A coalition government is a form of government in which political parties cooperate to form a government. The usual reason for such an arrangement is that no single party has achieved an absolute majority after an election. A coalition government might also be created in a time of national difficulty or crisis to, give a government the high degree of perceived political legitimacy or collective identity, it can also play a role in diminishing internal political strife. In such times, parties have formed all-party coalitions. If a coalition collapses, a confidence vote is held or a motion of no confidence is taken.

The politics of Japan are conducted in a framework of a multi-party bicameral parliamentary representative democratic constitutional monarchy in which the Emperor is the Head of State and the Prime Minister is the Head of Government and the Head of the Cabinet, which directs the executive branch.
The politics of the Maldives, as per the reports, take place in the framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President is the Head of Government. Executive power is exercised by the government. The President heads the executive branch and appoints the Cabinet; like many presidential democracies, each member of the cabinet need to be approved by the Parliament. The President, along with their pick for Vice President, is directly elected by the denizens to a five-year term by a secret ballot. Once in office, they could be re-elected to a second 5-year term, which is the limit allowed by the Constitution. The current President of the Maldives is Ibrahim Mohamed Solih, who was sworn into office on July 13, 2018, when his predecessor, Abdulla Yameen, lost the 2018 presidential election. Yameen followed his own predecessor Mohamed Nasheed's forced resignation in a coup led by the police. Nasheed reportedly resigned involuntarily to forestall an escalation of violence, and was placed in jail, before being forced into exile, from which he eventually returned.
The House of Representatives is the lower house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Councillors is the upper house.

The House of Councillors is the upper house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Representatives is the lower house. The House of Councillors is the successor to the pre-war House of Peers. If the two houses disagree on matters of the budget, treaties, or designation of the prime minister, the House of Representatives can insist on its decision. In other decisions, the House of Representatives can override a vote of the House of Councillors only by a two-thirds majority of members present.

The Democratic Party (DP) is a centre-left liberal political party in Hong Kong. Chaired by Lo Kin-hei, it is the flagship party in the pro-democracy camp and currently has 12 elected representatives in the District Councils.

The Landtag of Bavaria, officially known in English as the Bavarian State Parliament, is the unicameral legislature of the state of Bavaria in Germany. The parliament meets in the Maximilianeum in Munich.

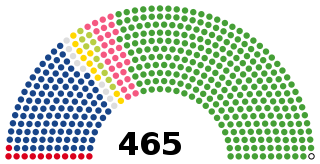
The National Assembly of the Republic of Korea, often shortened to the National Assembly in domestic English-language media, is the unicameral national legislature of South Korea. Elections to the National Assembly are held every four years. The latest legislative elections were held on 15 April 2020. The National Assembly has 300 seats, with 253 constituency seats and 47 proportional representation seats; 30 of the PR seats are assigned on additional member system, while 17 PR seats use the parallel voting method.
The Japanese political process has three types of elections: general elections to the House of Representatives held every four years, elections to the House of Councillors held every three years to choose half of its members, and local elections held every four years for offices in prefectures and municipalities. Elections are supervised by Election Administration Commissions at each administrative level under the general direction of the Central Election Management Council, an extraordinary organ attached to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). The minimum voting age in Japan's non-compulsory electoral system was reduced from twenty to eighteen years in June 2016. Voters must satisfy a three-month residency requirement before being allowed to cast a ballot.

The House of Representatives of Puerto Rico is the lower house of the Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico, the bicameral territorial legislature of Puerto Rico. The House, together with the Senate, control the legislative branch of the government of Puerto Rico.
Elections in Cyprus gives information on election and election results in Cyprus.

The Greens New South Wales, commonly known as Greens NSW, is a green political party in New South Wales and a member of the Australian Greens. First formed in 1991, the Greens NSW began as a state-level party before joining with other green parties in Australia to create the current federated structure.

The National Assembly of the Gambia is the unicameral legislature of the Gambia. The authorisation for the National Assembly lies in Chapter VII of the Constitution of the Gambia. It is composed of 53 members directly elected through first past the post, and a further five members appointed by the President.

The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010, in the middle of Democratic President Barack Obama's first term. Republicans ended unified Democratic control of Congress and the presidency by winning a majority in the House of Representatives.

Early legislative elections were held in Equatorial Guinea on 4 May 2008, alongside local elections; 100 seats in parliament and 230 council seats were up for election. The ruling Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea won 89 seats in parliament.

Starry Lee Wai-king, SBS, JP is a Hong Kong politician, chairperson of the largest pro-establishment Beijing-loyalist party, the Democratic Alliance for the Betterment and Progress of Hong Kong (DAB). She is a Legislative Councillor for the District Council (Second) functional constituency and a Kowloon City District Councillor. From 2012 to 2016, she was a member of the Executive Council.

The Neo Democrats was a pro-democracy, localist political group in Hong Kong composed mainly of former and disenchanted members of the Democratic Party New Territories East branch after the 2012 constitutional reform proposals. It had held one seat in the Legislative Council until Gary Fan lost his re-election in the 2016 Legislative Council election. Fan won the seat back in the 2018 by-election, but lost his seat after a court declared that he was not duly elected. It held 8 seats in the District Councils before its dissolution on 26 June 2021.

The North District Council is one of the 18 Hong Kong district councils and represents the North District. It is one of 18 such councils. Consisting of 22 members, the district council is drawn from 18 constituencies, which elect 18 members, along with four ex officio members who are the Ta Kwu Ling, Sheung Shui, Sha Tau Kok and Fanling rural committee chairmen. The latest election was held on 24 November 2019.

Wu Chi-wai, MH is a Hong Kong politician. He is the former chairman of the Democratic Party from 2016 to 2020 and a former member of the Legislative Council of Hong Kong for Kowloon East constituency since 2012. He has also been a member of Wong Tai Sin District Council since 1999 and member of the Urban Council from 1995 to 1999.

The 2016 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. Republican nominee Donald Trump defeated Democratic former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton in the presidential election, while Republicans retained control of Congress. This marked the first time Republicans won or held unified control of the presidency and Congress since 2004.

















