
North Jeolla Province, also known as Jeonbuk, is a province of South Korea in the Honam region in the southwest of the Korean Peninsula. North Jeolla borders the provinces of South Chungcheong to the north, North Gyeongsang and South Gyeongsang to the east and South Jeolla to the south. North Jeolla was established in 1896 from the northern part of the old Jeolla province, one of the Eight Provinces of Korea.

Jeolla Province was one of the historical Eight Provinces of Korea during the Kingdom of Joseon in today Southwestern Korea. It consisted of the modern South Korean provinces of North Jeolla, South Jeolla and Gwangju Metropolitan City as well as the Jeju Province. The provincial capital was Jeonju, the current capital of North Jeolla. The entire inland region was called Honam, which is still commonly used today.

Chungcheong was one of the eight provinces of Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. Chungcheong was located in the southwest of Korea. The provincial capital was located at Gongju, which had been the capital of the kingdom of Baekje from 475 to 538.

Legislative elections were held in South Korea on April 15, 2004. In the 17th election for the National Assembly, voters elected 299 members of the legislature. The newly formed Uri Party and other parties supporting President Roh Moo-hyun, who was impeached by the outgoing National Assembly, won a majority of seats. This was the first time a centre-left liberal party won a majority in the National Assembly.
South Korea is made up of 17 first-tier administrative divisions: 6 metropolitan cities, 1 special city, 1 special self-governing city, and 9 provinces, including two special self-governing provinces. These are further subdivided into a variety of smaller entities, including cities, counties, districts, towns, townships, neighborhoods and villages.
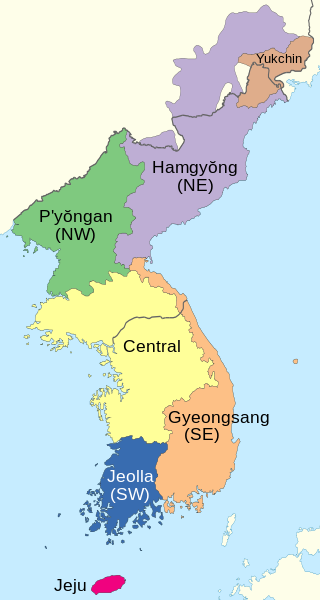
A number of Korean dialects are spoken on the Korean Peninsula. The peninsula is very mountainous and each dialect's "territory" corresponds closely to the natural boundaries between different geographical regions of Korea. Most of the dialects are named for one of the traditional Eight Provinces of Korea. Two are sufficiently distinct from the others to be considered separate languages, the Jeju and the Yukjin languages.

The Jogye Order, officially the Jogye Order of Korean Buddhism, is the representative order of traditional Korean Buddhism with roots that date back 1200 years to the Later Silla National Master Doui, who brought Seon and the practice taught by the Sixth Patriarch, Huineng, from China around 820 CE. The name of the Order, Jogye, was adopted from the name of the village where Patriarch Huineng's home temple, Nanhua Temple, is located,.
Righteous armies, sometimes called irregular armies or militias, are informal civilian militias that have appeared several times in Korean history, when the national armies were in need of assistance.

Provinces are one of the first-level divisions within South Korea. There are 9 provinces in South Korea: North Chungcheong, South Chungcheong, Gangwon, Gyeonggi, North Gyeongsang, South Gyeongsang, North Jeolla, South Jeolla, and Jeju Special Self-Governing Province.

Presidential elections were held in South Korea on 16 December 1987. They marked the establishment of the Sixth Republic, as well as the end of the authoritarian rule that had prevailed in the country for all but one year since its founding in 1948. They were the first direct presidential elections since 1971. For the previous 15 years, presidents had been indirectly elected by the National Conference for Unification, an electoral college dominated by the governing party.

The Chungcheong dialects of the Korean language are spoken in the Chungcheong (Hoseo) region of South Korea, including the metropolitan city of Daejeon. It may also include several areas in Gyeonggi Province, most notably Pyeongtaek, that are adjacent to Chungcheong Province. Chungcheong dialect can be divided into two categories: the Northern Chungcheong dialect, notable for its similarity capital Gyeonggi region speech, and the Southern dialect, which is similar to the Jeolla dialect. This dialect is notable for its slow enunciations, vowel changes, and unique jargon. However, as Seoul expands and standard language supremacy spreads, young people in Chungcheong Province, including Daejeon and Sejong, do not use original dialect, or use very little of it. Most young people use standard language and dialect alternately, and in cities located just below the Seoul metropolitan area (Sudogwon), like Cheonan, dialect is on the verge of extinction.
Geumseong (金城) was the capital of Silla, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea.
Hyun, also spelled Hyeon or Hyon, Hyoun, is a Korean surname, a single-syllable Korean given name, and an element in many two-syllable Korean given names. As given name meaning differs based on the hanja used to write it. There are 42 hanja with the reading "hyun" on the South Korean government's official list of hanja which may be used in given names.

Hot Young Bloods is a 2014 South Korean teen romantic comedy film that depicts the loves, rivalries, and friendships between four high school students in Hongseong County, South Chungcheong Province in the 1980s. Hot Young Bloods was inspired by the short film That's What I Told Her.
The 7.30 by-elections were held in South Korea on 30 July 2014. 15 seats to the National Assembly of South Korea were contested while re-election occurred for 1 seat to the Municipal Council of Suwon.
Mo (모) is an uncommon Korean surname. It originated from either of two hanja, which are also used respectively to write the Chinese surnames Móu or Máo. The 2000 South Korean census found a total of 19,834 people and 6,110 households with these surnames. The surname is spelled Mo in all standard methods of romanizing the Korean language. In a study by the National Institute of the Korean Language based on 2007 application data for South Korean passports, all the applicants spelled this surname as Mo. The alternative spelling Moh is occasionally seen.
The 2018 South Korean by-elections was held in South Korea on 13 June 2018, coinciding with the local elections. 12 seats to the National Assembly of South Korea were contested.









