
A train is a form of rail transport consisting of a series of connected vehicles that generally run along a railroad track to transport passengers or cargo. The word "train" comes from the Old French trahiner, derived from the Latin trahere meaning "to pull" or "to draw".

A people mover or automated people mover (APM) is a type of small scale automated guideway transit system for personal rapid transit. The term is generally used only to describe systems serving relatively small areas such as airports, downtown districts or theme parks.

Transrapid is a German-developed high-speed monorail train using magnetic levitation. Planning for the Transrapid system started in 1969 with a test facility for the system in Emsland, Germany completed in 1987. In 1991 technical readiness for application was approved by the Deutsche Bundesbahn in cooperation with renowned universities.

Birmingham International is a railway station located in Solihull in the West Midlands, to the east of the city of Birmingham, England.

Birmingham Airport, formerly Birmingham International Airport, is an international airport located 7 nautical miles east-southeast of Birmingham city centre, 9.5 nautical miles west-northwest of Coventry slightly north of Bickenhill village in the Metropolitan Borough of Solihull, England.

Doppelmayr/Garaventa Group is an international manufacturer of ropeways and people movers for ski areas, urban transport, amusement parks, and material handling systems. As of 2019, the group have produced over 15,000 installations in 96 countries. The Doppelmayr/Garaventa Group was formed in 2002 when Doppelmayr of Wolfurt, Austria merged with Garaventa AG of Switzerland to form the world's largest ropeway manufacturer.

The automated guideway transit (AGT) is a fully automated, driverless transit system in which vehicles are automatically guided along a guideway. The vehicles are often rubber tired or steel wheeled, but other systems including air cushion and maglev systems have also been used in experiments. The guideway normally provides both physical support, like a road, as well as the guidance. In the case of fixed-route systems, the two are often the same in the same way that a rail line provides both support and guidance for a train. For systems with multiple routes, most AGT systems use smaller wheels riding on the guideway to steer the vehicle using conventional steering arrangements like those on a car.

Maglev is a system of train transportation that uses two sets of magnets: one set to repel and push the train up off the track, and another set to move the elevated train ahead, taking advantage of the lack of friction. Along certain "medium-range" routes, maglev can compete favourably with high-speed rail and airplanes.

An elevated railway is a rapid transit railway with the tracks above street level on a viaduct or other elevated structure. The railway may be broad-gauge, standard-gauge or narrow-gauge railway, light rail, monorail, or a suspension railway. Elevated railways are normally found in urban areas where there would otherwise be multiple level crossings. Usually, the tracks of elevated railways that run on steel viaducts can be seen from street level.

The Shanghai maglev train or Shanghai Transrapid is a magnetic levitation train (maglev) line that operates in Shanghai, China. It is the oldest commercial maglev still in operation, and the first commercial high-speed maglev with cruising speed of 431 km/h (268 mph). It is also the fastest commercial electric train in the world. The line is the third commercially operated maglev line in history.

The Link Train is an automated people mover (APM) at Toronto Pearson International Airport in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada. The wheelchair-accessible train runs 24 hours a day, seven days a week and is completely free-of-charge to ride. In 2012, it transported 17,000 passengers daily, 60 to 70% of whom were airport staff.

The Mandalay Bay Tram is a 2,749-foot-long (838 m) people mover that opened on April 9, 1999 on the Las Vegas Strip in Paradise, Nevada. It was constructed to connect three gaming hotels belonging to the MGM Mirage Group. The line carries passengers from the major Tropicana – Las Vegas Boulevard intersection, via the Excalibur Hotel and Casino and Luxor Hotel to the Mandalay Bay Resort and Casino at the southern end.

The Cable Liner is a range of automated people mover products designed by Doppelmayr Cable Car for use at airports, in city centers, intermodal passenger transport connections, park and ride facilities, campuses, resorts and amusement parks.

The Aerotrén is a people mover monorail operating at Mexico City International Airport, near Mexico City, in Mexico. The 3-kilometre (1.9 mi) automated people mover (APM) provides a link between Terminal 1 and Terminal 2.

The People Mover in Venice is an automated elevated shuttle train, which connects the Piazzale Roma—the major transportation hub of the city—and the Tronchetto island with a car parking facility. The train also makes a stop at the Marittima station where the passenger terminal of the Port of Venice is located.

The Coliseum–Oakland International Airport line, also known informally as the BART to OAK line, is an automated guideway transit (AGT) system operated by Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) between BART's Coliseum station and Oakland International Airport station. The system opened for revenue service on November 22, 2014 and is integrated into BART’s fare system. During planning and construction, it was known as the Oakland Airport Connector(OAC) project. The route is colored beige on BART maps and BART has also referred to this route as the Beige Line.

Innovia APM is a rubber-tired automated people mover system (APM) manufactured by Bombardier Transportation. The APM technology was originally developed by Westinghouse, then owned by Adtranz, and most recently acquired by Bombardier in 2001. Since its market debut in 1971, there have been three generations – Innovia APM 100, Innovia APM 200 and the latest Innovia APM 300.
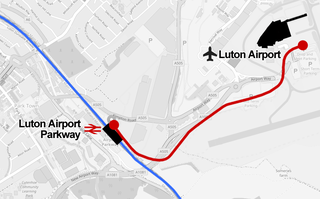
The Luton DART is an under-construction automated guided people mover which will connect Luton Airport Parkway station and Luton Airport in England. DART is an acronym for Direct Air-Rail Transit. It is scheduled to open in 2021 and will replace the existing Shuttle Bus, relieving its roads in peak times and providing a higher capacity.

The Gatwick Airport Shuttle Transit is a 0.75 miles (1.21 km) long elevated automated people mover that links the North and South Terminals at London's Gatwick Airport. The line is ground-side, and besides linking the two terminals also serves to link the North terminal to the airport railway station. Although sometimes colloquially, but erroneously, known as a "monorail", the transit vehicles are carried on rubber tyres running on a concrete track with twin running surfaces and are steered by separate guide rails.



















