed before the Massachusetts General Court because no candidate received the majority of the vote required for a candidate to be elected through the popular election.













