Phellodendron, or cork-tree, is a genus of deciduous, dioecious trees in the family Rutaceae, native to east and northeast Asia. It has leathery, pinnate leaves and yellow, clumped flowers. The name refers to the thick and corky bark of some species in the genus.

Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids.
The University of Rochester Arboretum is an arboretum located across the River Campus of the University of Rochester, 612 Wilson Boulevard, Rochester, New York.

Papilio protenor, the spangle, is a butterfly found in South East Asia belonging to the swallowtail family.

Phellodendron amurense is a species of tree in the family Rutaceae, commonly called the Amur cork tree. It is a major source of huáng bò, one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Chinese medicine. The Ainu people used this plant, called shikerebe-ni, as a painkiller. It is known as hwangbyeok in Korean and (キハダ) kihada in Japanese.

Scutellaria lateriflora, is a hardy perennial herb of the mint family, Lamiaceae, native to North America.

Styphnolobium japonicum, the Japanese pagoda tree is a species of deciduous tree in the subfamily Faboideae of the pea family Fabaceae.

Anthocyanins, also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart named a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color, Anthokyan, in his treatise "Die Farben der Blüthen". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.

Phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—occur naturally in wine. These include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

Vitexin is an apigenin flavone glucoside, a chemical compound found in the passion flower, Vitex agnus-castus, in the Phyllostachys nigra bamboo leaves, in the pearl millet, and in Hawthorn.

The flavanonols are a class of flavonoids that use the 3-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone.

Astilbin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. Astilbin is the (2R-trans)-isomer; neoisoastilbin is the (2S-cis)-isomer and isoastilbin is the (2R-cis)-isomer.

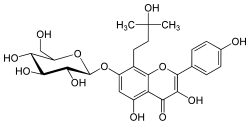
Phellamurin, a flavonoid, is the 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, 8-C-prenyl derivative of the flavan-on-ol Aromadendrin, and may be seen as the 7-O-glucoside of noricaritin. Being a flavanonol, it has two stereocenters on the C-ring, so four stereoisomers of phellamurin are possible.

Sakuranin is a flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It is the O-glucoside of sakuranetin. It can be found in Prunus sp.

Huáng bǎi, huáng bó or huáng bò is one of the fifty fundamental herbs of traditional Chinese medicine. Known also as Cortex Phellodendri, it is the bark of one of two species of Phellodendron tree: Phellodendron amurense or Phellodendron chinense.

Phellodendrine is an alkaloid isolated originally from Phellodendron amurense (Rutaceae).

Kaempferol 7-O-glucoside is a flavonol glucoside. It can be found in Smilax china, and in the fern Asplenium rhizophyllum, and its hybrid descendants, as part of a complex with caffeic acid.
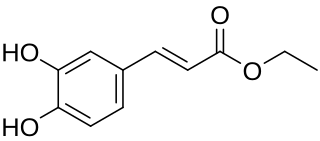
Ethyl caffeate is an ester of a hydroxycinnamic acid, a naturally occurring organic compound.

Veronicastroside is a flavone, a type of flavonoid. It is the 7-O-neohesperidoside of luteolin. It can be found in Veronicastrum sibiricum var. japonicum and in Teucrium gnaphalodes.