
The single transferable vote (STV) or proportional-ranked choice voting (P-RCV) is a multi-winner electoral system in which each voter casts a single vote in the form of a ranked ballot. Voters have the option to rank candidates, and their vote may be transferred according to alternative preferences if their preferred candidate is eliminated or elected with surplus votes, so that their vote is used to elect someone they prefer over others in the running. STV aims to approach proportional representation based on votes cast in the district where it is used, so that each vote is worth about the same as another.

Mixed-member proportional representation is a type of representation provided by some mixed electoral systems which combine local winner-take-all elections with a compensatory tier with party lists, in a way that produces proportional representation overall. Like proportional representation, MMP is not a single system, but a principle and goal of several similar systems. Some systems designed to achieve proportionality are still called mixed-member proportional, even if they generally fall short of full proportionality. In this case, they provide semi-proportional representation.

The 1998 Northern Ireland Assembly election took place on Thursday, 25 June 1998. This was the first election to the new devolved Northern Ireland Assembly. Six members from each of Northern Ireland's eighteen Westminster Parliamentary constituencies were elected by single transferable vote, giving a total of 108 Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs).

At the national level, the Republic of Cyprus holds elections for its head of state, the President of Cyprus, and for its legislature, the House of Representatives.

The 1930 Alberta general election was held on June 19, 1930, to elect members of the Legislative Assembly of Alberta.

The National Assembly is the directly elected house of the Parliament of South Africa, located in Cape Town, Western Cape. It consists of four hundred members who are elected every five years using a party-list proportional representation system where half of the members are elected proportionally from nine provincial lists and the remaining half from national lists so as to restore proportionality.
Elections in Hungary are held at two levels: general elections to elect the members of the National Assembly and local elections to elect local authorities. European Parliament elections are also held every 5 years.
The Edmonton provincial electoral district also known as Edmonton City from 1905 to 1909, was a provincial electoral district in Alberta, Canada mandated to return members to the Legislative Assembly of Alberta from 1905 to 1917 and again from 1921 to 1959.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislative house of the Parliament of Mauritania. The legislature currently has 176 deputies, elected for five-year terms in electoral districts or nationwide proportional lists.

Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 9 April 2006, with a second round of voting in 110 of the 176 single-member constituencies on 23 April. The Hungarian Socialist Party (MSZP) emerged as the largest party in the National Assembly with 186 of the 386 seats, and continued the coalition government with the Alliance of Free Democrats (SZDSZ). It marked the first time a government had been re-elected since the end of Communist rule. To date, this is the most recent national election in Hungary not won by Fidesz-KDNP, and the last in which the victorious party did not win a two-thirds supermajority in parliament.

General elections were held in Italy on Sunday 2 and also on Monday 3 June 1946. They were the first after World War II and elected 556 deputies to the Constituent Assembly. Theoretically, a total of 573 deputies were to be elected, but the election did not take place in the Julian March and in South Tyrol, which were under military occupation by the United Nations.
Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 10 May 2003. The Independence Party remained the largest party in the Althing, winning 22 of the 63 seats. The coalition government of the Independence Party and Progressive Party remained in office, with Davíð Oddsson continuing as prime minister.

Legislative elections were held in South Korea on 26 April 1988. The result was a victory for the ruling Democratic Justice Party (DJP), which won 125 of the 299 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was 75.8%. This was the first time the ruling party did not win a majority in the National Assembly since 1960, the first free and fair elections in Korean history. In January 1990, the DJP merged with other two opposition parties, leaving the Kim Dae-jung-led Peace Democratic Party to be the sole opposition party.

Legislative elections were held in South Korea on 12 February 1985. The result was a victory for the Democratic Justice Party, which won 148 of the 276 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was 84.6%.

An electoral or voting system is a set of rules used to determine the results of an election. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, non-profit organisations and informal organisations. These rules govern all aspects of the voting process: when elections occur, who is allowed to vote, who can stand as a candidate, how ballots are marked and cast, how the ballots are counted, how votes translate into the election outcome, limits on campaign spending, and other factors that can affect the result. Political electoral systems are defined by constitutions and electoral laws, are typically conducted by election commissions, and can use multiple types of elections for different offices.

Legislative elections were held in South Korea on 26 November 1963. They were the first held after the 1961 coup and subsequent approval of a new constitution the previous December, which inaugurated the Third Republic. All candidates had to run under the banner of a political party.

Legislative elections were held in South Korea on 25 May 1971. The result was a victory for the Democratic Republican Party, which won 113 of the 204 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was 73.2%.

Legislative elections were held in South Korea on 25 March 1981. The elections were held following coups in 1979 and 1980, with major opposition political figures including Kim Young-sam and Kim Jong-pil barred from running and the Democratic Republican Party of late president Park Chung-hee forcibly dissolved. Kim Dae-jung was arrested on 17 May 1980, and was sentenced to death on a of "inciting rebellion". While ostensibly multi-party, the elections are widely considered to have been fraudulent, with opposition politicians being heavily vetted by the Agency for National Security Planning and the South Korean Army Security Command.
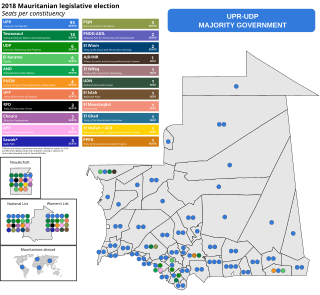
Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania in September 2018; the first round took place on 1 September, with a second round held on 15 September. At the national level, elections were held in 157 constituencies, each electing one member to the National Assembly. Elections were also held in 13 regional councils and 219 municipalities.



















