
The 1952 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 83rd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 4, 1952, while Maine held theirs on September 8. This was the first election after the congressional reapportionment based on the 1950 census. It also coincided with the election of President Dwight Eisenhower. Eisenhower's Republican Party gained 22 seats from the Democratic Party, gaining a majority of the House. However, the Democrats had almost 250,000 more votes (0.4%) thanks to overwhelming margins in the Solid South, although this election did see the first Republican elected to the House from North Carolina since 1928, and the first Republicans elected from Virginia since 1930. It was also the last election when both major parties increased their share of the popular vote simultaneously, largely due to the disintegration of the American Labor Party and other third parties.

The 1868–69 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 1, 1868, and August 2, 1869. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 41st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1869. They coincided with the 1868 United States presidential election, which was won by Ulysses S. Grant. Elections were held for all 243 seats, representing 37 states. All of the former Confederate states were represented in Congress for the first time since they seceded from the Union.

Parliamentary elections were held in Bulgaria on 25 June 2005, for the 240 members of the National Assembly. According to exit polls, the Socialists had a lead with around 31%, but without a majority, necessitating the creation of a coalition. The National Movement for Simeon II, in power before the election, was in second place, with around 21%. Following the election, Socialist Party leader Sergei Stanishev became prime minister.
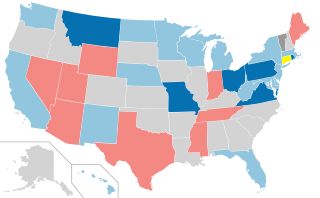
The 2006 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 7, 2006, in the middle of Republican President George W. Bush's second term against the backdrop of the war on terror. These elections marked a major political shift, ending twelve years of Republican dominance in Congress and state governments. The Democratic Party achieved sweeping victories, gaining control of both chambers of Congress, and a majority of governorships, and state legislatures. These elections were widely categorized as a Democratic wave.

The 1974 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 18 May 1974. All 127 seats in the House of Representatives and all 60 seats in the Senate were up for election, due to a double dissolution. The incumbent Labor Party led by Prime Minister Gough Whitlam defeated the opposition Liberal–Country coalition led by Billy Snedden. This marked the first time that a Labor leader won two consecutive elections.

The 1951 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 28 April 1951. All 121 seats in the House of Representatives and all 60 seats in the Senate were up for election, due to a double dissolution called after the Senate rejected the Commonwealth Bank Bill. The incumbent Liberal–Country coalition led by Prime Minister Robert Menzies defeated the opposition Labor Party led by Ben Chifley with a modestly reduced majority, and secured a majority in the Senate. This was the last time the Labor party ever held a Senate majority. Chifley died just over a month after the election. This was the sixth and last federal election prior to the death of George VI a year later.

The 2003 Harlow District Council election took place on 1 May 2003 to elect members of Harlow District Council in Essex, England. One third of the council was up for election and the council stayed under no overall control.

The 2002 United States elections were held on November 5, in the middle of Republican President George W. Bush's first term. Republicans won unified control of Congress, picking up seats in both chambers of Congress, making Bush the first president since Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1934 to gain seats in both houses of Congress. In the gubernatorial elections, Democrats won a net gain of one seat. The elections were held just a little under fourteen months after the September 11 attacks. Thus, the elections were heavily overshadowed by the War on Terror.

The 2012 United States elections took place on November 6, 2012. Democratic President Barack Obama won reelection to a second term and the Democrats gained seats in both chambers of Congress, retaining control of the Senate even though the Republican Party retained control of the House of Representatives. As of 2024, this is the most recent election cycle in which neither the presidency nor a chamber of Congress changed partisan control, and the last time that the party that won the presidency simultaneously gained seats in both the House of Representatives and the Senate.

The 2011 council elections in Guildford saw the Conservatives retain control over Guildford Borough Council with an increased majority of 20 seats. Full results for each ward can be found at Guildford Council election, full results, 2011.
Five referendums were held in Switzerland in 1891. The first was held on 15 March on a federal law on federal officials who had become unemployable due to disability, and was rejected by 79.4% of voters. The second was held on 5 July on a constitutional amendment, and was approved by 60.3% of voters. Two referendums were held on 18 October, one on revising article 39 of the federal constitution and one on a federal law on Swiss tariffs; both were approved. The last was held on 6 December on the question of whether the federal government should purchase the Swiss Central Railway, but was rejected by 68.9% of voters.
Four referendums were held in Switzerland during 1939. The first two were held on 22 January on a popular initiative on civil rights and a federal resolution on the restricted use of the urgency clause in the constitution. The third was held on 4 June on a constitutional amendment regarding the funding for government policies on defence and unemployment, and was approved by voters. The fourth was held on 3 December on a federal law on the employment status and insurance for federal civil servants, and was rejected by voters.
Two referendums were held in Switzerland during 1942. The first was held on 25 January on a popular initiative that would provide for the direct election of the Federal Council, as well as increasing the number of members. It was rejected by voters. The second was held on 3 May on a popular initiative "for the reorganisation of the National Council", and was also rejected.
Five referendums were held in Switzerland during 1950. The first was held on 29 January on extending a federal resolution on promoting housebuilding, and was rejected by voters. The second was held on 4 June on the federal budget, and was also rejected by voters. The third was held on 1 October on a popular initiative "for the protection of ground and labour by prohibiting speculation", and was rejected by voters. The final two were held on 3 December on revising article 72 of the constitution regarding the election of the National Council and a federal resolution on financial order between 1951 and 1954. Both were approved by voters.

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 26 October 1902. The Free Democratic Party retained its majority in the National Council.

Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 29 October 1911. The Free Democratic Party retained its majority in the National Council.

A general election was held in the U.S. state of New Jersey on November 7, 2017. Primary elections were held on June 6. All elected offices at the state level were on the ballot in this election cycle, including Governor and Lieutenant Governor for four-year terms, all 80 seats in the New Jersey General Assembly for two-year terms, and all 40 seats in the State Senate for four-year terms. In addition to the gubernatorial and State Legislative elections, numerous county offices and Freeholders in addition to municipal offices were up for election. There were two statewide ballot questions and some counties and municipalities also had a local ballot question. Non-partisan local elections, some school board elections, and some fire district elections were also held throughout the year.

The 2018 Kentucky House of Representatives elections were held on November 6, 2018, as part of the biennial United States elections. All 100 of Kentucky's state representatives were up for reelection. In Kentucky, members of the House of Representatives serve two-year terms. Accordingly, they are up for reelection in both presidential and midterm election years.

A general election was held in the U.S. state of New Jersey on November 2, 2021. Primary elections were held on June 8. All elected offices at the state level are on the ballot in this election cycle, including Governor and Lieutenant Governor for four-year terms, all 80 seats in the New Jersey General Assembly for two-year terms, and all 40 seats in the State Senate for four-year terms. In addition to the gubernatorial and State Legislative elections, numerous county offices and County Commissioners in addition to municipal offices were up for election. There were also two statewide ballot questions as well.
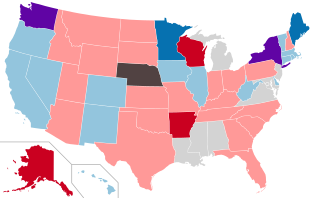
The 2012 United States state legislative elections were held on November 6, 2012, for 86 state legislative chambers in 44 states. Across the fifty states, approximately 65 percent of all upper house seats and 85 percent of all lower house seats were up for election. Nine legislative chambers in the five permanently-inhabited U.S. territories and the federal district of Washington, D.C. also held elections. The elections took place concurrently with several other federal, state, and local elections, including the presidential election, U.S. Senate elections, U.S. House elections, and gubernatorial elections.















