
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement on August 6, 1965, and Congress later amended the Act five times to expand its protections. Designed to enforce the voting rights protected by the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments to the United States Constitution, the Act sought to secure the right to vote for racial minorities throughout the country, especially in the South. According to the U.S. Department of Justice, the Act is considered to be the most effective piece of federal civil rights legislation ever enacted in the country. The National Archives and Records Administration stated: "The Voting Rights Act of 1965 was the most significant statutory change in the relationship between the federal and state governments in the area of voting since the Reconstruction period following the Civil War".
Electoral fraud, sometimes referred to as election manipulation, voter fraud, or vote rigging, involves illegal interference with the process of an election, either by increasing the vote share of a favored candidate, depressing the vote share of rival candidates, or both. It differs from but often goes hand-in-hand with voter suppression. What exactly constitutes electoral fraud varies from country to country, though the goal is often election subversion.

The League of Women Voters (LWV) is a nonpartisan American nonprofit political organization. Founded in 1920, its ongoing major activities include registering voters, providing voter information, boosting voter turnout and advocating for voting rights. In addition, the LWV works with partners for specific campaigns including support for campaign finance reform, women's rights, health care reform and gun control.

The secret ballot, also known as the Australian ballot, is a voting method in which a voter's identity in an election or a referendum is anonymous. This forestalls attempts to influence the voter by intimidation, blackmailing, and potential vote buying. This system is one means of achieving the goal of political privacy.

In political science, voter turnout is the participation rate of a given election. This is typically either the percentage of registered voters, eligible voters, or all voting-age people. According to Stanford University political scientists Adam Bonica and Michael McFaul, there is a consensus among political scientists that "democracies perform better when more people vote."

In the politics of the United States, elections are held for government officials at the federal, state, and local levels. At the federal level, the nation's head of state, the president, is elected indirectly by the people of each state, through an Electoral College. Today, these electors almost always vote with the popular vote of their state. All members of the federal legislature, the Congress, are directly elected by the people of each state. There are many elected offices at state level, each state having at least an elective governor and legislature. There are also elected offices at the local level, in counties, cities, towns, townships, boroughs, and villages; as well as for special districts and school districts which may transcend county and municipal boundaries.
In electoral systems, voter registration is the requirement that a person otherwise eligible to vote must register on an electoral roll, which is usually a prerequisite for being entitled or permitted to vote.

Voter suppression are tactics used to discourage or prevent specific groups of people from voting or registering to vote. It is distinguished from political campaigning in that campaigning attempts to change likely voting behavior by changing the opinions of potential voters through persuasion and organization, activating otherwise inactive voters, or registering new supporters. Voter suppression, instead, attempts to gain an advantage by reducing the turnout of certain voters. Suppression is an anti-democratic tactic associated with authoritarianism.

Elections in Ukraine are held to choose the president, Verkhovna Rada (legislature), and local governments. Referendums may be held on special occasions. Ukraine has a multi-party system, often no single party has a chance of gaining power alone, and parties must work with each other to form coalition governments.

Voter turnout in US elections is the total number of votes cast by the voting age population (VAP), or more recently, the voting eligible population (VEP), divided by the entire voting eligible population. It is usually displayed as a percentage, showing which percentage of eligible voters actually voted.

The election of the president and for vice president of the United States is an indirect election in which citizens of the United States who are registered to vote in one of the fifty U.S. states or in Washington, D.C., cast ballots not directly for those offices, but instead for members of the Electoral College. These electors then cast direct votes, known as electoral votes, for president and for vice president. The candidate who receives an absolute majority of electoral votes is then elected to that office. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of the votes for president, the House of Representatives elects the president; likewise if no one receives an absolute majority of the votes for vice president, then the Senate elects the vice president.

Parliamentary elections were held in Germany on 12 November 1933. They were the first since the Nazi Party seized complete power with the enactment of the Enabling Act in March. All opposition parties had been banned by the Law Against the Formation of Parties, and voters were presented with a single list containing Nazis and 22 non-party "guests" (Gäste) of the Nazi Party. These "guests", who included the likes of Alfred Hugenberg, still fully supported the regime of Adolf Hitler in any event.
A Massachusetts general election was held on November 5, 2002 in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.

In the United States, cannabis is legal in 38 of 50 states for medical use and 24 states for recreational use. At the federal level, cannabis is classified as a Schedule I drug under the Controlled Substances Act, determined to have a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use, prohibiting its use for any purpose. Despite this prohibition, federal law is generally not enforced against the possession, cultivation, or intrastate distribution of cannabis in states where such activity has been legalized. Beginning in 2024, the Drug Enforcement Administration has initiated a review to potentially move cannabis to the less-restrictive Schedule III.
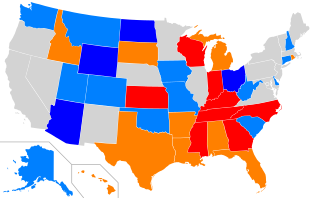
Voter ID laws in the United States are laws that require a person to provide some form of official identification before they are permitted to register to vote, receive a ballot for an election, or to actually vote in elections in the United States.
Shelby County v. Holder, 570 U.S. 529 (2013), is a landmark decision of the Supreme Court of the United States regarding the constitutionality of two provisions of the Voting Rights Act of 1965: Section 5, which requires certain states and local governments to obtain federal preclearance before implementing any changes to their voting laws or practices; and subsection (b) of Section 4, which contains the coverage formula that determines which jurisdictions are subject to preclearance based on their histories of racial discrimination in voting.
Voter suppression in the United States consists of various legal and illegal efforts to prevent eligible citizens from exercising their right to vote. Such voter suppression efforts vary by state, local government, precinct, and election. Voter suppression has historically been used for racial, economic, gender, age and disability discrimination. After the American Civil War, all African-American men were granted voting rights, but poll taxes or language tests were used to limit and suppress the ability to register or cast a ballot. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 improved voting access. Since the beginning of voter suppression efforts, proponents of these laws have cited concerns over electoral integrity as a justification for various restrictions and requirements, while opponents argue that these constitute bad faith given the lack of voter fraud evidence in the United States.

The Election Commission of India (ECI) is a constitutional body established by the Constitution of India empowered to conduct free and fair elections in India. The Election commission is headed by a Chief Election Commissioner and consists of two other Election Commissioners.
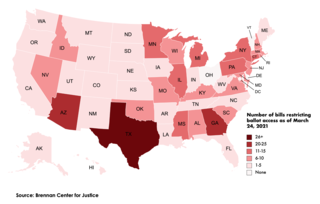
Following the 2020 United States presidential election and the unsuccessful attempts by Donald Trump and various other Republican officials to overturn it, Republican lawmakers initiated a sweeping effort to make voting laws more restrictive within several states across the country. According to the Brennan Center for Justice, as of October 4, 2021, more than 425 bills that would restrict voting access have been introduced in 49 states—with 33 of these bills enacted across 19 states so far. The bills are largely centered around limiting mail-in voting, strengthening voter ID laws, shortening early voting, eliminating automatic and same-day voter registration, curbing the use of ballot drop boxes, and allowing for increased purging of voter rolls. Republicans in at least eight states have also introduced bills that would give lawmakers greater power over election administration after they were unsuccessful in their attempts to overturn election results in swing states won by Democratic candidate Joe Biden in the 2020 election. The efforts garnered press attention and public outrage from Democrats, and by 2023 Republicans had adopted a more "under the radar" approach to achieve their goals.

The 2024 United States presidential election in Wisconsin took place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States elections in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Wisconsin voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote. The state of Wisconsin has 10 electoral votes in the Electoral College, following reapportionment due to the 2020 United States census in which the state neither gained nor lost a seat.















