Related Research Articles
456 Abnoba, provisional designation 1900 FH, is a stony background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 40 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 4 June 1900, by astronomers Max Wolf and Arnold Schwassmann at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid was named after the Celtic deity Abnoba.
478 Tergeste is a rare-type stony asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 78 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 21 September 1901, by Italian astronomer Luigi Carnera at Heidelberg Observatory in southern Germany. It was named after the Italian city of Trieste.

771 Libera, provisional designation 1913 TO, is a metallic asteroid from the middle region of the asteroid belt, about 29 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Joseph Rheden at the Vienna Observatory in Austria, on 21 November 1913.

1069 Planckia, provisional designation 1927 BC, is a background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 39 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 28 January 1927, by astronomer Max Wolf at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in Germany. The asteroid was named after German physicist Max Planck.
1027 Aesculapia, provisional designation A923 YO11, is a Themistian asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 33 kilometers in diameter.
1043 Beate, provisional designation 1925 HB, is a stony asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 32 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory on 22 April 1925. Any reference of its name to a person is unknown.
1113 Katja, provisional designation 1928 QC, is a background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 39 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Pelageya Shajn at the Simeiz Observatory in 1928, and named after Ekaterina Iosko, a staff member at the discovering observatory.
1124 Stroobantia, provisional designation 1928 TB, is a metallic asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 25 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 6 October 1928, by Belgian astronomer Eugène Delporte at Uccle Observatory in Belgium. It is named for astronomer Paul Stroobant.
1213 Algeria is a carbonaceous asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 32 kilometers in diameter. Discovered by Guy Reiss at Algiers Observatory in 1931, it was named after the North African country of Algeria.
1712 Angola, provisional designation 1935 KC, is a dark asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 66 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 28 May 1935, by English-born South African astronomer Cyril Jackson at Johannesburg Observatory in South Africa. It is named after the Republic of Angola.
1304 Arosa, provisional designation 1928 KC, is a metallic asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 40 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 21 May 1928, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. It was named after the Swiss mountain village of Arosa.

1277 Dolores is a carbonaceous background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 27 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 18 April 1933, by Soviet astronomer Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The asteroid was named after Spanish communist Dolores Ibárruri.
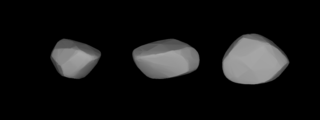
1241 Dysona, provisional designation 1932 EB1, is a dark background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 77 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 4 March 1932, by English astronomer Harry Edwin Wood at the Union Observatory in Johannesburg, South Africa. The asteroid was named after English astronomer Frank Watson Dyson.
3642 Frieden, provisional designation 1953 XL1, is a carbonaceous asteroid from the middle region of the asteroid belt, approximately 35 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by German astronomer Herta Gessner at Sonneberg Observatory on 4 December 1953. It is named after the goddess of peace, Pax.
2140 Kemerovo, provisional designation 1970 PE, is a dark asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 30 kilometers in diameter.
1605 Milankovitch, provisional designation 1936 GA, is an Eoan asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 31 kilometers in diameter. It was named after Serbian scientist Milutin Milanković.
1426 Riviera, provisional designation 1937 GF, is a bright asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 16 kilometers in diameter. Discovered by Marguerite Laugier at the Nice Observatory in 1937, the asteroid was later named for the Côte d'Azur, also known as French Riviera.
1737 Severny, provisional designation 1966 TJ, is a stony Eoan asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 21 kilometers in diameter.
2443 Tomeileen, provisional designation A906 BJ, is a stony Eoan asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 32 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 24 January 1906, by German astronomer Max Wolf at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in Heidelberg, Germany. The S-type asteroid was named after the parents of British astronomer Brian G. Marsden. It has a rotation period of 3.97 hours.
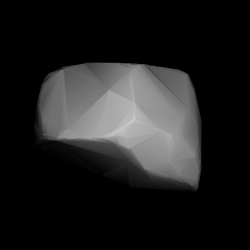
1236 Thaïs is a dark background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. The rare T-type asteroid has a notably long rotation period of 72 hours and measures approximately 18 kilometers. It was discovered on 6 November 1931, by Soviet astronomer Grigory Neujmin at Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula, and named after the ancient Greek prostitute Thaïs.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 666 Desdemona (1908 DM)" (2016-06-16 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- ↑ "Desdemona". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary .
- 1 2 3 Schmadel, Lutz D. (2007). "(666) Desdemona". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names – (666) Desdemona. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. pp. 65–66. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29925-7_667. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3.
- 1 2 3 4 Tedesco, E. F.; Noah, P. V.; Noah, M.; Price, S. D. (October 2004). "IRAS Minor Planet Survey V6.0". NASA Planetary Data System. 12: IRAS-A-FPA-3-RDR-IMPS-V6.0. Bibcode:2004PDSS...12.....T . Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "LCDB Data for (666) Desdemona". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Usui, Fumihiko; Kuroda, Daisuke; Müller, Thomas G.; Hasegawa, Sunao; Ishiguro, Masateru; Ootsubo, Takafumi; et al. (October 2011). "Asteroid Catalog Using Akari: AKARI/IRC Mid-Infrared Asteroid Survey". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 63 (5): 1117–1138. Bibcode:2011PASJ...63.1117U. doi:10.1093/pasj/63.5.1117. (online, AcuA catalog p. 153)
- 1 2 3 4 Mainzer, A.; Grav, T.; Masiero, J.; Hand, E.; Bauer, J.; Tholen, D.; et al. (November 2011). "NEOWISE Studies of Spectrophotometrically Classified Asteroids: Preliminary Results". The Astrophysical Journal. 741 (2): 25. arXiv: 1109.6407 . Bibcode:2011ApJ...741...90M. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/741/2/90. S2CID 118700974.
- 1 2 3 4 Masiero, Joseph R.; Mainzer, A. K.; Grav, T.; Bauer, J. M.; Cutri, R. M.; Nugent, C.; et al. (November 2012). "Preliminary Analysis of WISE/NEOWISE 3-Band Cryogenic and Post-cryogenic Observations of Main Belt Asteroids". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 759 (1): 5. arXiv: 1209.5794 . Bibcode:2012ApJ...759L...8M. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/759/1/L8. S2CID 46350317 . Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- 1 2 Behrend, Raoul. "Asteroids and comets rotation curves – (666) Desdemona". Geneva Observatory . Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- 1 2 Marciniak, A.; Pilcher, F.; Oszkiewicz, D.; Santana-Ros, T.; Urakawa, S.; Fauvaud, S.; et al. (December 2015). "Against the biases in spins and shapes of asteroids". Planetary and Space Science. 118: 256–266. arXiv: 1711.02429 . Bibcode:2015P&SS..118..256M. doi:10.1016/j.pss.2015.06.002. S2CID 118212841 . Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- 1 2 Stephens, R. D. (June 2001). "Rotational Periods and Lightcurves of 1277 Dolores, 666 Desdemona and (7505) 1997 AM2". The Minor Planet Bulletin. 28: 28–29. Bibcode:2001MPBu...28...28S . Retrieved 4 July 2016.
- 1 2 "666 Desdemona (1908 DM)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 4 July 2016.