
Acacia aneura, commonly known as mulga or true mulga, is a shrub or small tree native to arid outback areas of Australia. It is the dominant tree in the habitat to which it gives its name (mulga) that occurs across much of inland Australia. Specific regions have been designated the Western Australian mulga shrublands in Western Australia and Mulga Lands in Queensland.
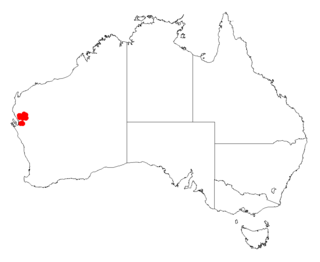
Acacia anastema, commonly known as sandridge gidgee or just gidgee, is a tree in the family Fabaceae. Endemic to Western Australia, it occurs within a fairly small area of semi-arid land east of Carnarvon.

Acacia kempeana, commonly known as wanderrie wattle, witchetty bush or granite wattle, is a shrub in subfamily Mimosoideae of family Fabaceae that is endemic to arid parts of central and western Australia.

Acacia tetragonophylla, commonly known as curara, kurara or dead finish, is a tree in the family Fabaceae that is endemic to arid and semi-arid parts of central and western Australia.

Acacia pruinocarpa, commonly known as black gidgee, gidgee or tawu, is a tree in the family Fabaceae that is endemic to arid parts of Australia.

Acacia papyrocarpa, commonly known as western myall, is a tree in the family Fabaceae native to arid areas of central and western Australia.

Acacia murrayana is a tree in the family Fabaceae. It has numerous common names, including sandplain wattle, Murray's wattle, fire wattle, colony wattle and powder bark wattle that is endemic to arid areas in every mainland State except Victoria.

Acacia harpophylla, commonly known as brigalow, brigalow spearwood or orkor, is an endemic tree of Australia. The Aboriginal Australian group the Gamilaraay peoples know the tree as Barranbaa or Burrii. It is found in central and coastal Queensland to northern New South Wales. It can reach up to 25 m (82 ft) tall and forms extensive open-forest communities on clay soils.

Acacia colei is a perennial bush or tree native to northern Australia. A common name for it is Cole's wattle. Acacia colei blooms from May through September and the flowers are bright yellow.

Acacia gunnii, commonly known as ploughshare wattle or dog's tooth wattle, is a woody shrub which is endemic to south-eastern Australia found in dry heaths and woodlands. It ranges from Queensland, then New South Wales, Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, South Australia, down to Tasmania. Acacia gunnii grows to up to 1 metre high and has prickly phyllodes which are 4 to 15 mm long. The cream to pale yellow globular flowerheads appear singly in the axils of the phyllodes in June to October, followed by curved or coiled seed pods which are 40 mm long and 4 to 5 mm wide. Acacia gunnii grows up to 1 meter tall and has prickly phyllodes which are 4 to 15mm in length with cream to pale-yellow globular flower heads appearing in phyllode axils in June through to October, followed by curved or coiled seed pods which are 40mm long and 4 to 5 mm wide. The species was first formally described by English botanist George Bentham in the London Journal of Botany in 1842. It occurs in South Australia, Victoria, Tasmania, New South Wales, Australian Capital Territory, and Queensland.

Acacia lineataA.Cunn. ex G.Don, commonly known as streaked wattle or narrow lined-leaved wattle, occurs naturally inland eastern Australia. The genus Acacia is the largest genus of flowering plants in Australia, containing around 1000 species throughout a diverse range of environments from coast to desert.

Acacia argyrodendron, known colloquially as black gidyea or blackwood, is a species of Acacia native to Australia. Czech botanist Karel Domin described this species in 1926 and it still bears its original name. Domin reported collecting the type specimen from somewhere between Camooweal and Burketown in northwestern Queensland, though it is more likely to have been northeast of Aramac.

Acacia ramulosa, commonly known as horse mulga or bowgada wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae endemic to arid areas of Australia.

Acacia stipuligera is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to arid and tropical parts of northern Australia.

Acacia tenuissima, commonly known as narrow-leaved wattle, broom wattle, minyana, slender mulga or slender wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae endemic to temperate and tropical areas of Australia. Indigenous Australians the Kurrama peoples know the plant as Janangungu and the Banyjima know it as Murruthurru.

Acacia calcicola is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is native to parts of central Australia. Common names for this species include; shrubby wattle, shrubby mulga, myall-gidgee, northern myall and grey myall. Indigenous Australians the Pitjantjatjara peoples know the tree as ikatuka, the Warlpiri know it as jirlarti and the Arrernte know it as irrakwetye.

Acacia oswaldii, commonly known as boree, umbrella wattle, umbrella bush, whyacka, middia, miljee, nella and curly yarran, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves.

Acacia crombiei, commonly known as pink gidgee, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to central Queensland.

Acacia glandulicarpa, commonly known as the hairy-pod wattle, is a perennial shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodinea that is native to parts of south eastern Australia.

Acacia microsperma, commonly known as bowyakka, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of eastern Australia]. It is rated as least concern according to the Nature Conservation Act 1992.





















