
Spermidine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the propylamine group from S-adenosylmethioninamine to putrescine in the biosynthesis of spermidine. The systematic name is S-adenosyl 3-(methylthio)propylamine:putrescine 3-aminopropyltransferase and it belongs to the group of aminopropyl transferases. It does not need any cofactors. Most spermidine synthases exist in solution as dimers.
In enzymology, a 3'-demethylstaurosporine O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 7-methylxanthosine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a corydaline synthase (EC 2.1.1.147) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cyclopropane-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a methylene-fatty-acyl-phospholipid synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
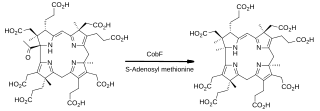
In enzymology, precorrin-6A synthase (deacetylating) (EC 2.1.1.152) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a putrescine N-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a theobromine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

[Methionine synthase] reductase, or Methionine synthase reductase, encoded by the gene MTRR, is an enzyme that is responsible for the reduction of methionine synthase inside human body. This enzyme is crucial for maintaining the one carbon metabolism, specifically the folate cycle. The enzyme employs one coenzyme, flavoprotein.
In enzymology, lovastatin nonaketide synthase (EC 2.3.1.161) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a discadenine synthase (EC 2.5.1.24) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an isonocardicin synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nicotianamine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The fluorinase enzyme catalyzes the reaction between fluoride ion and the co-factor S-adenosyl-L-methionine to generate L-methionine and 5'-fluoro-5'-deoxyadenosine, the first committed product of the fluorometabolite biosynthesis pathway. The fluorinase was originally isolated from the soil bacterium Streptomyces cattleya, but homologues have since been identified in a number of other bacterial species, including Streptomyces sp. MA37, Nocardia brasiliensis and Actinoplanes sp. N902-109. This is the only known enzyme capable of catalysing the formation of a carbon-fluorine bond, the strongest single bond in organic chemistry.
Methyl halide transferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosylmethionine:iodide methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Tricin synthase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:tricetin 3',5'-O-dimethyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Naringenin 7-O-methyltransferase is a methyltransferase isolated from rice, which catalyzes the biosynthesis of sakuranetin.
Trans-resveratrol di-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:trans-resveratrol 3,5-O-dimethyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin synthase (EC 4.3.1.32, FO synthase) and 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil—L-tyrosine 4-hydroxyphenyl transferase (EC 2.5.1.147) are two enzymes always complexed together to achieve synthesis of FO, a precursor to Coenzyme F420. Their systematic names are 5-amino-5-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-6-(D-ribitylimino)-5,6-dihydrouracil ammonia-lyase (7,8-didemethyl-8-hydroxy-5-deazariboflavin-forming) and 5-amino-6-(D-ribitylamino)uracil:L-tyrosine, 4-hydroxyphenyl transferase respectively. The enzymes catalyse the following chemical reactions:




