Related Research Articles
Elections in Sweden are held once every four years. At the highest level, all 349 members of Riksdag, the national parliament of Sweden, are elected in general elections. Elections to the 20 county councils and 290 municipal assemblies – all using almost the same electoral system – are held concurrently with the legislative elections on the second Sunday in September.
Electoral systems of the Australian states and territories are broadly similar to the electoral system used in federal elections in Australia.
There are eleven types of elections in Taiwan which, since 2012, have been unified into general and local elections, each held every four years, typically in January and November respectively. There may also be by-elections. Electoral systems include first-past-the-post, proportional representation, single non-transferable voting, and a parallel mixture of the above.
Regular elections in Croatia are mandated by the Constitution and legislation enacted by Parliament. The presidency, Parliament, county prefects and assemblies, city and town mayors, and city and municipal councils are all elective offices. Since 1990, seven presidential elections have been held. During the same period, ten parliamentary elections were also held. In addition, there were nine nationwide local elections. Croatia has also held three elections to elect members of the European Parliament following its accession to the EU on 1 July 2013.

Elections in Belgium are organised for legislative bodies only, and not for executive functions. Direct elections take place for the European Parliament, the Chamber of Representatives, the Parliaments of the Regions, the Parliaments of the Communities, the provincial councils, the municipal councils and the councils of Districts of Antwerp. Voting is mandatory and all elections use proportional representation which in general requires coalition governments.
Some parts of the Government of Thailand are selected through democratic elections. These include the House of Representatives of Thailand,, local Administrations, Governorship of Bangkok and national referendums. Thailand has so far had 28 general elections since 1933; the last election was in 2019. Voting in elections in Thailand is compulsory. All elections in Thailand are regulated by the Election Commission of Thailand.
Elections in South Korea are held on a national level to select the President and the National Assembly. Local elections are held every four years to elect governors, metropolitan mayors, municipal mayors, and provincial and municipal legislatures.
Elections in the Philippines are of several types. The president, vice-president, and the senators are elected for a six-year term, while the members of the House of Representatives, governors, vice-governors, members of the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, mayors, vice-mayors, members of the Sangguniang Panlungsod/members of the Sangguniang Bayan, barangay officials, and the members of the Sangguniang Kabataan are elected to serve for a three-year term.
Elections in Hungary are held at two levels: general elections to elect the members of the National Assembly and local elections to elect local authorities. European Parliament elections are also held every 5 years.
Historically, the single transferable vote (STV) electoral system has seen a series of relatively modest periods of usage and disusage throughout the world; however, today it is seeing increasing popularity and proposed implementation as a method of Proportional representation and a goal of electoral reform. STV has been used in many different local, regional and national electoral systems, as well as in various other types of bodies, around the world.
Plurality block voting, also known as plurality-at-large voting, block vote or block voting (BV) is a non-proportional voting system for electing representatives in multi-winner elections. Each voter may cast as many votes as the number of seats to be filled. The usual result where the candidates divide into parties is that the most popular party in the district sees its full slate of candidates elected in a seemingly landslide victory.
Politics of Cardiff refers to the political representation of the city of Cardiff, capital of Wales. Cardiff is represented politically at a local, Wales and United Kingdom level and previously at the European level.

On 25 October 2015 local elections took place in Ukraine. The elections were conducted a little over a year since the 2014 snap local elections, which were only held throughout parts of the country. A second round of voting for the election of mayors in cities with more than 90,000 residents where no candidate gained more than 50% of the votes were held on 15 November 2015.

Elections to the provincial, county (district) and city (municipal) people's assemblies in North Korea were held on 21 July 2019.
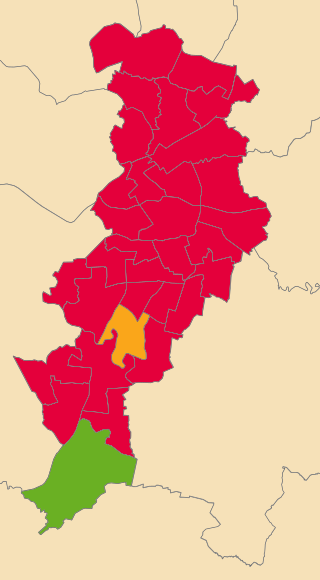
The 2022 Manchester City Council election took place on 5 May 2022. One third of councillors on Manchester City Council were elected. This election was a part of the other local elections across the United Kingdom.
The 2022 Rochdale Metropolitan Borough Council election took place as of 5 May 2022. Due to boundary changes, all 60 councillors were elected at the same time. The election took place alongside other local elections across the United Kingdom.
The 2022 Gateshead Metropolitan Borough Council election took place on 5 May 2022. One third of councillors — 22 out of 66 — on Gateshead Metropolitan Borough Council were elected. The election took place alongside other local elections across the United Kingdom.
The 2022 Knowsley Metropolitan Borough Council election took place on 5 May 2022. One third of councillors — 15 out of 45 — on Knowsley Metropolitan Borough Council were elected. The election took place alongside other local elections across the United Kingdom.
The 2022 Newcastle City Council election took place on 5 May 2022. One third of councillors — 26 out of 78 — on Newcastle City Council were elected. The election took place alongside other local elections across the United Kingdom.
The 2022 Salford City Council election took place on 5 May 2022 along with other local elections across the United Kingdom. One third—20 out of 60—of councillor seats on Salford City Council were up for election.