
Liechtenstein, officially the Principality of Liechtenstein, is a doubly landlocked German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east and north and Switzerland in the west and south. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarchy headed by the prince of Liechtenstein of the House of Liechtenstein, currently led by Hans-Adam II. It is Europe's fourth-smallest country, with an area of just over 160 square kilometres and a population of 40,023. It is the world's smallest country to border two countries, and is one of the few countries with no debt.

Political identity came to the territory now occupied by the Principality of Liechtenstein in 814, with the formation of the subcountry of Lower Rhætia. Liechtenstein's borders have remained unchanged since 1434, when the Rhine established the border between the Holy Roman Empire and the Swiss cantons.

Vaduz is the capital of Liechtenstein and also the seat of the national parliament. The village, which is located along the Rhine, has 5,696 residents. The most prominent landmark of Vaduz is Vaduz Castle, perched atop a steep hill overlooking the village. It is home to the reigning prince of Liechtenstein and the Liechtenstein princely family. The village's distinctive architecture is also displayed in landmarks such as the Cathedral of St. Florin, Government House, Village Hall, the National Art Gallery, as well as the National Museum. Although Vaduz is the best-known village in the principality internationally, it is not the largest; neighbouring Schaan has a larger population.

Henry Somerset-Scudamore, 3rd Duke of Beaufort, born Lord Henry Somerset, was an English nobleman and peer who supported Jacobitism.

The House of Liechtenstein, from which the principality takes its name, is the family which reigns by hereditary right over the principality of Liechtenstein. Only dynastic members of the family are eligible to inherit the throne. The dynasty's membership, rights and responsibilities are defined by a law of the family, which is enforced by the reigning prince and may be altered by vote among the family's dynasts, but which may not be altered by the Government or Parliament of Liechtenstein.

Francis Thomas Baring, 6th Baron Northbrook, is a British peer and Conservative politician.

The Constitution of the Principality of Liechtenstein was promulgated on 5 October 1921, replacing the 1862 constitution.
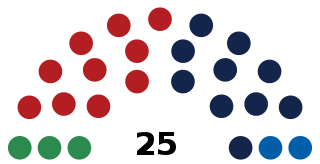
The Landtag of the Principality of Liechtenstein, commonly referred to as the Landtag of Liechtenstein, is the unicameral parliament of Liechtenstein.

The National Police of the Principality of Liechtenstein, is the national police force of Liechtenstein. It is composed of 125 employees, with 91 officers and 34 staff, who police the 160 km2 (62 sq mi) doubly landlocked alpine state in Western-Central Europe. The current chief of police is Jules Hoch, since 2013.

Liechtenstein passports are issued to nationals of Liechtenstein for the purpose of international travel. Beside serving as proof of Liechtenstein citizenship, they facilitate the process of securing assistance from Liechtenstein consular officials abroad.
The 2008 Liechtenstein tax affair is a series of tax investigations in numerous countries whose governments suspect that some of their citizens may have evaded tax obligations by using banks and trusts in Liechtenstein; the affair broke open with the biggest complex of investigations ever initiated for tax evasion in the Federal Republic of Germany. It is seen also as an attempt to put pressure on Liechtenstein, one of the remaining uncooperative tax havens, as identified by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) on money laundering of the Paris-based Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, along with Andorra and Monaco, in 2007.

Liechtenstein, a multiparty constitutional monarchy with a unicameral parliament and a government chosen by the reigning prince at its direction, is generally considered to be a prosperous and free country that is also generally considered to have an excellent human-rights record.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Liechtenstein.

Josef Ospelt was a political figure from Liechtenstein who served as the first Prime Minister of Liechtenstein from 1921 to 1922.
This article provides details of international football games played by the Liechtenstein national football team from 2020 to present.
Women's suffrage in Liechtenstein was introduced on 1 July 1984, after the 1984 Liechtenstein women's suffrage referendum. This was the last nation in Europe to introduce this right.

Josef Peer was an Austrian lawyer and politician who served as the Governor of Liechtenstein from 1920 to 1921.

The Josef Ospelt cabinet was the governing body of Liechtenstein from 23 March 1921 to 27 April 1922. It was appointed by Johann II and was chaired by Josef Ospelt.














