| 7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin synthase (CofG) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 4.3.1.32 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil--L-tyrosine 4-hydroxyphenyl transferase (CofH) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 2.5.1.147 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin synthase (EC 4.3.1.32, FO synthase) and 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil--L-tyrosine 4-hydroxyphenyl transferase (EC 2.5.1.147) are two enzymes always complexed together to achieve synthesis of FO, a precursor to Coenzyme F420. Their systematic names are 5-amino-5-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-6-(D-ribitylimino)-5,6-dihydrouracil ammonia-lyase (7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin-forming) and 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil:L-tyrosine, 4-hydroxyphenyl transferase respectively. [1] [2] The enzymes catalyse the following chemical reactions:
The Enzyme Commission number is a numerical classification scheme for enzymes, based on the chemical reactions they catalyze. As a system of enzyme nomenclature, every EC number is associated with a recommended name for the respective enzyme.
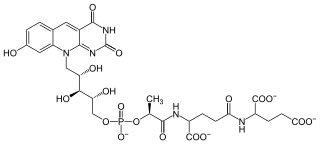
Coenzyme F420 or 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin is a coenzyme involved in redox reactions in methanogens, in many Actinobacteria, and sporadically in other bacterial lineages. It is a flavin derivative. The coenzyme is a substrate for coenzyme F420 hydrogenase, 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase and methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase.
Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst, which is not consumed in the catalyzed reaction and can continue to act repeatedly. Because of this, only very small amounts of catalyst are required to alter the reaction rate in principle.
- (2.5.1.147) 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil + L-tyrosine + S-adenosyl-L-methionine = 5-amino-5-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-6-(D-ribitylimino)-5,6-dihydrouracil + 2-iminoacetate + L-methionine + 5'-deoxyadenosin
- (4.3.1.32) 5-amino-5-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-6-(D-ribitylimino)-5,6-dihydrouracil + S-adenosyl-L-methionine = 7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin + NH3 + L-methionine + 5'-deoxyadenosine
Enzyme 2.5.1.147 binds a 4Fe-4S cluster. The condensation reaction is initiated by the 5'-deoxyadenosyl radical. The complex was formerly named as a single entity under EC 2.5.1.77.
| CofG | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | CofG |
| InterPro | IPR019939 |
| CofH | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | CofH |
| InterPro | IPR019940 |
All members of these enzymes belong to a single clade of the CofH (2.5.1.147) and CofG (4.3.1.32) families, sharing a TIM barrel structure. The two EC numbers represent discrete steps in this reaction. Some enzyme complexes have CofG and CofH (subunits 1 and 2) in different chains assembled into a heterodimer, while others like the bifunctional fbiC has the two domains on one single chain.

In biochemistry and molecular biology, the TIM barrel is a conserved protein fold consisting of eight α-helices and eight parallel β-strands that alternate along the peptide backbone. The structure is named after triosephosphate isomerase, a conserved metabolic enzyme. TIM barrels are one of the most common protein folds. One of the most intriguing features among members of this class of proteins is although they all exhibit the same tertiary fold there is very little sequence similarity between them. At least 15 distinct enzyme families use this framework to generate the appropriate active site geometry, always at the C-terminal end of the eight parallel beta-strands of the barrel.