4769 Castalia is a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 1.4 kilometers in diameter and was the first asteroid to be modeled by radar imaging. It was discovered on 9 August 1989, by American astronomer Eleanor Helin (Caltech) on photographic plates taken at Palomar Observatory in California. It is named after Castalia, a nymph in Greek mythology. It is also a Mars- and Venus-crosser asteroid.
1998 KY26 is a nearly spherical sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group. It measures approximately 30 meters (100 feet) in diameter and is a fast rotator, having a rotational period of only 10.7 minutes. It was first observed on 2 June 1998, by the Spacewatch survey at Kitt Peak National Observatory during 6 days during which it passed 800,000 kilometers (half a million miles) away from Earth (a little more than twice the Earth–Moon distance).
(179806) 2002 TD66 (also written 2002 TD66) is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Apollo group. It was discovered on 5 October 2002, by the LINEAR project at Lincoln Laboratory's ETS in Socorro, New Mexico. It was announced on 7 October 2002 and appeared later that day on the JPL current risk page.

2007 TU24 is an Apollo near-Earth asteroid that was discovered by the Catalina Sky Survey in Arizona on 11 October 2007. Imaging radar has estimated that it is 250 meters (820 ft) in diameter. The asteroid passed 554,209 kilometer (344,370 mile or 1.4-lunar distance) from Earth on 29 January 2008 at 08:33 UTC. (At the time of the passage it was believed the closest for any known potentially hazardous asteroid (PHA) of this size before 2027, but in 2010 2005 YU55 was measured to be 400 meters in diameter.) At closest approach the asteroid had an apparent magnitude of 10.3 and was about 50 times fainter than the naked eye can see. It required about a 3-inch (76 mm) telescope to be seen.
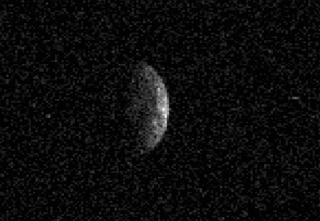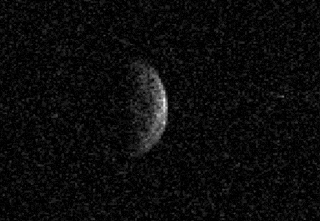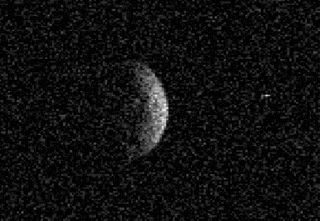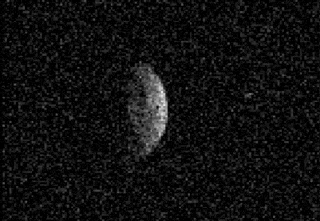
(136617) 1994 CC is a sub-kilometer trinary asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group.

2010 AL30 is a near-Earth asteroid that was discovered on 10 January 2010.
(5496) 1973 NA, is a very eccentric and heavily tilted asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 2 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 4 July 1973, by American astronomer Eleanor Helin at the U.S. Palomar Observatory in California. At the time of its discovery, it was the most highly inclined minor planet known to exist. It may be the parent body of the Quadrantids.
(153814) 2001 WN5 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group.
(7888) 1993 UC is a near-Earth minor planet in the Apollo group. It was discovered by Robert H. McNaught at the Siding Spring Observatory in Coonabarabran, New South Wales, Australia, on 20 October 1993. The asteroid has an observation arc of 23 years and has a well determined orbit. Its estimated size is 2.3 to 5.2 km.
2005 WY55 is a near-Earth Asteroid belonging to the Apollo group. It was first discovered on 26 November 2005. The asteroid will pass within 330,000 km (0.9 lunar distances) from the Earth on 28 May 2065. It has an absolute magnitude (H) of 20.68. It is estimated to be 190 to 250 meters in diameter. It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 1 July 2006.
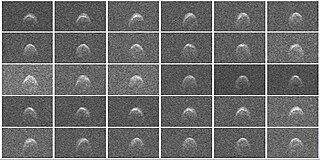
(277475) 2005 WK4, provisional designation 2005 WK4, is a stony, sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group that passed Earth within 8.2 lunar distances on 8 August 2013. It was discovered on 27 November 2005, by astronomers of the Siding Spring Survey at Siding Spring Observatory, Australia.

2014 HQ124 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group, approximately 400 meters (1,300 feet) in diameter. It passed 3.25 lunar distances (LD) from Earth on 8 June 2014. It was discovered on 23 April 2014 by NEOWISE. It is estimated that an impact event would have had the energy equivalent of 2,000 megatons of TNT and would have created a 5 km (3 mi) impact crater. The news media misleadingly nicknamed it The Beast. 2014 HQ124 previously passed this close to Earth in 1952 and will not again until at least 2307. Radar imaging suggests it may be a contact binary.

(85989) 1999 JD6 is an Aten asteroid, near-Earth object, and potentially hazardous object in the inner Solar System that makes frequent close approaches to Earth and Venus. On the Earth approach in 2015, it was observed by the Goldstone Solar System Radar and found to be a contact binary with the largest axis approximately 2 kilometers wide, and each lobe about 200–300 meters large. Although 1999 JD6 in its current orbit never passes closer than 0.047 AU to Earth, it is listed as a potentially hazardous object because it is large and might pose a threat in the future.
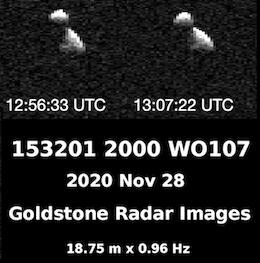
(153201) 2000 WO107 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group with a very well determined orbit. It was discovered on 29 November 2000, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. It is a contact binary.
2015 HM10 is an irregular shaped asteroid and sub-kilometer near-Earth object that passed near the Earth on 7 July 2015, at a distance of 442,000 kilometers or 1.15 lunar distances.
2012 TV is a near-Earth Apollo asteroid with an estimated diameter of 50 metres (160 ft). Its closest approach to the Earth was on October 7, 2012 with a distance of 0.0017 astronomical units. It also approached the Moon an hour earlier with a distance of 0.0028 astronomical units

2015 TB145 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 650 meters (2,000 feet) in diameter. It safely passed 1.27 lunar distances from Earth on 31 October 2015 at 17:01 UTC, and passed by Earth again in November 2018.

(163899) 2003 SD220 is a sub-kilometer asteroid and tumbling slow rotator, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Aten group, which orbit the Sun between Venus and Earth. Its orbital period of 0.75 years means that it orbits the sun about 4 times for every 3 of the Earth. It was discovered on 29 September 2003, by astronomers of the Lowell Observatory Near-Earth-Object Search at Anderson Mesa Station near Flagstaff, Arizona.

(85990) 1999 JV6, provisional designation 1999 JV6, is a sub-kilometer near-Earth asteroid and a potentially hazardous object of the Apollo group. It was discovered by astronomers of the LINEAR program at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico. 1999 JV6 is a contact binary object consisting of two distinct lobes, as seen in radar images from various observatories including Arecibo and Goldstone in January 2015.

(231937) 2001 FO32 is a near-Earth asteroid classified as a potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. With an estimated diameter around 550 m (1,800 ft), it was discovered by the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at Socorro, New Mexico on 23 March 2001. The asteroid safely passed by Earth on 21 March 2021 16:03 UTC from a closest approach distance of 0.0135 AU (2.02 million km; 1.25 million mi), or 5.25 lunar distances (LD). During the day before closest approach, 2001 FO32 reached a peak apparent magnitude of 11.7 and was visible to ground-based observers with telescope apertures of at least 20 cm (8 in). It is the largest and one of the fastest asteroids to approach Earth within 10 LD (3.8 million km; 2.4 million mi) in 2021.












