Brunhild is a stony S-type main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on July 31, 1872, and named after Brünnehilde, a Valkyrie in Norse mythology. Brunhild has been mistaken for the non-existent variable star KN Gem.
Velleda is a main-belt asteroid. It is probably a rather typical, albeit sizable, S-type asteroid. Named for Veleda, a priestess and prophet of the Germanic tribe of the Bructeri. It was discovered by Paul Henry on November 5, 1872, in Paris, France. It was his first credited discovery. He and his brother Prosper Henry discovered a total of 14 asteroids.
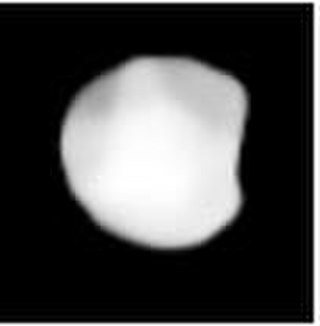
Ino is a large asteroid and the parent body of the Ino family, located in the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 150 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 1 August 1877, by French astronomer Alphonse Borrelly at Marseille Observatory in southern France, and named after the queen Ino from Greek mythology. The dark Xk-type asteroid has a rotation period of 6.15 hours.

Irma is a fairly large and dark main belt asteroid. It was discovered by the French brothers Paul Henry and Prosper Henry on November 5, 1877. Paul was credited for this discovery. The meaning of the name Irma is unknown.

Ampella is a Main belt asteroid that was discovered by Alphonse Borrelly on June 13, 1879. The name seems to be the feminine form of Ampelos, a satyr and good friend of Dionysus in Greek mythology. It could also derive from the Ampelose, a variety of hamadryad. It is an S-type asteroid.

Philosophia is a large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by the French astronomer Paul-Pierre Henry on August 12, 1882, in Paris and named after the topic of philosophy. Based upon photometric observations, it has a synodic rotation period of 52.98 ± 0.01 with a brightness variation of 0.15 ± 0.02 in magnitude.

Elvira is a typical main belt asteroid and is a member of the Koronis asteroid family. It was discovered by Auguste Charlois on 3 May 1888 in Nice. (277) Elvira is possibly named for a character in Alphonse de Lamartine's Méditations poétiques (1820) and Harmonies poétiques et religieuses (1830).

Constantia is a stony background asteroid from the inner region of the asteroid belt, approximately 6.5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa at the Vienna Observatory on 4 September 1891. The asteroid is a member of the Flora family. It is spinning with a rotation period of 5.345±0.003 h and shows a brightness variation of 0.57±0.2 in magnitude.

Campania is a large main belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 20 September 1893 in Nice.
Patientia is approximately the 15th-largest asteroid in the asteroid belt with a diameter of 225 km. It was discovered by French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 4 December 1899, and assigned a provisional designation 1899 EY.
649 Josefa is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid, orbiting primarily in the asteroid belt. Photometric observations provide a rotation period of 10.481±0.001 h with a brightness variation of 0.33±0.04 in magnitude.
678 Fredegundis is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered 22 January 1909 from Heidelberg by German astronomer K. Wilhelm Lorenz, and was named after the French opera Frédégonde. This object is orbiting at a distance of 2.57 AU with a period of 4.13 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.22. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 6.1° to the plane of the ecliptic

720 Bohlinia is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered by Franz Kaiser, a German astronomer in 1911. It is named for Swedish astronomer Karl Petrus Theodor Bohlin, to mark his 65th birthday. He had worked on the orbits of asteroids.
737 Arequipa is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered by American astronomer Joel Hastings Metcalf on 7 December 1912 from Winchester, Massachusetts. This stony S-type asteroid was named after the Peruvian city of Arequipa, where Harvard's Boyden Observatory was located prior to 1927. It is orbiting at a distance of 2.59 AU from the Sun, with an orbital eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.245 and a period of 4.17 yr. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 12.4° to the ecliptic.
833 Monica is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. Measurements of the lightcurve made in 2010 give a rotation period of 12.09 ± 0.01 hours. It has a diameter of 21.2 km.
880 Herba is a minor planet orbiting the Sun that was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf on 22 July 1917 in Heidelberg.
937 Bethgea is a background asteroid from the inner region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 12 September 1920 by German astronomer Karl Wilhelm Reinmuth, from Heidelberg.
947 Monterosa is a minor planet orbiting the Sun.

5027 Androgeos is a large Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 59 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 21 January 1988, by American astronomer Carolyn Shoemaker at the Palomar Observatory in California. The dark D-type asteroid is one of the 70 largest Jupiter trojans and has a rotation period of 11.4 hours. It was named from Greek mythology after the warrior Androgeos, who was killed by Aeneas.

16974 Iphthime (; prov. designation: 1998 WR21) is a Jupiter trojan and a binary system from the Greek camp, approximately 57 kilometers (35 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 18 November 1998, by astronomers with the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the ETS Test Site in Socorro, New Mexico. The dark Jovian asteroid belongs to the 80 largest Jupiter trojans and has a notably slow rotation of 78.9 hours. It was named after Iphthime from Greek mythology. The discovery of its companion by Hubble Space Telescope was announced in March 2016.










