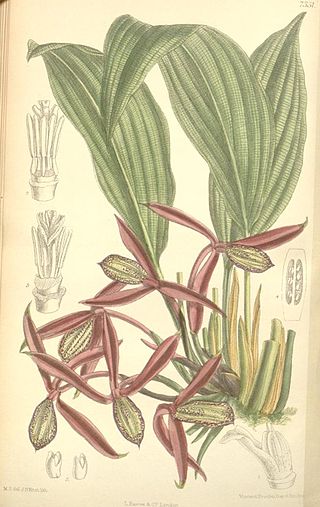
Orchidantha is a genus of flowering plants. In the APG III system, it is placed in the family Lowiaceae, as the sole genus. It includes the plants in the formerly recognised genera Lowia and Protamomum.

Gnetum is a genus of gymnosperms, the sole genus in the family Gnetaceae within the Gnetophyta. They are tropical evergreen trees, shrubs and lianas. Unlike other gymnosperms, they possess vessel elements in the xylem. Some species have been proposed to have been the first plants to be insect-pollinated as their fossils occur in association with extinct pollinating scorpionflies. Molecular phylogenies based on nuclear and plastid sequences from most of the species indicate hybridization among some of the Southeast Asian species. Fossil-calibrated molecular-clocks suggest that the Gnetum lineages now found in Africa, South America and Southeast Asia are the result of ancient long-distance dispersal across seawater.

Acampe, abbreviated as Acp in horticultural trade, is a genus of monopodial, epiphytic vandaceous species of orchids, distributed from tropical Asia from India, eastwards to China and southwards to Malaysia, and the Philippines as well as from tropical Africa, Madagascar and islands of the Indian Ocean. The name Acampe was derived from the Greek word akampas, meaning "rigid", referring to the small, brittle, inflexible flowers.

Blachia is a genus of plants under the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1858. It is native to Southeast Asia, southern China, and the Indian Subcontinent.

Ancistrocladus is a genus of woody lianas in the monotypic family Ancistrocladaceae. The branches climb by twining other stems or by scrambling with hooked tips. They are found in the tropics of the Old World.

Daphniphyllum is the sole genus in the flowering plant family Daphniphyllaceae and was described as a genus in 1826. The genus includes evergreen shrubs and trees mainly native to east and southeast Asia, but also found in the Indian Subcontinent and New Guinea.

Hiptage is a genus in the Malpighiaceae, a family of about 75 genera of flowering plants in the order Malpighiales. Hiptage species are native to: Andaman Is., Assam, Bangladesh, Borneo, Cambodia, China South-Central, China Southeast, East Himalaya, Fiji, Hainan, India, Jawa, Laos, Lesser Sunda Is., Malaya, Myanmar, Nepal, Nicobar Is., Pakistan, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Sulawesi, Sumatera, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam. The genus is distinctive in its three-winged samaras; most species bear an elongated commissural gland on the calyx.

Plectocomia is a genus of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae native to China, the Himalayas, and Southeast Asia. Plants are dioecious, with male and female flowers produced on separate individuals.
Parepigynum is a genus of liana in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1973. It contains only one known species, Parepigynum funingense, native to Guizhou and Yunnan Provinces in China.
Callostylis is a genus of orchids. It was previously considered as a synonym of the genus Eria, but eventually it has become an accepted name. It is native to Southeast Asia from Assam and southern China to Java.

Rhynchostylis is a genus in the orchid family (Orchidaceae), closely allied to the genus Vanda and comprising four currently accepted species native to the Indian Subcontinent, China, Indochina, Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines.
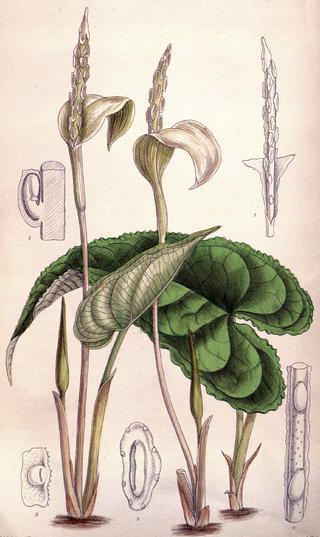
Hapaline is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It contains 7 species that are found from southern China to Borneo.

Germainia is a genus of plants in the grass family. Species of the genus are found in China, Asia and Australia.

Beaumontia is a small genus of evergreen woody vines in the milkweed family. It is native to China, the Indian subcontinent, and Southeast Asia.

Ancistrocladus tectorius is a species in the monogeneric family Ancistrocladaceae found in China (Hainan), Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. The Vietnamese name is trung quân lợp nhà; Chinese: 钩枝藤, gou zhi teng.
Pycnobotrya is a monotypic genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae found in tropical Africa. As of August 2013 the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families recognises the single species Pycnobotrya nitida.

Eberhardtia is a genus of plant in the Sapotaceae described as a genus in 1920.
Sindechites is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1888. It is native to southern China, Laos, and Thailand.

Amphineurion is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1948. It contains only one known species, Amphineurion marginatum, native to Cambodia, S China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam.

Mickelopteris is a genus of ferns in the subfamily Cheilanthoideae of the family Pteridaceae with a single species Mickelopteris cordata. Synonyms include Parahemionitis cordata and Hemionitis cordataRoxb. ex Hook. & Grev. The species is native to south-eastern Asia, from India to Taiwan and the Philippines.
















