
Acacia baileyana or Cootamundra wattle is a shrub or tree in the flowering plant family Fabaceae. The scientific name of the species honours the botanist Frederick Manson Bailey. It is indigenous to a very small area in southern inland New South Wales, comprising Temora, Cootamundra, Stockinbingal and Bethungra districts. However, it has been widely planted in other Australian states and territories. In many areas of Victoria, it has become naturalised and is regarded as a weed, outcompeting indigenous Victorian species.

Acacia cultriformis, known as the knife-leaf wattle, dogtooth wattle, half-moon wattle or golden-glow wattle, is a perennial tree or shrub of the genus Acacia native to Australia. It is widely cultivated, and has been found to have naturalised in Asia, Africa, North America, New Zealand and South America. A. cultriformis grows to a height of about 4 m (13 ft) and has triangle-shaped phyllodes. The yellow flowers appear from August to November in its natural range. Its attractive foliage and bright flowers make it a popular garden plant.

Acacia pycnantha, most commonly known as the golden wattle, is a tree of the family Fabaceae. It grows to a height of 8 metres and has phyllodes instead of true leaves. The profuse fragrant, golden flowers appear in late winter and spring, followed by long seed pods. Explorer Thomas Mitchell collected the type specimen, from which George Bentham wrote the species description in 1842. The species is native to southeastern Australia as an understorey plant in eucalyptus forest. Plants are cross-pollinated by several species of honeyeater and thornbill, which visit nectaries on the phyllodes and brush against flowers, transferring pollen between them.

Banksia aemula, commonly known as the wallum banksia, is a shrub of the family Proteaceae. Found from Bundaberg south to Sydney on the Australian east coast, it is encountered as a shrub or a tree to 8 m (26 ft) in coastal heath on deep sandy soil, known as Wallum. It has wrinkled orange bark and shiny green serrated leaves, with green-yellow flower spikes, known as inflorescences, appearing in autumn. The flower spikes turn grey as they age and large grey follicles appear. Banksia aemula resprouts from its woody base, known as a lignotuber, after bushfires.

Acacia longifolia is a species of Acacia native to southeastern Australia, from the extreme southeast of Queensland, eastern New South Wales, eastern and southern Victoria, southeastern South Australia, and Tasmania. Common names for it include long-leaved wattle, acacia trinervis, aroma doble, golden wattle, coast wattle, sallow wattle and Sydney golden wattle. It is not listed as being a threatened species, and is considered invasive in Portugal, New Zealand and South Africa. In the southern region of Western Australia, it has become naturalised and has been classed as a weed due to its out-competing indigenous species. It is a tree that grows very quickly, reaching 7–10 m in five to six years.

Acacia verticillata is a perennial shrub to small tree native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia myrtifolia, known colloquially as myrtle wattle, red stem wattle or red-stemmed wattle, is a species of Acacia native to coastal areas of southern and eastern Australia.

Acacia triptera, commonly known as spurwing wattle, is an erect or spreading shrub which is endemic to Australia.

Acacia brownii, commonly known as heath wattle, is an erect or spreading shrub which is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia oxycedrus, commonly known as spike wattle, is an erect or spreading shrub which is endemic to Australia.

Acacia gunnii, commonly known as ploughshare wattle or dog's tooth wattle, is a woody shrub which is endemic to south-eastern Australia found in dry heaths and woodlands. It ranges from Queensland, then New South Wales, Australian Capital Territory, Victoria, South Australia, down to Tasmania. Acacia gunnii grows to up to 1 metre high and has prickly phyllodes which are 4 to 15 mm long. The cream to pale yellow globular flowerheads appear singly in the axils of the phyllodes in June to October, followed by curved or coiled seed pods which are 40 mm long and 4 to 5 mm wide. Acacia gunnii grows up to 1 meter tall and has prickly phyllodes which are 4 to 15mm in length with cream to pale-yellow globular flower heads appearing in phyllode axils in June through to October, followed by curved or coiled seed pods which are 40mm long and 4 to 5 mm wide. The species was first formally described by English botanist George Bentham in the London Journal of Botany in 1842. It occurs in South Australia, Victoria, Tasmania, New South Wales, Australian Capital Territory, and Queensland.

Acacia rigens, commonly known as nealie, is an erect or spreading shrub or small tree that is endemic to Australia. Other common names include needle wattle, needlebush acacia, nealia and nilyah.

Acacia beckleri commonly known as Barrier Range wattle, is a flowering plant in the family Acacia. It is an upright or spreading shrub with green or bluish-green leaves and yellow ball flowers.

Acacia burkittii is a species of wattle endemic to Western Australia, South Australia and western New South Wales, where it is found in arid zones, and is a perennial shrub in the family Fabaceae. Common names for it include Burkitt's wattle, fine leaf jam, gunderbluey, pin bush and sandhill wattle. It has also been introduced into India. Previously this species was referred to as Acacia acuminata subsp. burkittii, but is now considered to be a separate species. It grows in mallee, eucalypt and mulga woodland or shrubland, often on sandhills.

Acacia havilandiorum, also known as Haviland's wattle or needle wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to areas in South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria.

Acacia trineura, known colloquially as three-nerve wattle or three nerved wattle or green wattle, is a species of Acacia native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia rubida, commonly known as red stem wattle, red stemmed wattle or red leaved wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of eastern Australia.

Acacia ulicifolia, commonly known as prickly Moses or juniper wattle is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae, native to Australia.

Acacia kybeanensis, commonly known as kybean wattle or kybeyan wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south eastern Australia.
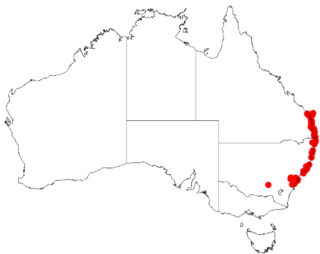
Acacia baueri, commonly known as tiny wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Lycopodiifoliae that is native to an area along the coast in eastern Australia.

























