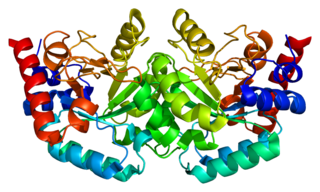
The enzyme Uridine monophosphate synthase catalyses the formation of uridine monophosphate (UMP), an energy-carrying molecule in many important biosynthetic pathways. In humans, the gene that codes for this enzyme is located on the long arm of chromosome 3 (3q13).
Methylotrophs are a diverse group of microorganisms that can use reduced one-carbon compounds, such as methanol or methane, as the carbon source for their growth; and multi-carbon compounds that contain no carbon-carbon bonds, such as dimethyl ether and dimethylamine. This group of microorganisms also includes those capable of assimilating reduced one-carbon compounds by way of carbon dioxide using the ribulose bisphosphate pathway. These organisms should not be confused with methanogens which on the contrary produce methane as a by-product from various one-carbon compounds such as carbon dioxide. Some methylotrophs can degrade the greenhouse gas methane, and in this case they are called methanotrophs. The abundance, purity, and low price of methanol compared to commonly used sugars make methylotrophs competent organisms for production of amino acids, vitamins, recombinant proteins, single-cell proteins, co-enzymes and cytochromes.

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.
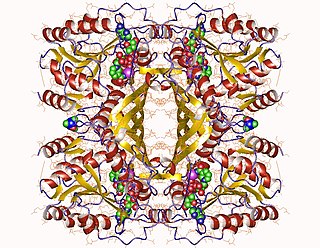
In enzymology, an inositol-3-phosphate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase catalyzes the synthesis of 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC), a precursor for ethylene, from S-Adenosyl methionine, an intermediate in the Yang cycle and activated methyl cycle and a useful molecule for methyl transfer:
4-amino-4-deoxychorismate lyase is an enzyme that participates in folate biosynthesis by catalyzing the production of PABA by the following reaction
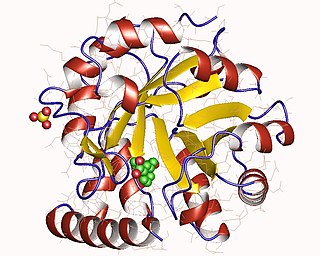
The enzyme indole-3-glycerol-phosphate synthase (IGPS) (EC 4.1.1.48) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.111) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme 3-dehydroquinate synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme methylthioribulose 1-phosphate dehydratase (EC .2.1.109) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a formaldehyde transketolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
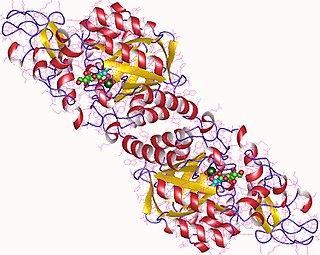
In enzymology, a N-acetylneuraminate synthase (EC 2.5.1.56) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
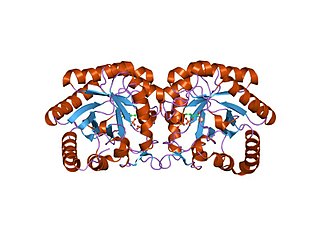
3-Deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthase is the first enzyme in a series of metabolic reactions known as the shikimate pathway, which is responsible for the biosynthesis of the amino acids phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan. Since it is the first enzyme in the shikimate pathway, it controls the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Enzyme inhibition is the primary method of regulating the amount of carbon entering the pathway. Forms of this enzyme differ between organisms, but can be considered DAHP synthase based upon the reaction that is catalyzed by this enzyme.

3-Deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate (DAHP) is a 7-carbon ulonic acid. This compound is found in the shikimic acid biosynthesis pathway and is an intermediate in the production of aromatic amino acids.
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4,6-dehydratase (configuration-inverting) (EC 4.2.1.115, FlaA1, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 5-inverting 4,6-dehydratase, PseB, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine hydro-lyase (inverting, UDP-2-acetamido-2,6-dideoxy-β-L)arabino-hex-4-ulose-forming)) is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-α-D-glucosamine hydro-lyase (inverting; UDP-2-acetamido-2,6-dideoxy-β-L-arabino-hex-4-ulose-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phyllocladan-16α-ol synthase (EC 4.2.3.45, PaDC1) is an enzyme with systematic name (+)-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (phyllocladan-16α-ol-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
2-deoxy-scyllo-Inosose synthase is an enzyme with systematic name D-glucose-6-phosphate phosphate-lyase (2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate synthase (glutamine hydrolysing) (EC 4.3.3.6, PdxST) is an enzyme with systematic name D-ribose 5-phosphate,D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
6-phospho-3-hexuloisomerase is an enzyme with systematic name D-arabino-hex-3-ulose-6-phosphate isomerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Streptomyces mobaraensis is a spore forming bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces mobaraensis produces bleomycin, detoxin, piericidin A, piericidin B, reticulol and transglutaminase. Streptomyces mobaraensis is used in the food industry to produce transglutaminase to texture meat and fish products.










